ABSTRACT
This project seeks to transform a plot in Poblenou’s 22@ district into a pioneering model of metabolic co-living and circular urbanism. By leveraging the district’s technological ecosystem and repurposing e-waste from nearby Green Points, the project integrates a localized recycling and up-cycling facility with innovative prefabrication techniques. Modular co-living units, structural frames, and facades are crafted using 3D-printed materials derived from recycled steel, plastic, and aluminum. The design establishes a seamless connection between sustainable living and industrial efficiency. Mobility pods, powered by an autonomous rail system, link shared spaces such as urban farms and recreational platforms, promoting dynamic community engagement. This vision redefines urban density and resource management, merging sustainable architecture with advanced material reuse to create a self-sustaining, scalable co-living framework for the cities of tomorrow.
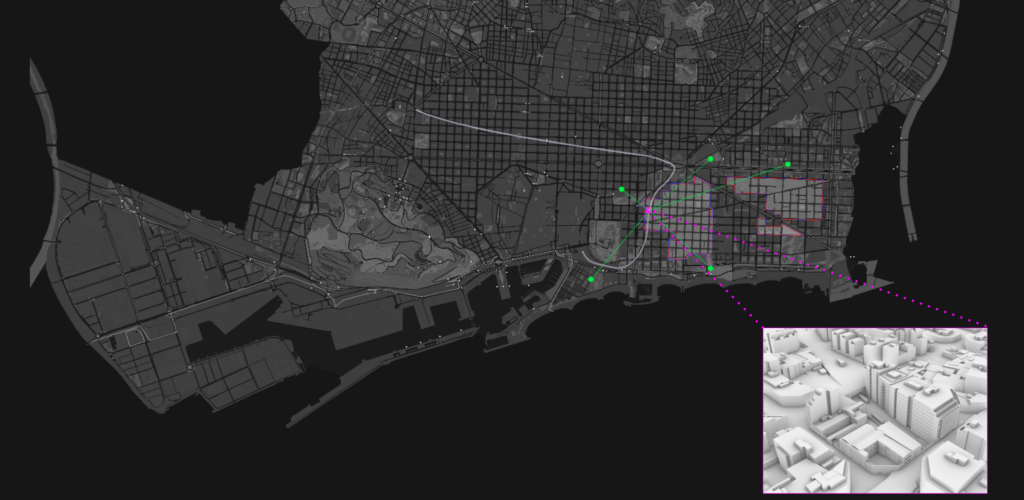
MACRO SITE ANALYSIS
The site coordinates are 41,39555 N, 2,18931* E in the Poblenou region. Despite the place being located in a melting pot of various industries and other functional spaces, the site had a train track. Barcelona city is also undergoing a ” Zero waste program” , collecting various types of waste materials to locations called ” Green Points” , where they could be distributed to the recycling plants and be re-used .
MICRO SITE ANALYSIS
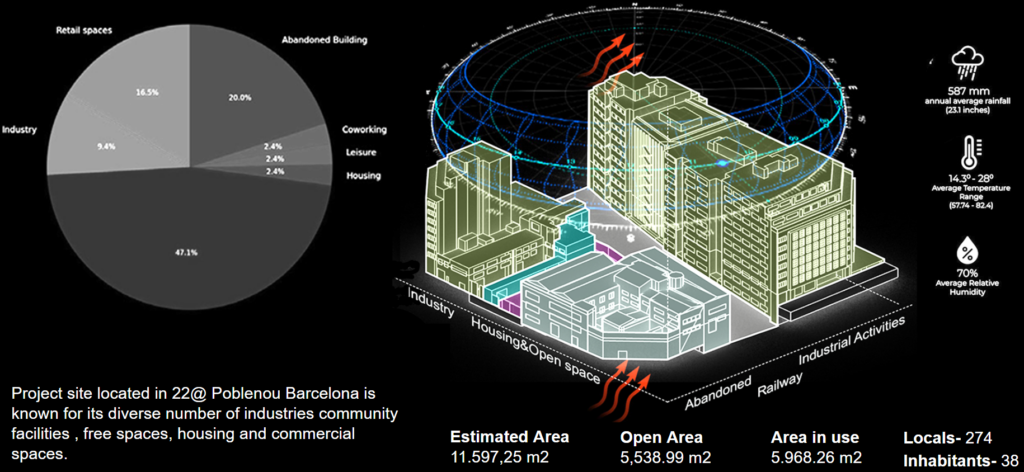
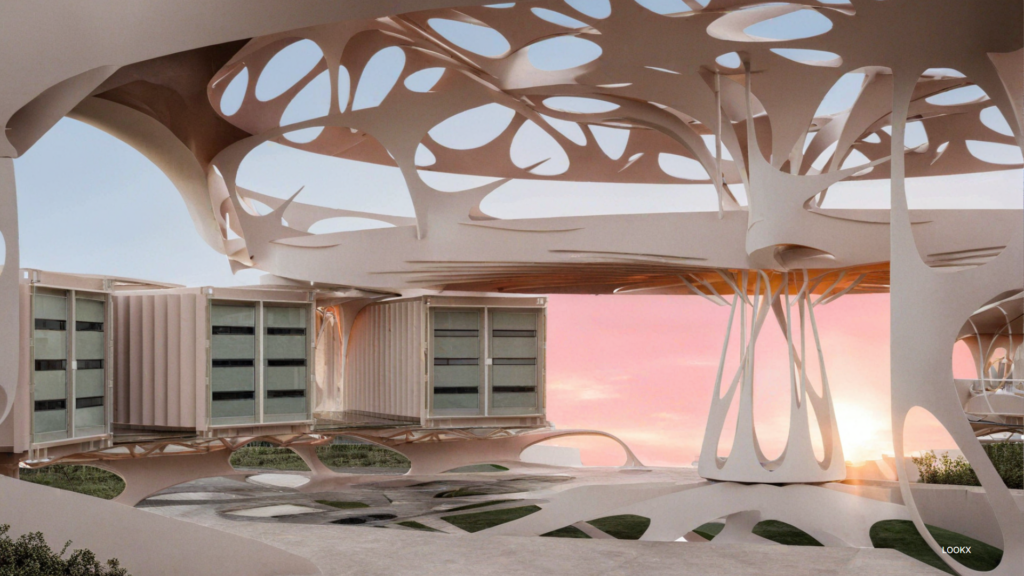
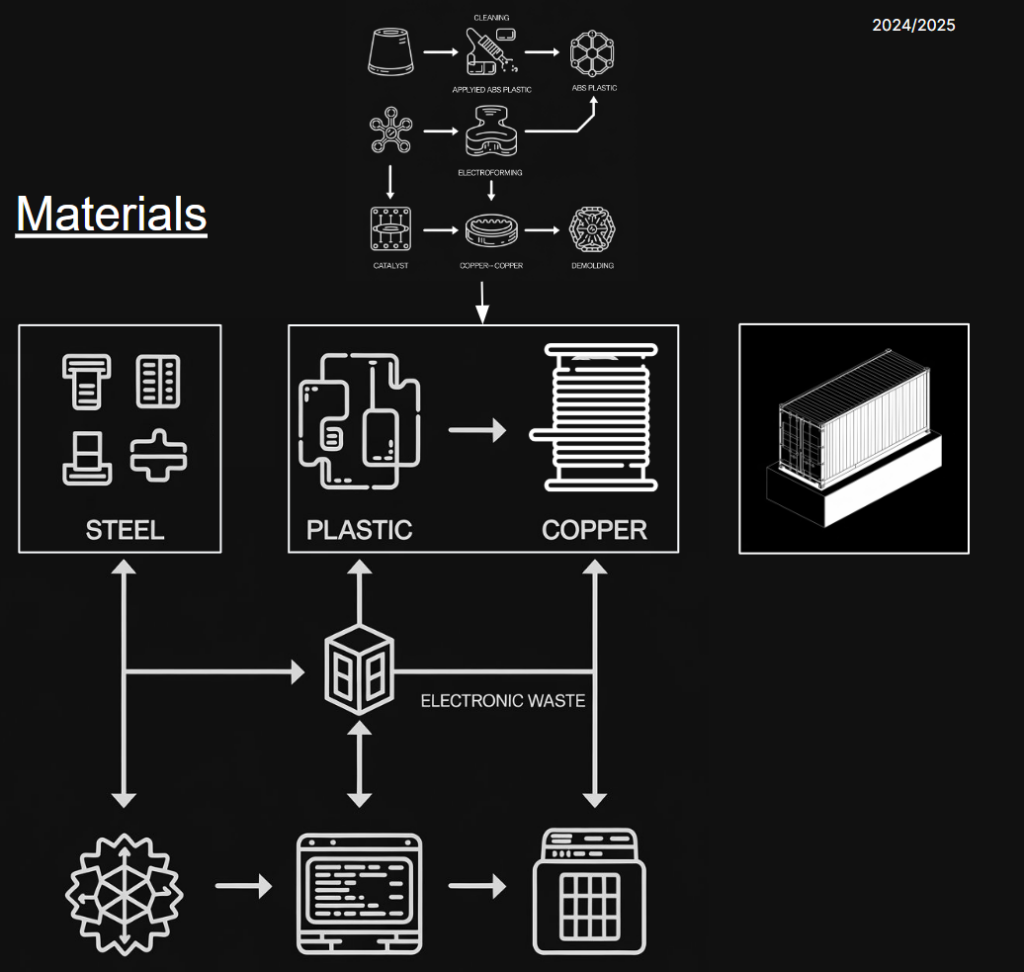
The Site block has an abandoned , empty building, that can be adaptively re-used as a recycling and a pre-fabrication construction industry to manufacture the components for the pre-fabricated structure. Mostly, the pre-fabricated components would be steel and plastic 3D printed.
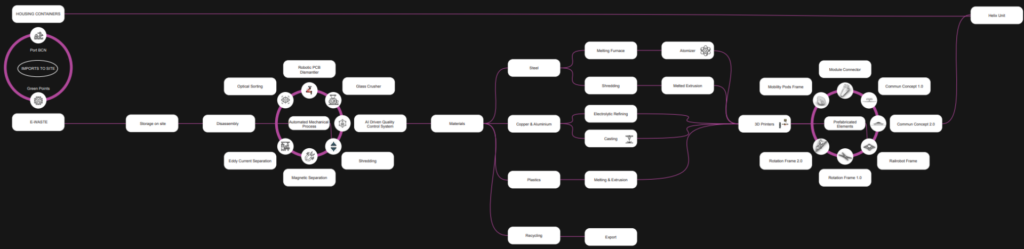
SANKEY
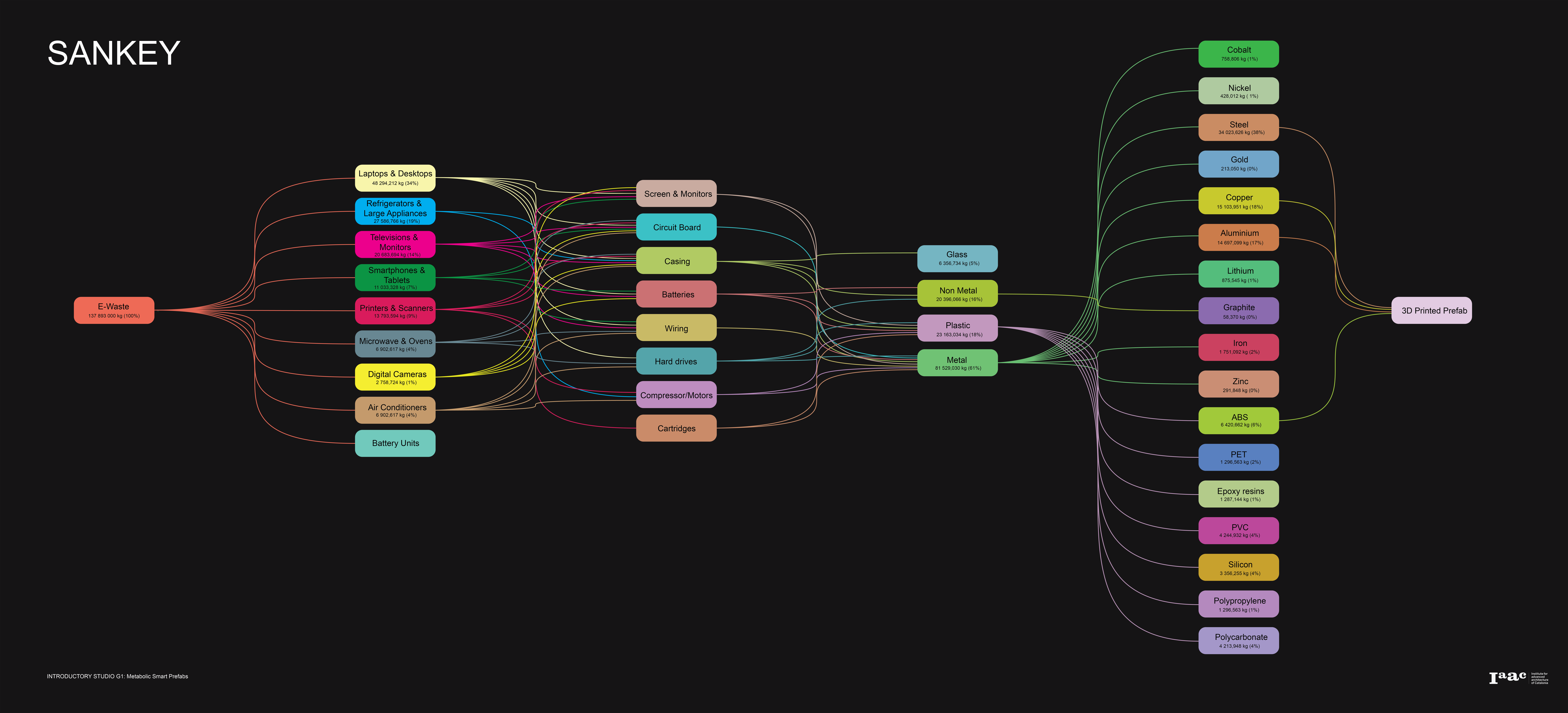
Electronic waste or e-waste for short, was selected for raw materials for pre-fabrication of the structures. E-waste are basically electronics that are discarded , such as fridge etc. Its one of the types of waste that are part of the zero waste program, as they are abandoned in the open, allowing strangers or collectors to open and take away metals used highly in industries, allowing harmful gasses to escape.
In the sankey diagram, four main materials were then selected ; non metals, plastic, glass and metals, which are then further divided into types found in the electronics.
METABOLIC
SENTANCE
“We are redefining urban living by transforming e-waste into a sustainable and modular co-living system, leveraging 3D printing technology, innovative mobility solutions, and adaptable design to create a scalable and forward-thinking solution for modern cities.”
PREFABRICATED ELEMENTS
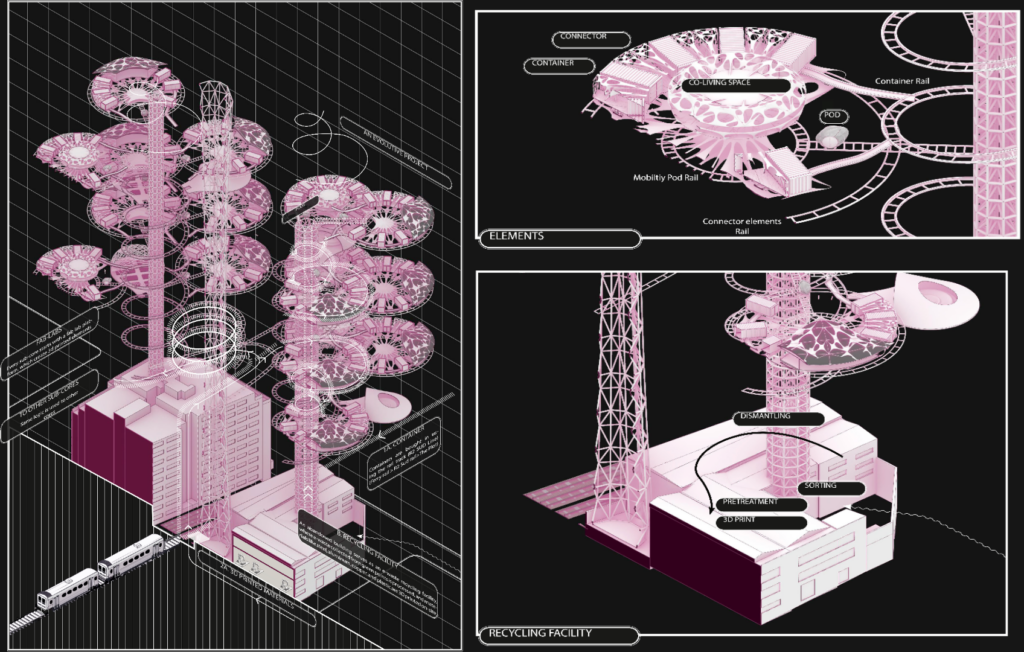
The transport components were 3D printed to act as carriers of other 3d manufactured components.
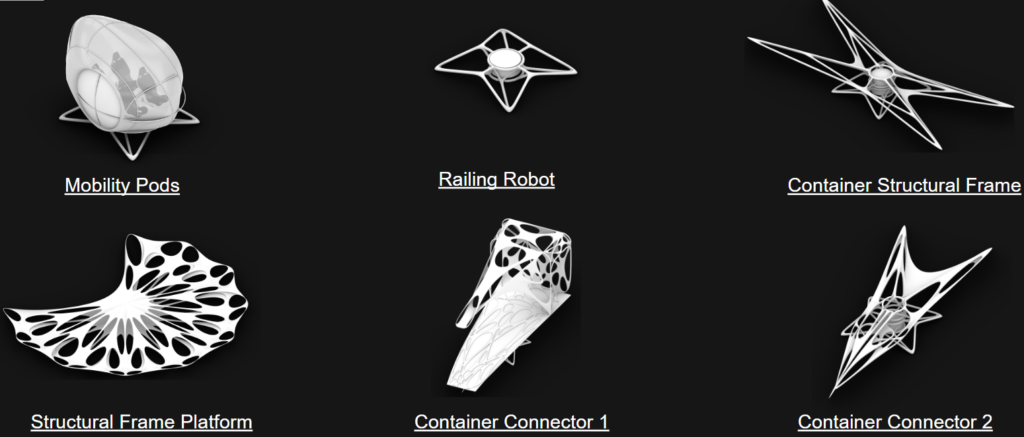
Mobility Pods carry the residents to their destinations within the project. The Railing robot transports the functional space capsule and 3D printed balconies for the accommodation units. The container structural frames carry wider forms of spaces such as the accommodation container spaces. The structural frame platform acts as a foundation for the accommodation units and common space, which has shared kitchens and living rooms etc. The container connector acts as an additional space, making a connection space between two accommodation containers. These carriers can move and rotate to fit into available spaces.
MOBILITY PODS
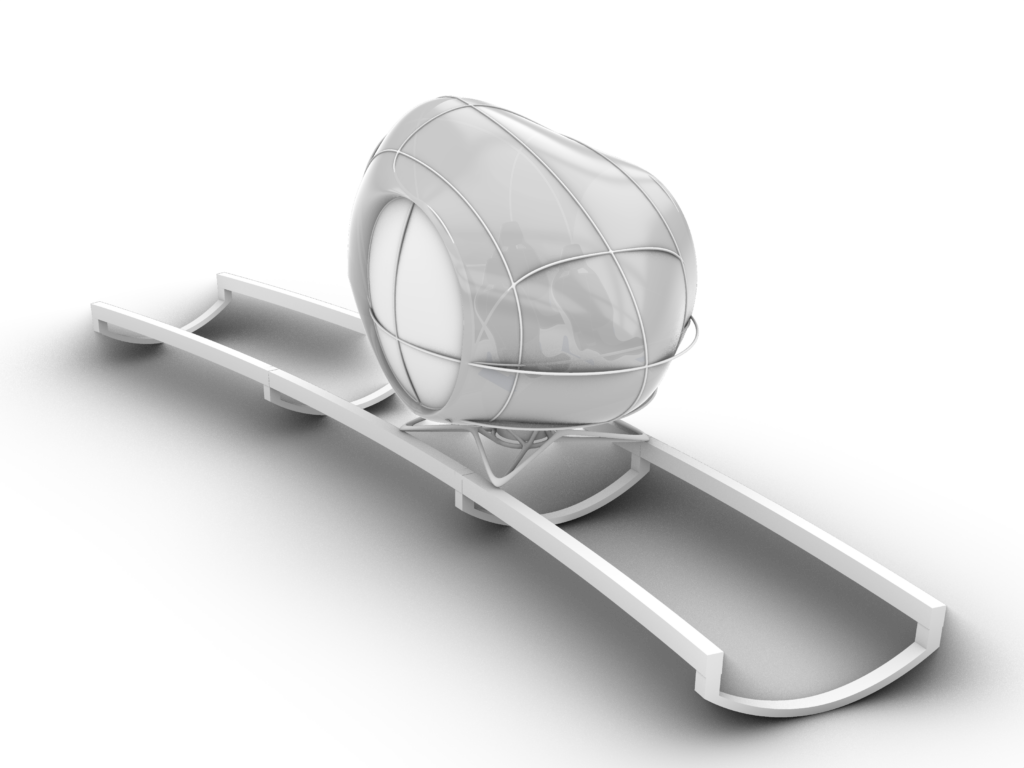

The Mobility pods are like transport for the residents, taking them to their accommodation spaces or other public spaces designed to be community spaces and urban spaces. The shell is 3D printed using plastic whereas the metal line cage is 3D printed using metal to reinforce the structural strength of the pod.
FUNCTIONAL ACTIVITY CAPSULE
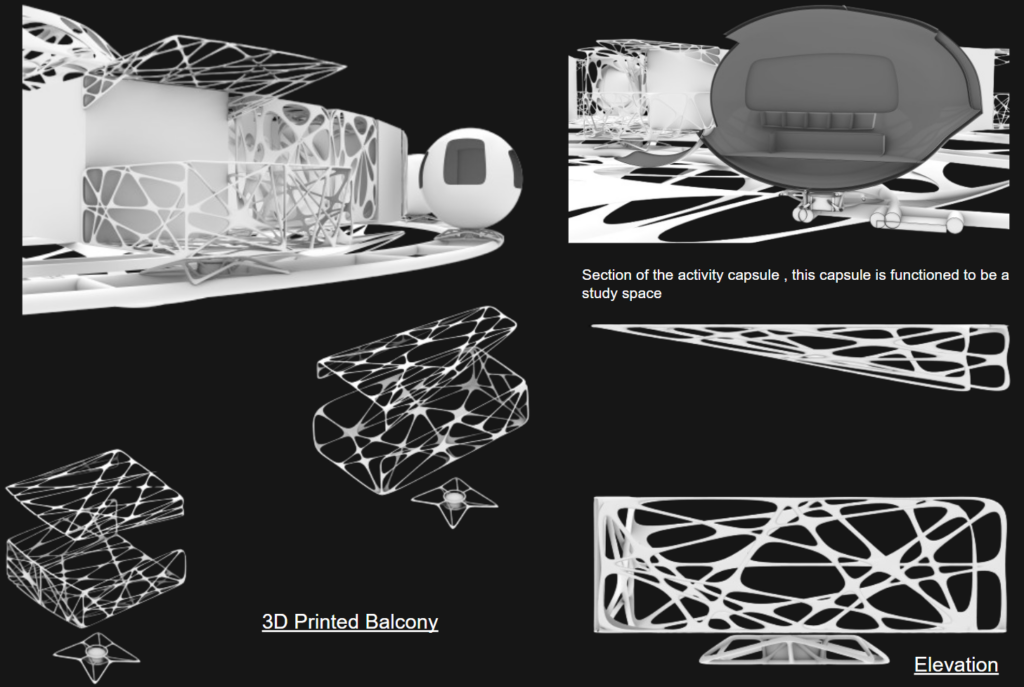
These 3D-printed modules extend the functionality of the container living spaces, allowing users to customize their environment. Residents can order modules with diverse programs, such as balconies, BBQ areas, saunas, reading spaces, or even living room extensions.
The concept focuses on convenience and adaptability—residents simply request the desired module, which is transported to their container via the AI-driven rail system, eliminating the need for relocation. With infinite possibilities for personalization, these modules redefine how space adapts to individual needs.
THE HELIX PROGRAM

Just like train tracks were made to guide the trains to their locations, the Helix program functions similarly as a pathway to the project’s locations. While the main railing in the center acts as the core road towards the spaces, the railings in the base structures are different. The exterior railing are for functional or activity capsules whereas as the mobility pods go inside the co living spaces, dropping residents to their accommodation. All these functions are AI programmed to ensure functionality.
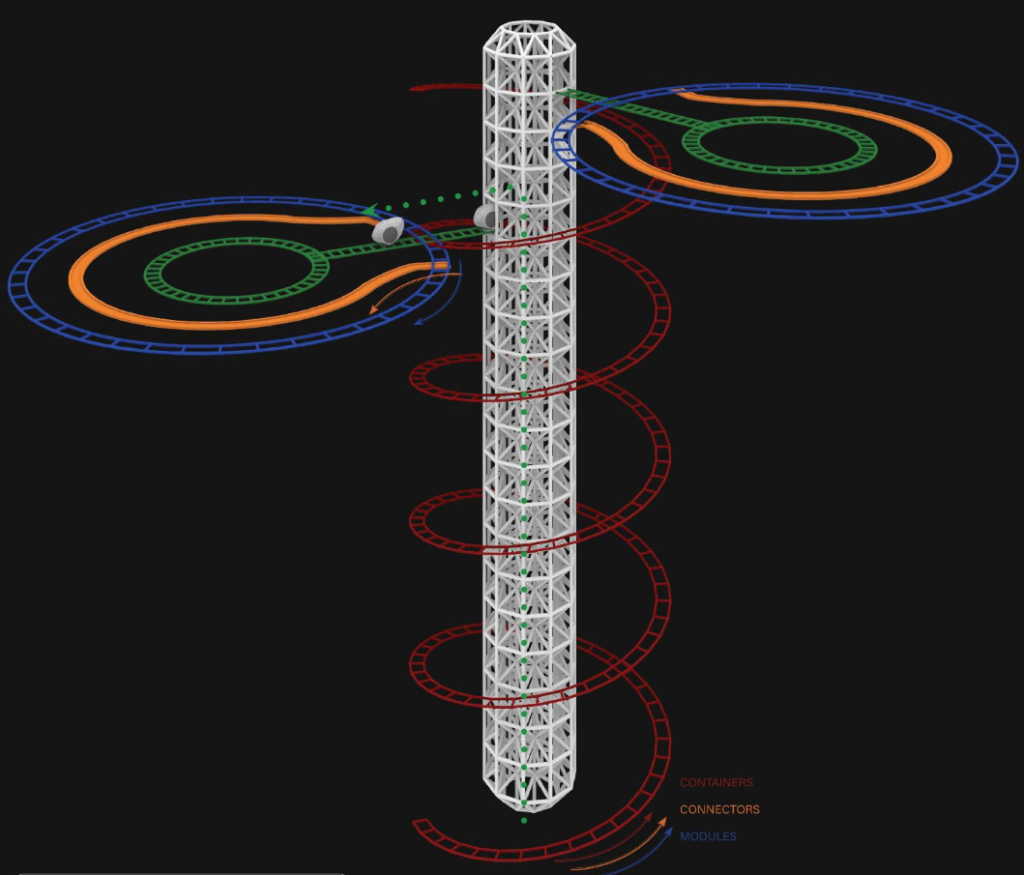
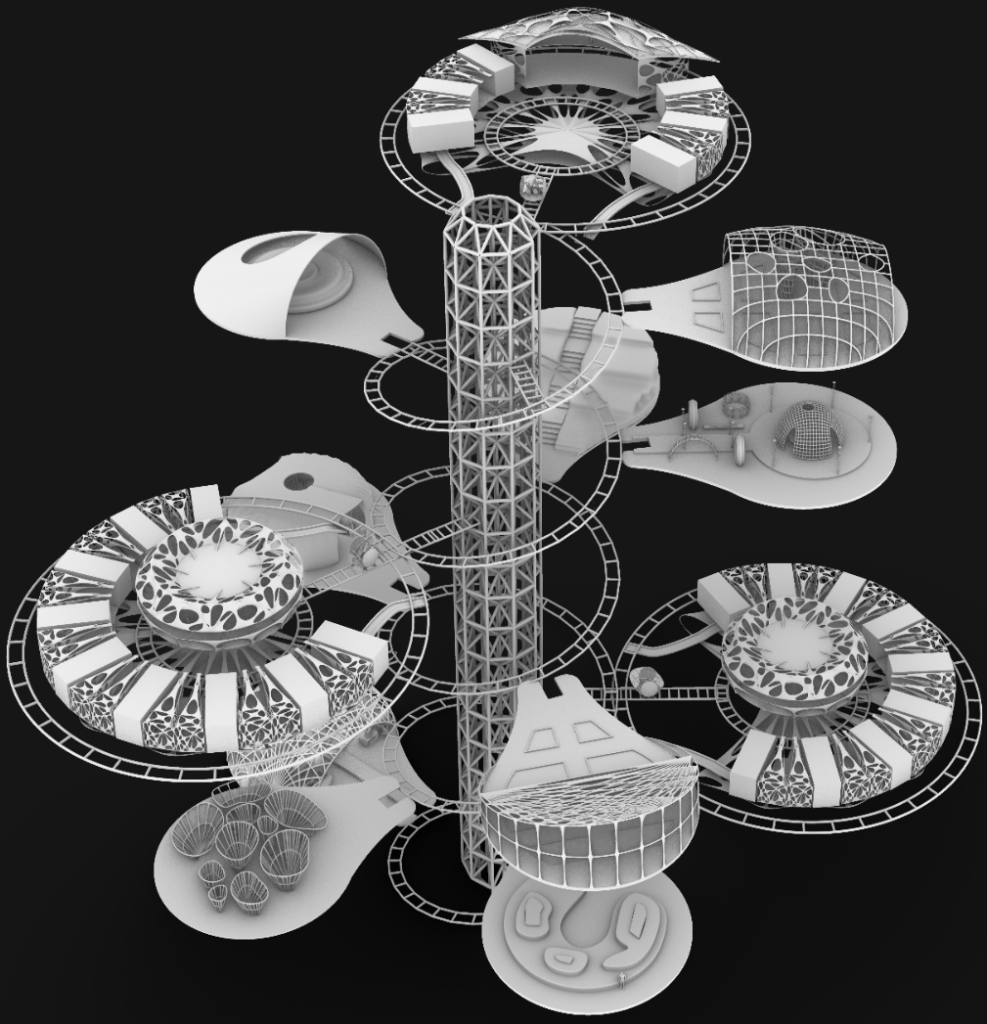
THE SPACES
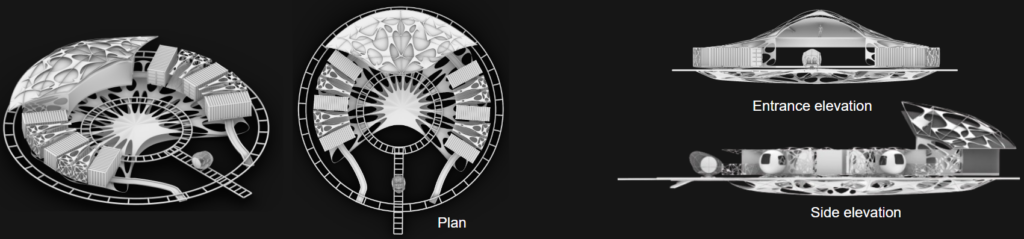
The spaces consist of two co living , four communal , four urban and one fabrication laboratory.

In the first co-living , the center is open or public activity or a view for the common space on the edge .
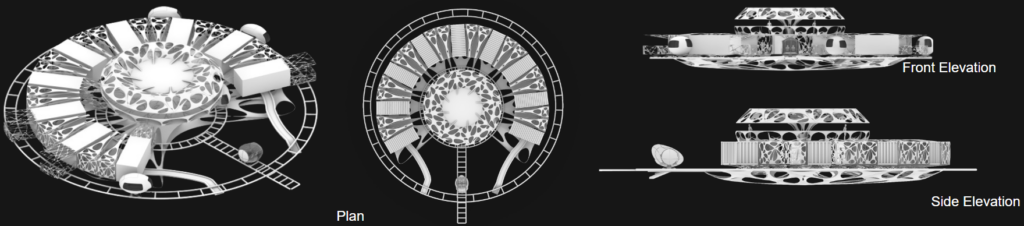
In the second co-living space, having a communal space in the center.
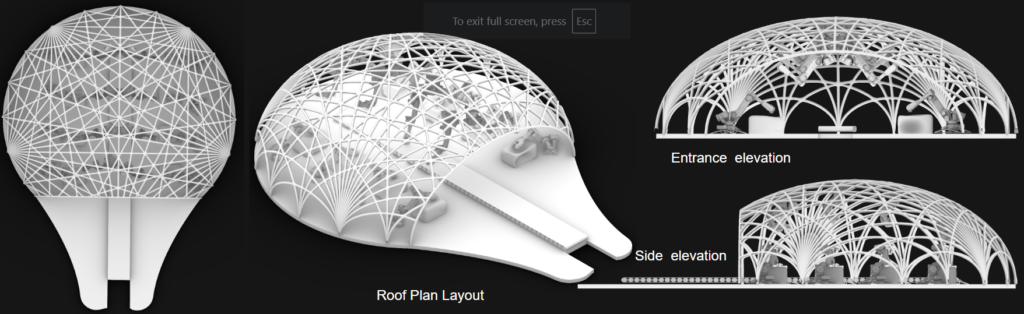
The prefabrication laboratory is considered the healing factor of the structure, functioned to optimize the whole structure, repairing damages and 3D printing more components.
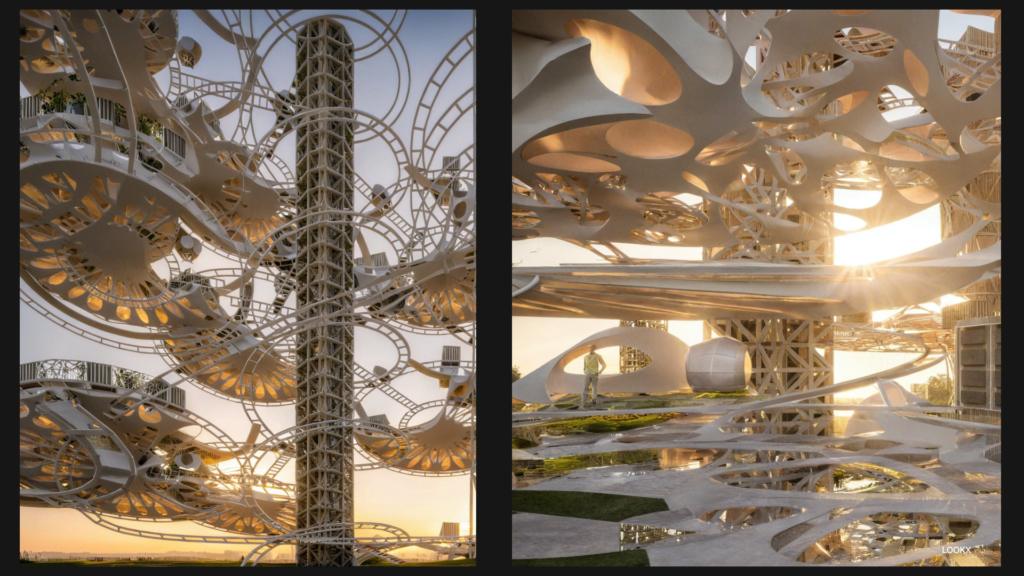
THE PROTO-TYPE

THE JELLY-FISH SECTION
One platform with co-living modules and associated elements requires
50,000 kg of 3D-printed steel/aluminum per year.
Starting in 2025, the total material usage will be:
By 2030 (6 platforms): 300,000 kg
By 2040 (16 platforms): 800,000 kg
By 2050 (25 platforms): 1,250,000 kg
By 2100 (76 platforms): 3,800,000 kg
THE OVERALL MODEL AND RENDERS