The construction industry creates a waste that is expected to reach 2.2 billion tons globally by 2025 (Transparency market research). Because of this the market started trying different new techniques to construct with less waste, that is how with the 4.0 industrial revolution came the Additive manufacturing process, that fabricates physical 3D objects layer by layer from a computer-aided design model, and with the possibility to use different materials. The AM allows us to have mass customization objects and complex geometries and heterogeneous composition. This sector started growing to be a €13.4 billion industry in 2020 and with a 22% annual growth rate (McKinsey).

But it is not a completely perfect technique yet, by now there exist a lot of variables in the process that make it less accurate. To look more into the details, the Limitless project made an expert panel to know more about the problems in this process.

Some of the conclusions were the importance of the use of six axis robots and having more freedom on how to deposit materials, also there are common variations in parameters even if there are different materials which makes the prototyping time too long.

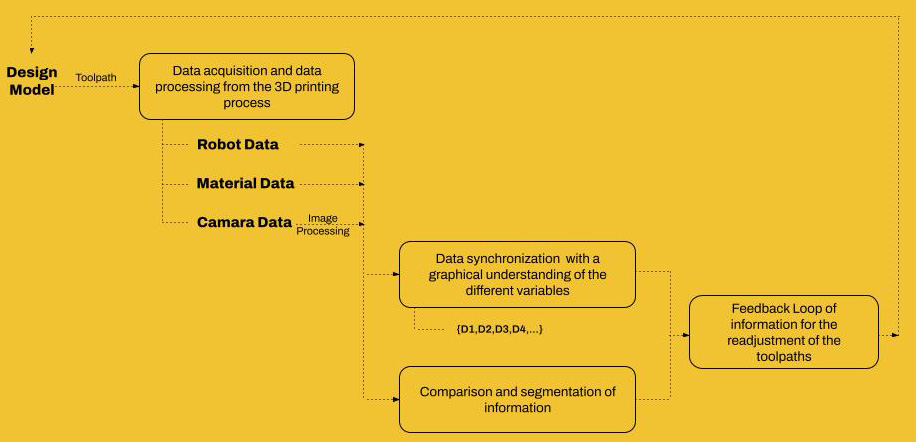
Limitless project is looking to be a tool that allows the monitoring, measure and documentation of the AM process at the moment of the printing with the help of conventional cameras, analog sensors, robot Data and open source technology. Basically when fails, why, and what was happening at that moment with more complete information about the process.

To make this possible there is a workflow to follow: Scanning, Understanding, Comparison, Segmentation, Planning, Readjustment and Execution. For this early stage of the project we are looking to resolve till the comparison on the process.
To extract the Data of the AM we spread the information on three types: Robot Data, Material Data and Image Data. After synchronizing this information became a graphical understanding of the different variables.
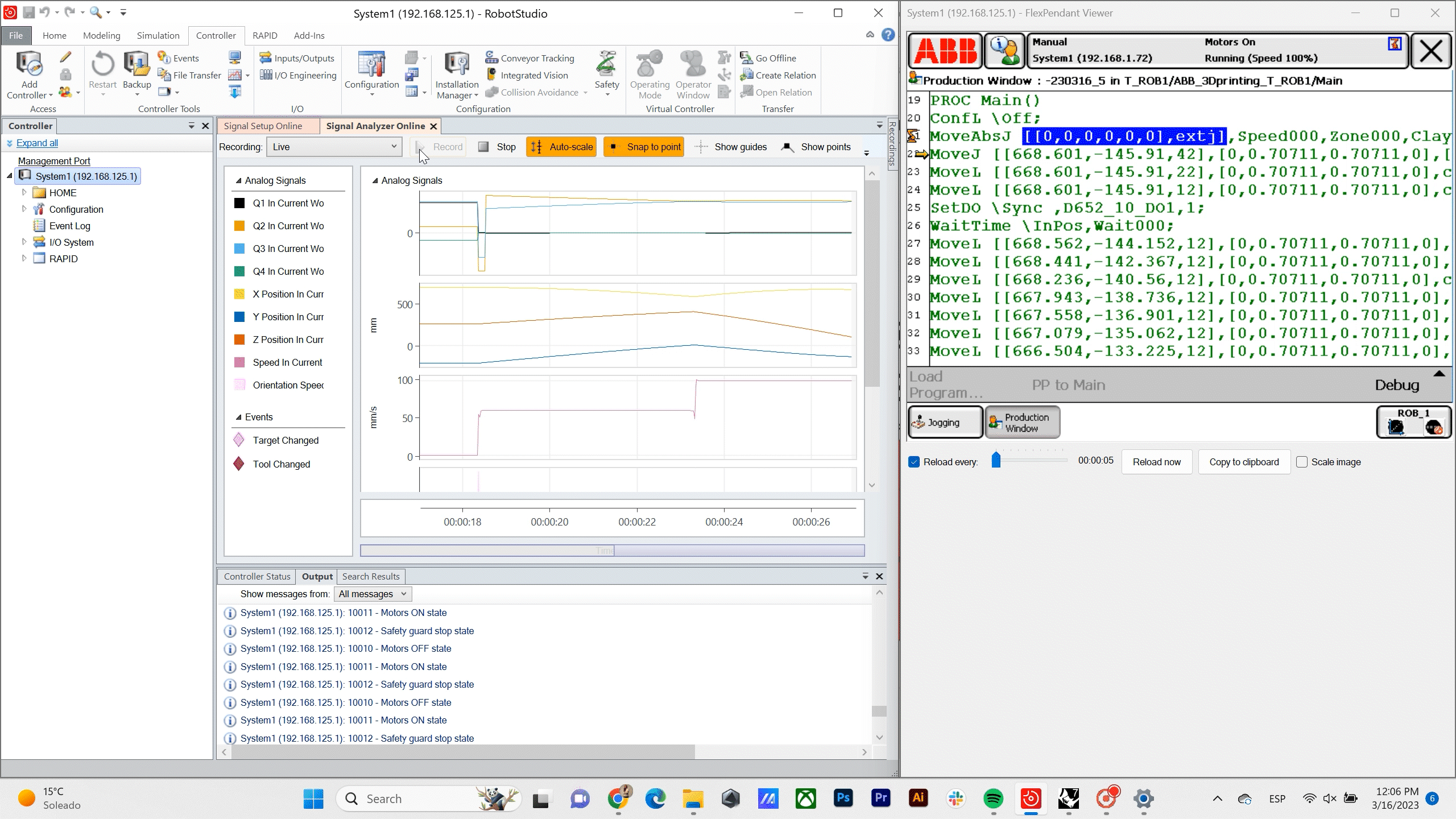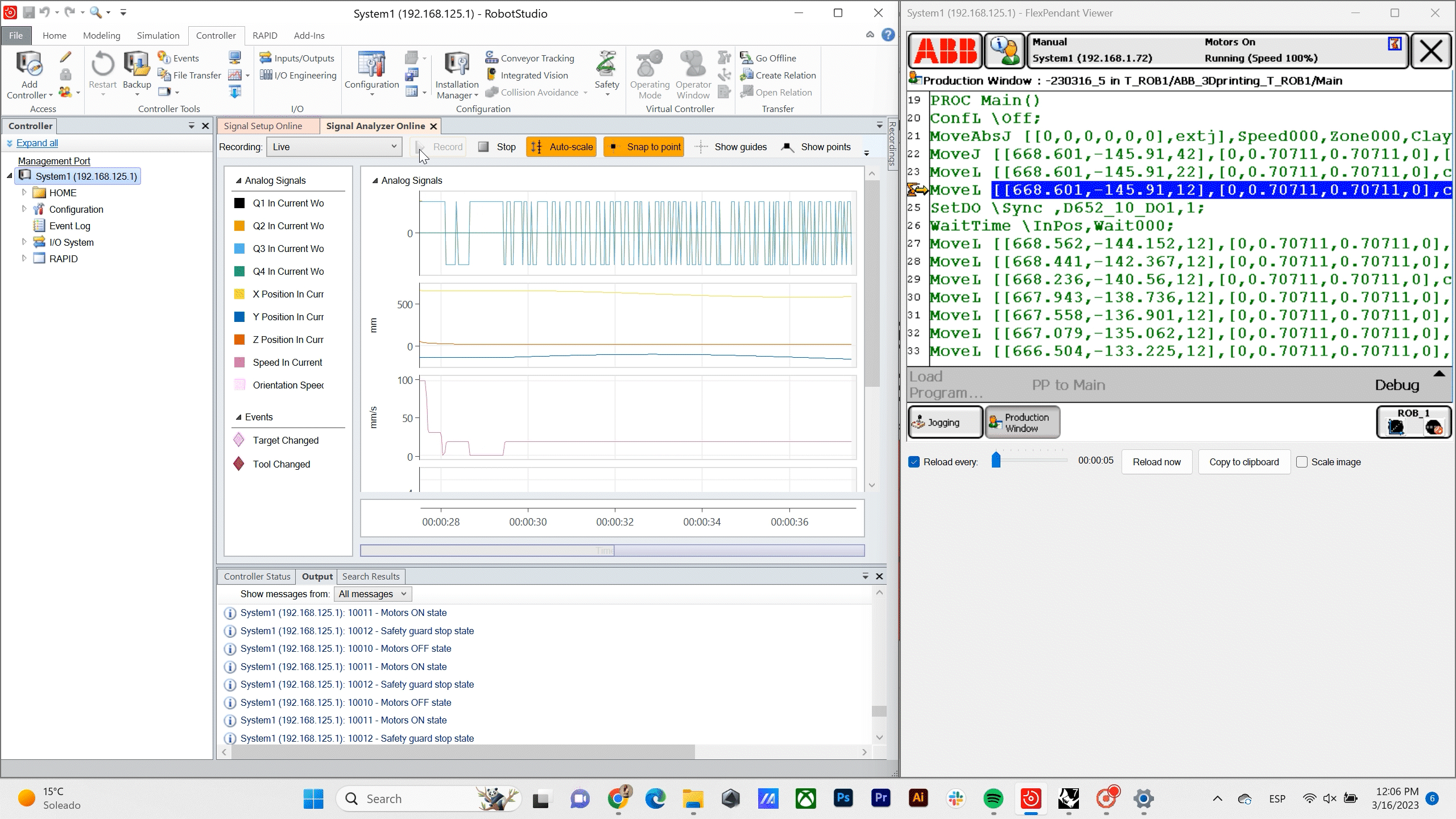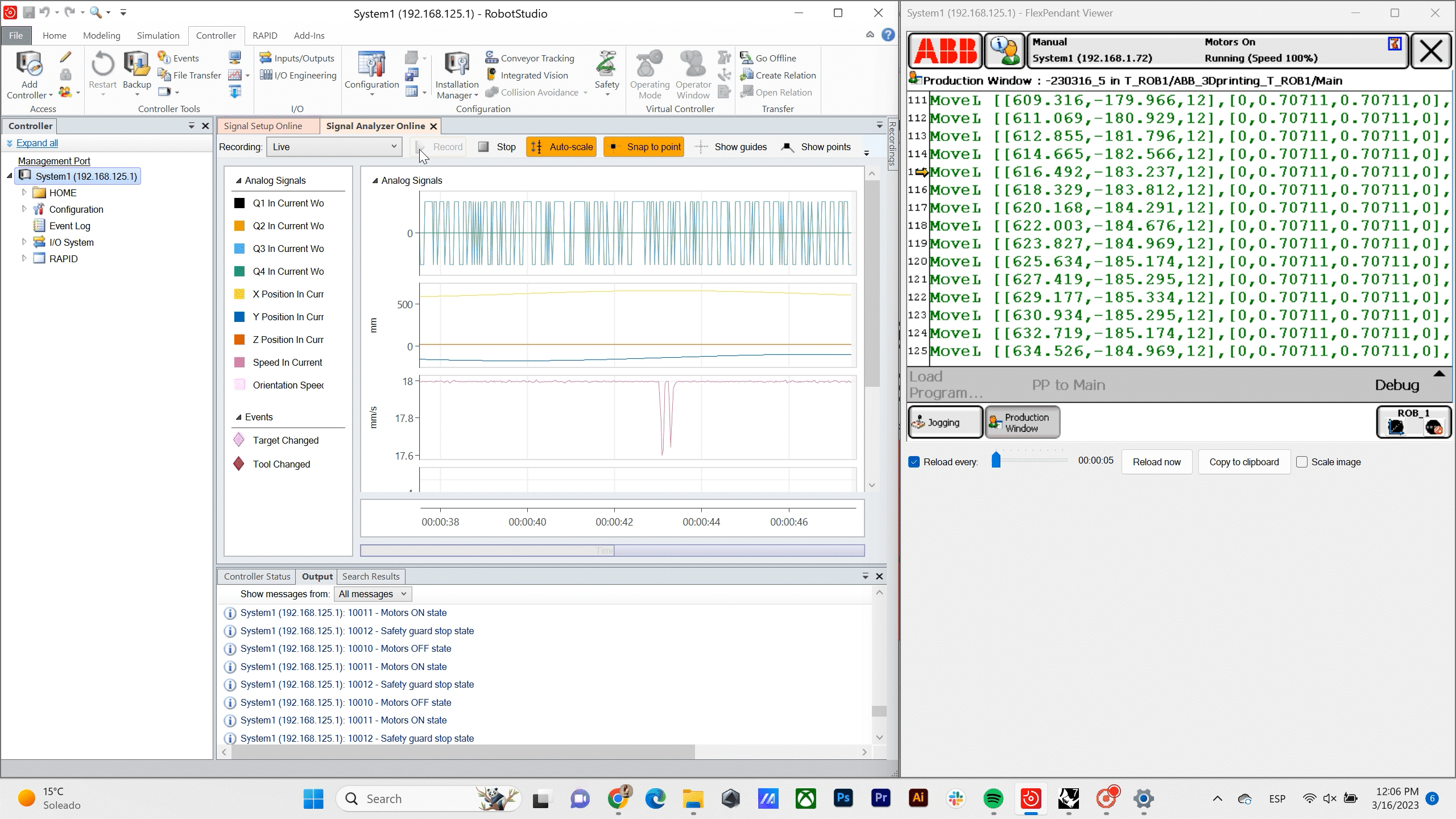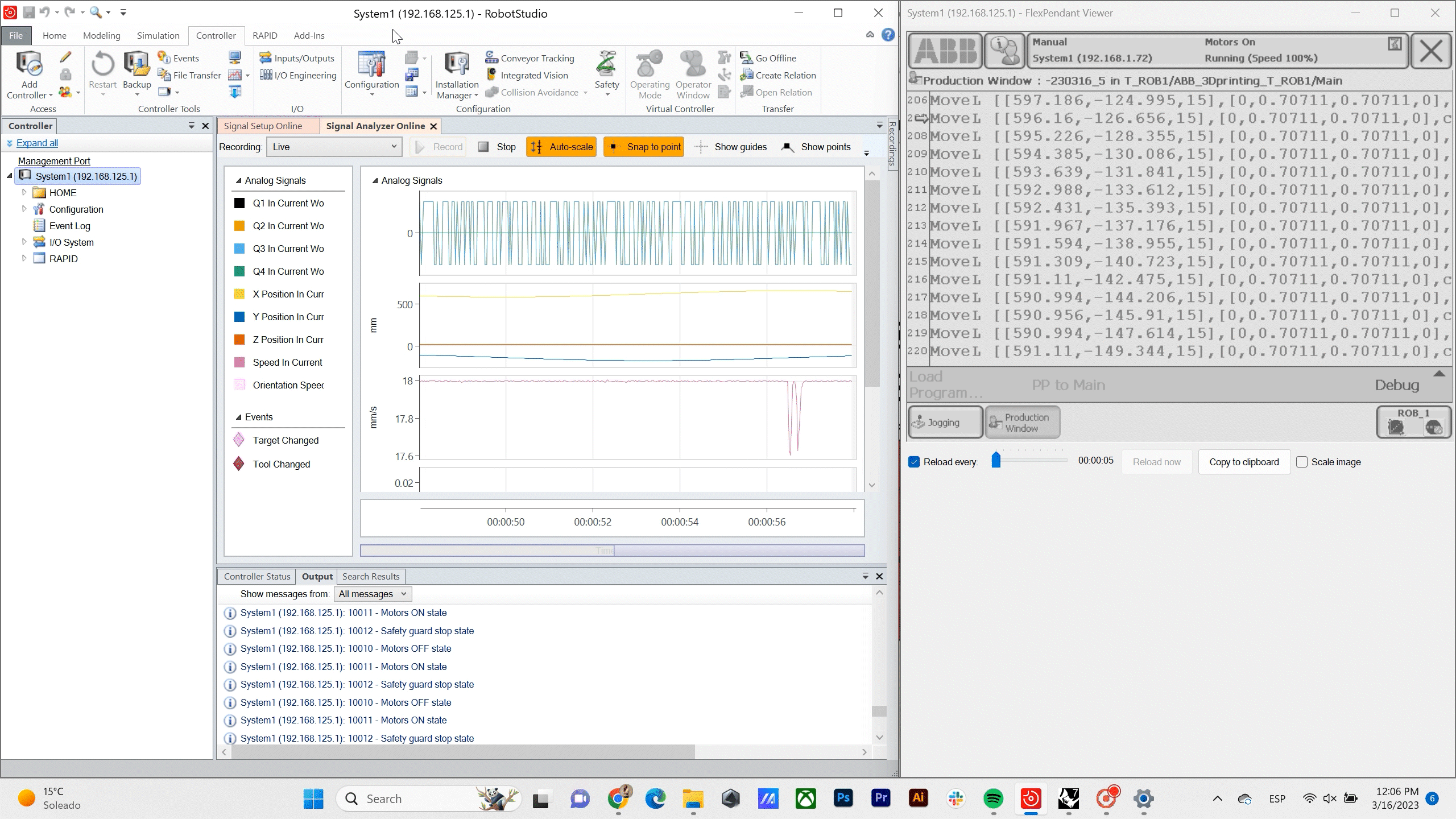
Robot Data – For the proof of concept in this stage of the project we are using a ABB 140 IRB so with the help of program ABB RobotStudio we are Recording the position, orientation and Speed of the TCP in relation to the Time.
Material Data – In this situation where we are using clay for tasting the workflow we have variables on the consistency of the material, that is why we are monitoring the moisture on the mix before printing.
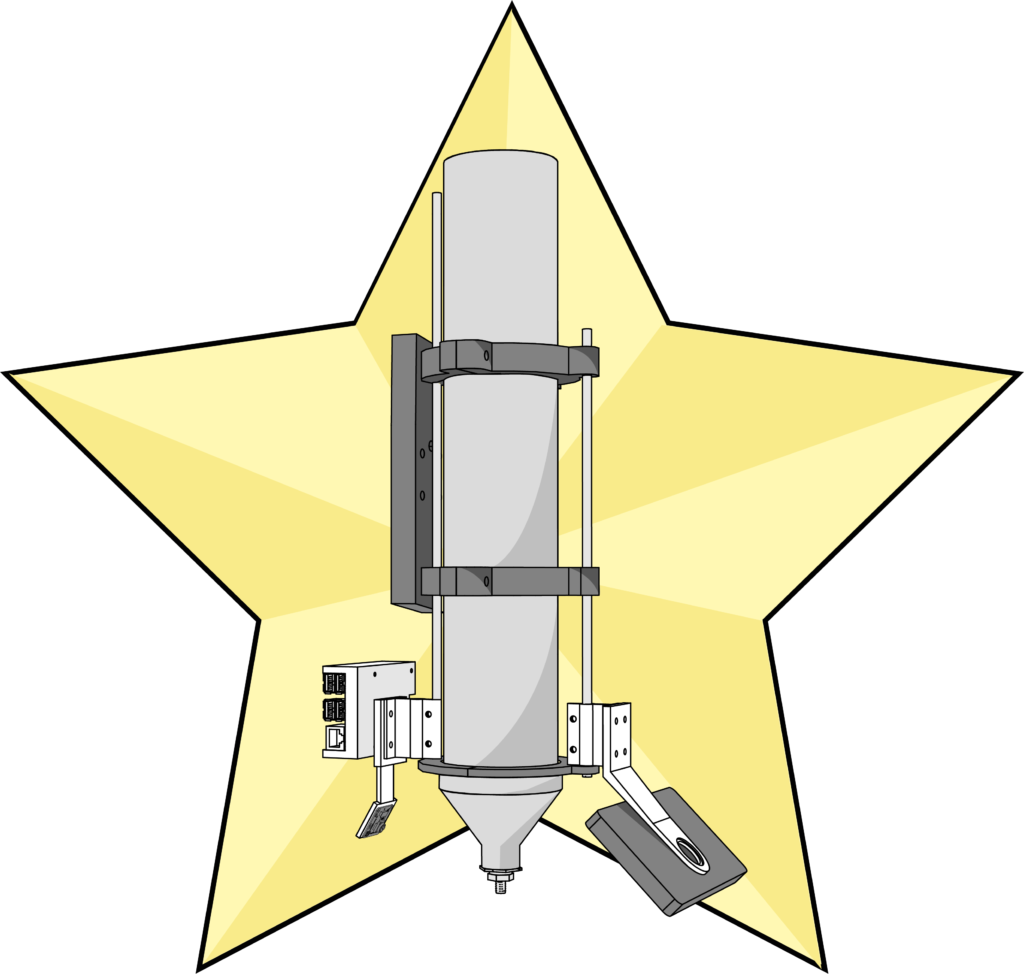
Image Data – To get the different images we create “La Garra” which is a multiple camera holder attached to the extruder, this allows us to have different perspectives of the extrusion and after processing it extract information. “La Garra” is composed of a Raspberry pi camera and a Iphone LiDar.
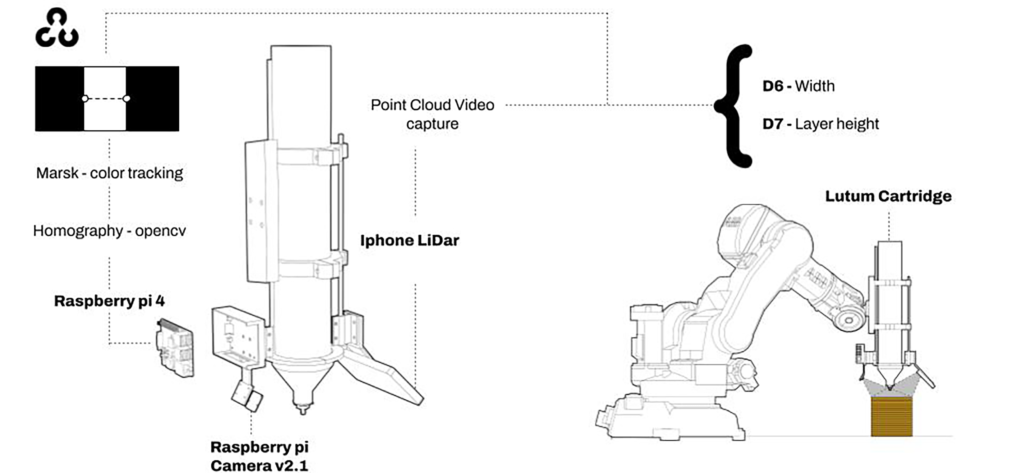
Now, How do we see this information?
The information is synchronized by time on the printing process and given to a segmentation of planes on the toolpath.
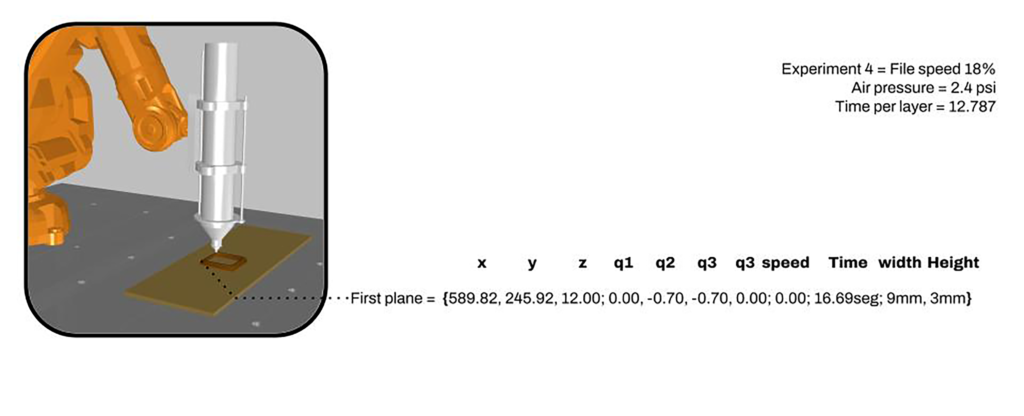
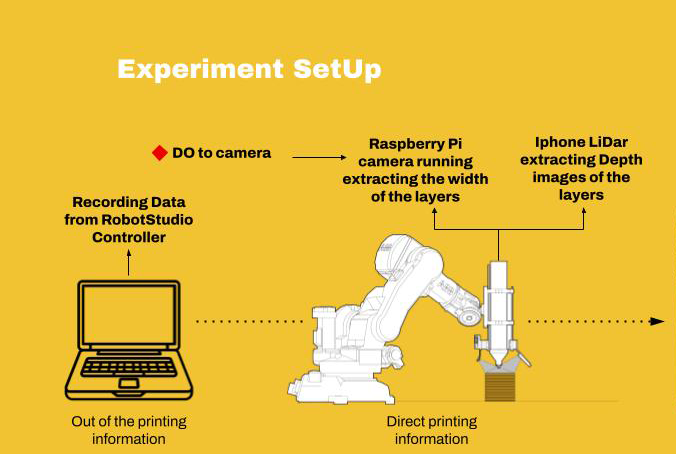
After the first batch of experiments to extract information we conclude the importance of merging the information between the xml Data and the 3D model, also the possibility of informing the tool path and creating possible variables as a element of design and the possibility of after the creation of catalogs predict the variables in simulations.
“Limitless Project” is a project of IAAC, Institute for Advanced Architecture of Catalonia developed in the Master of Robotics and Advanced Architecture 2022/23 by: Students: Andrea Najera and Faculty: Alex Dubor and Aldo Sollazzo

