EcoTessara
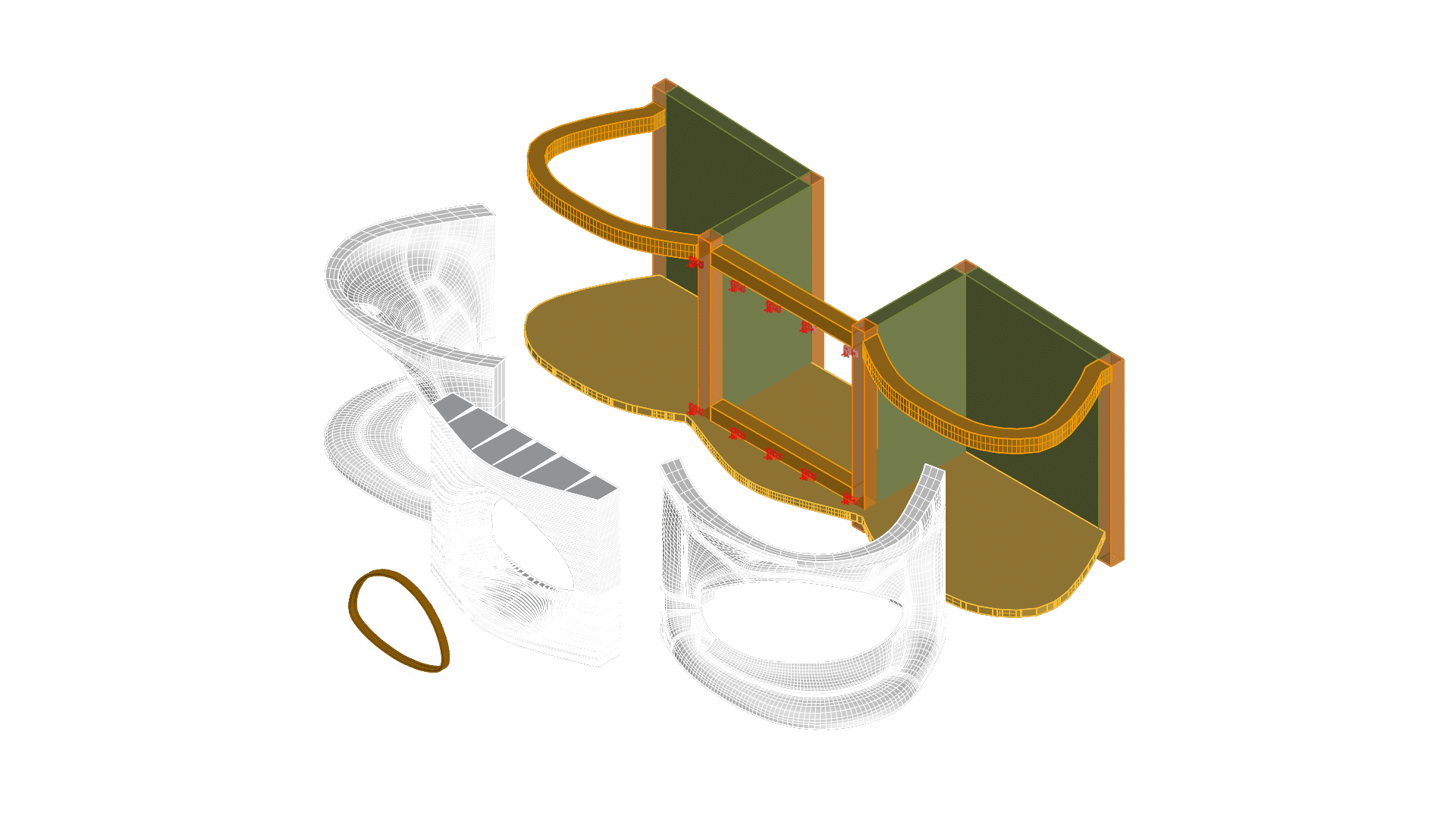
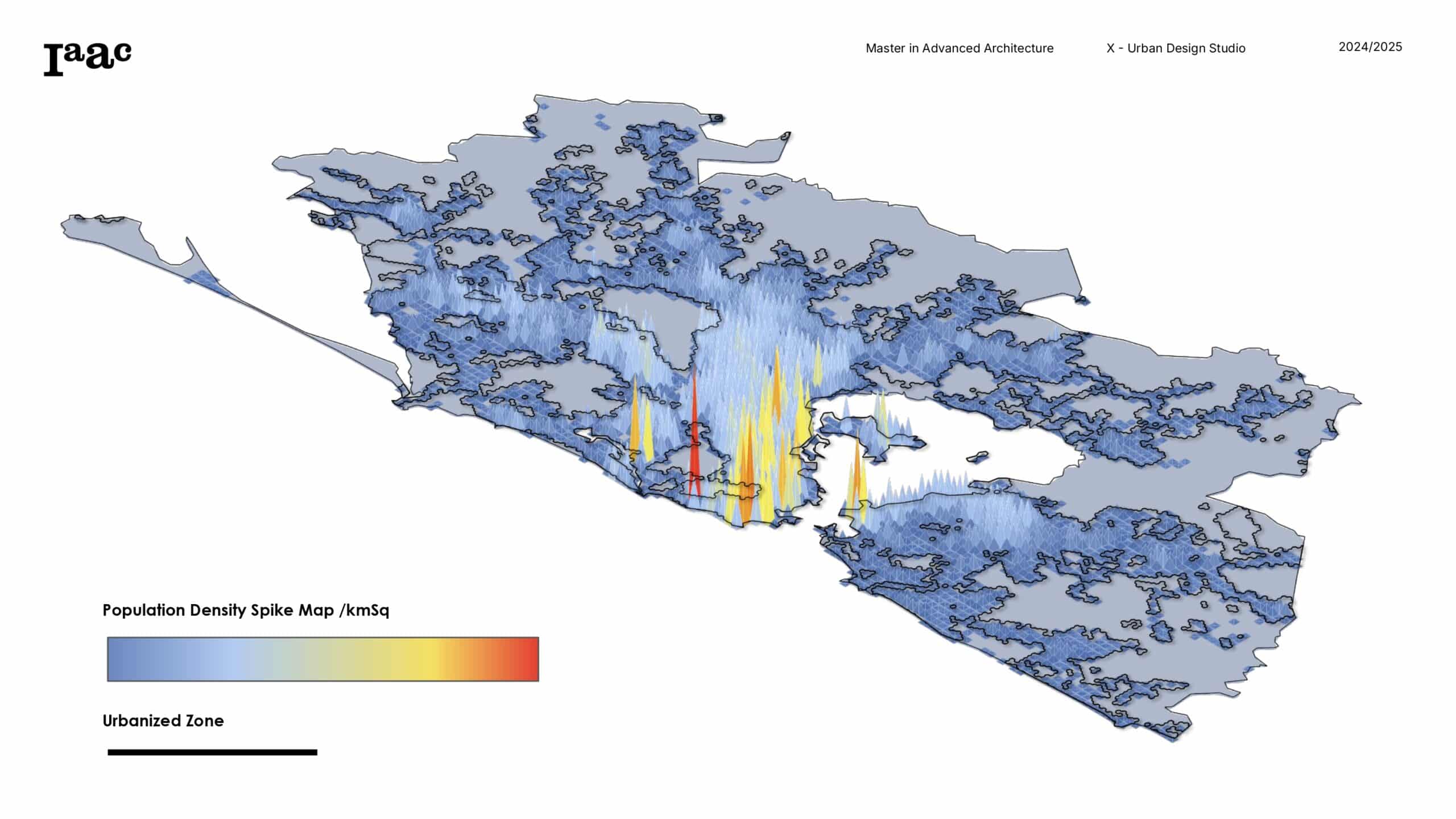
MANIFESTO In the tightly packed neighborhood of To Kwa Wan, space is limited and buildings are pressed close together, making it tough to design high-rises that feel light, breezy, and livable.This project uses generative design tools like Grasshopper and Wallacei to explore better ways of shaping a new tower near Kwun Shan Court.The goal is … Read more