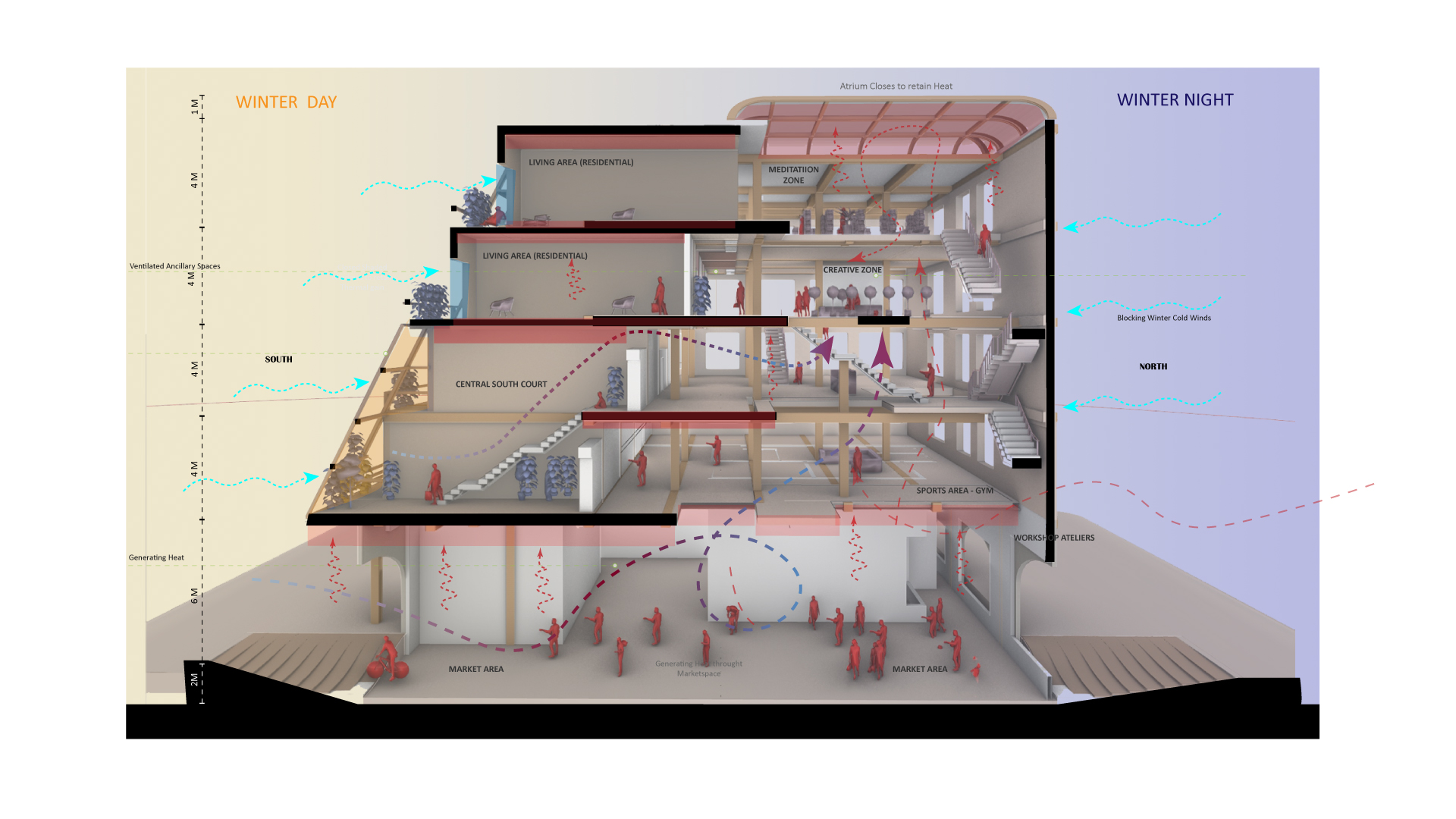
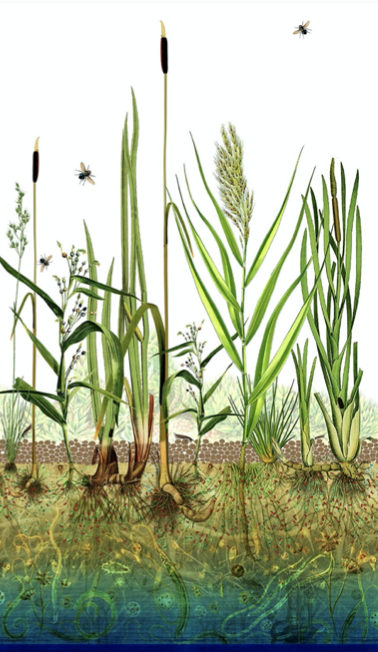
Defining Biocities | Words defined by Hans Joachim Schellnhuber
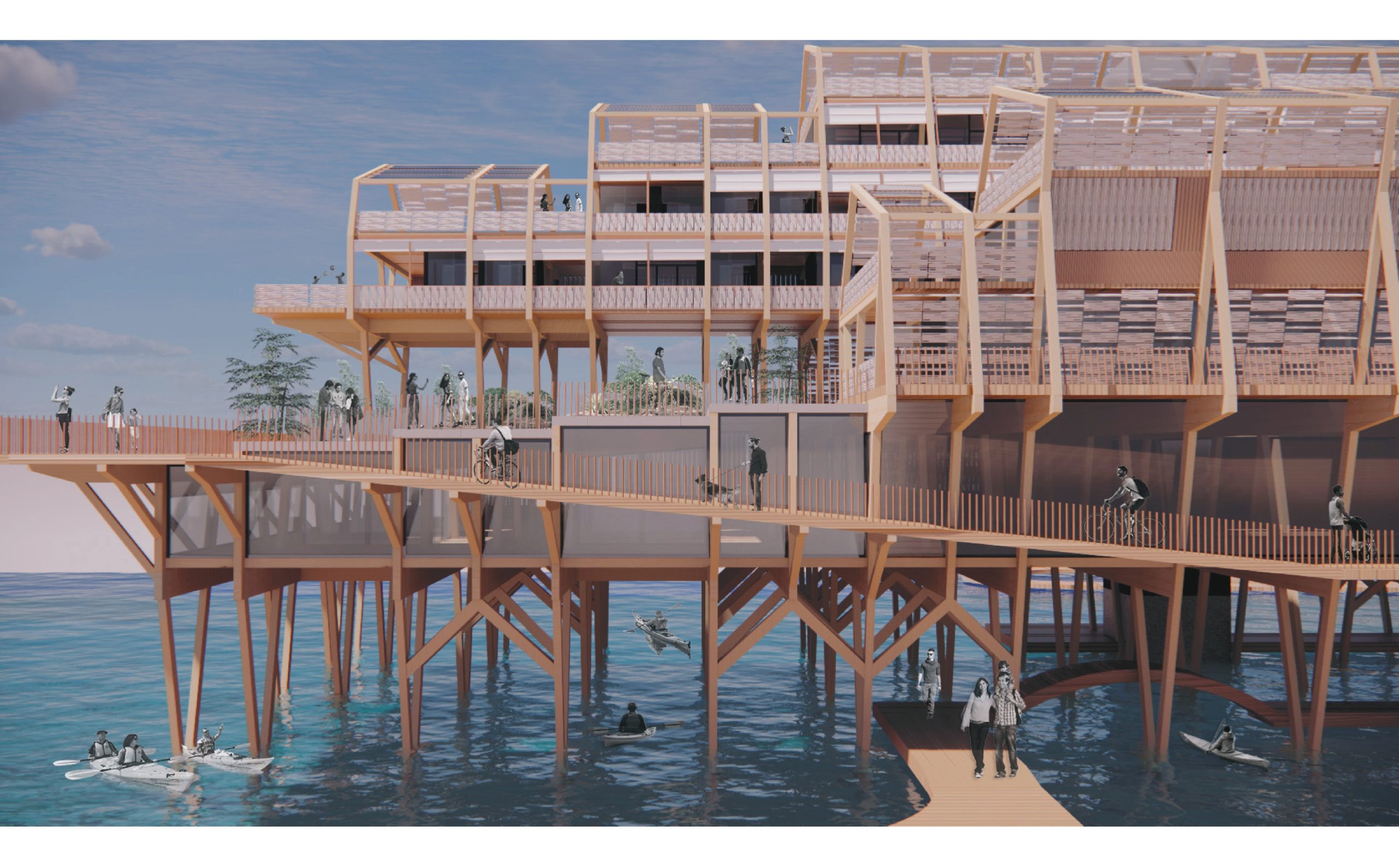
Defining BioCities is set to be the second addition to the First series titled ” The Metapolis Dictionary of Advanced Architecture”. The book was published 25 years ago and since then the world has transitioned into the age of sustainability and regenerative design. For the same, the new edition looks into the compilation of words, … Read more