Workshop 2.1 – AIRFLIP
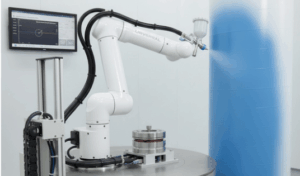
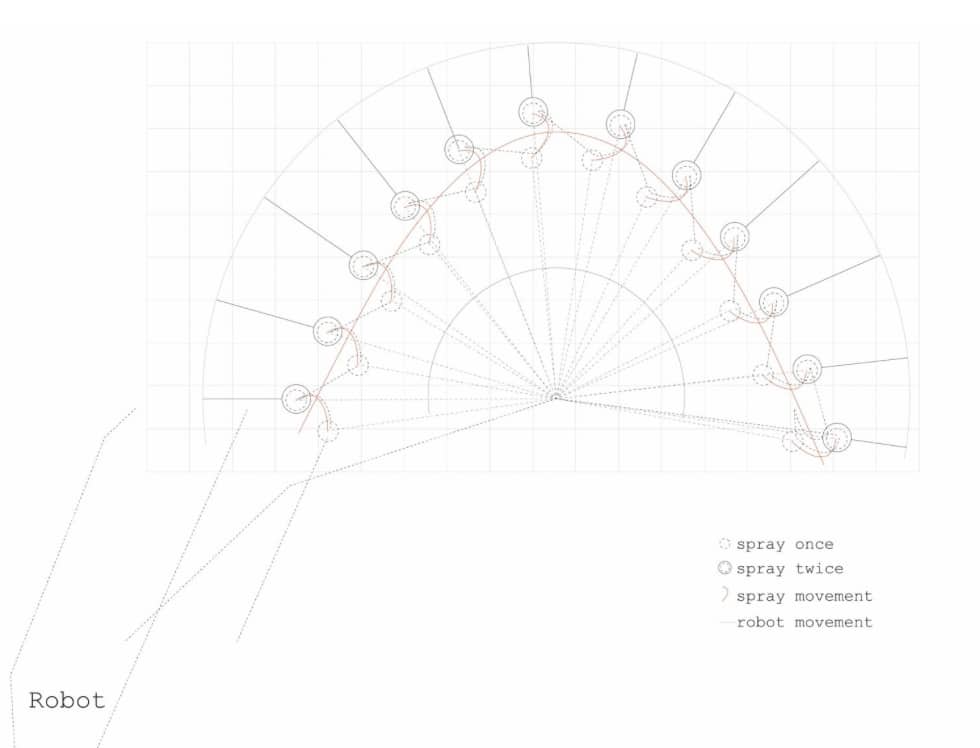
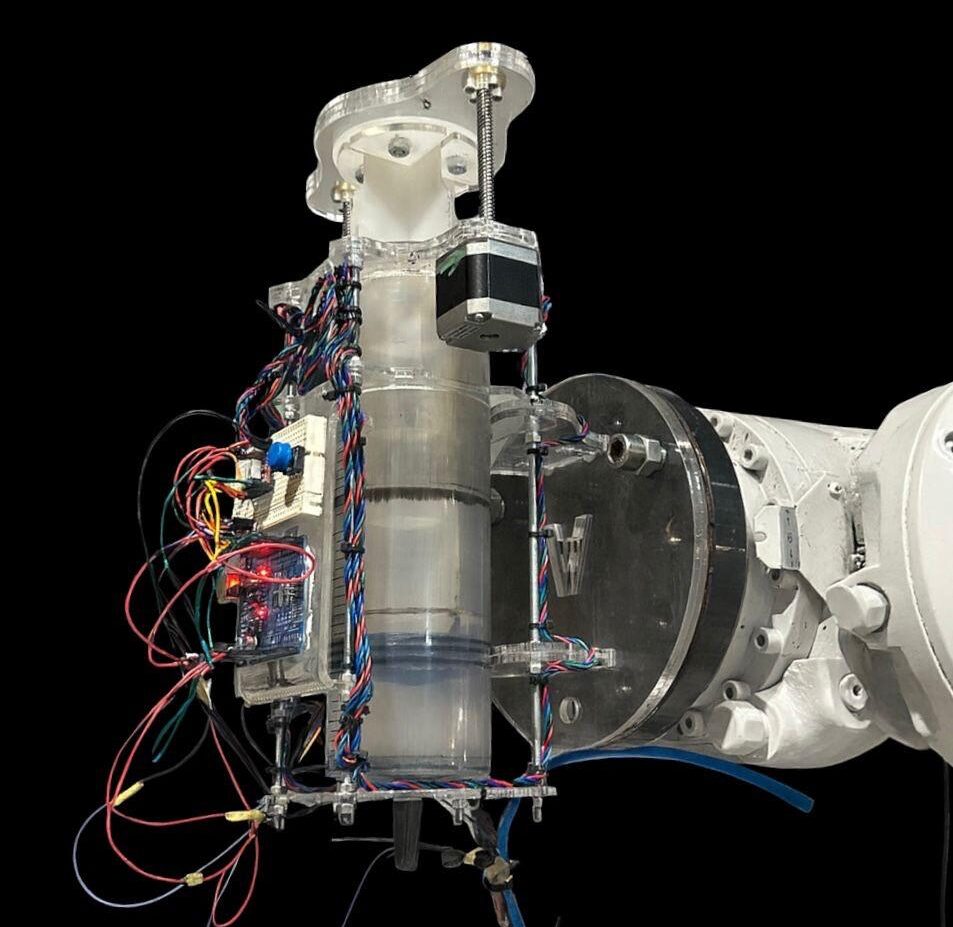
In the following blog post, we will analyse the development of the concept of our project carried out in Workshop 2.1. Team Collaborative Workflow and Modular System Development Guide, in which a Rotatory Gantry structure is proposed for the flip-type movement of a robotic arm. AIRFLIP – Rotary Gantry System for Small-Scale Cobots Overview The … Read more