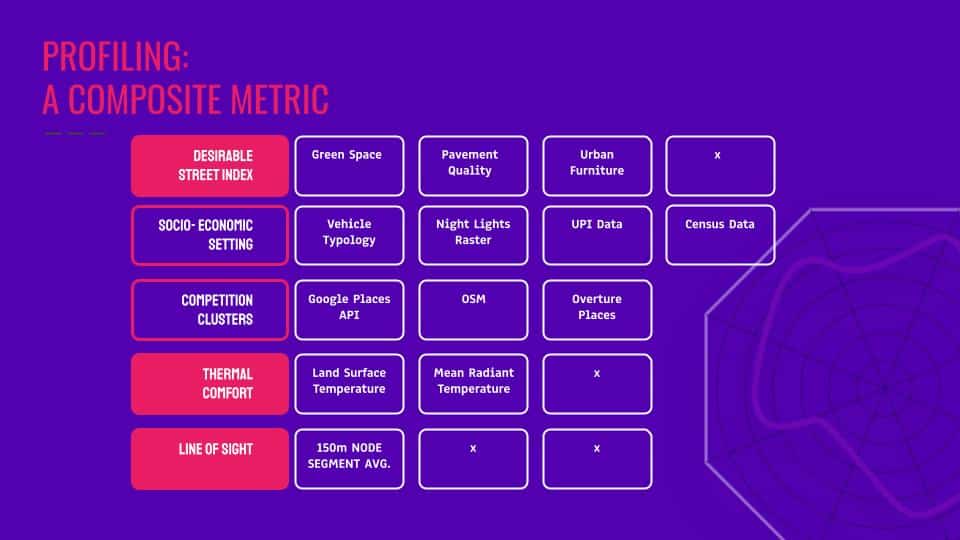
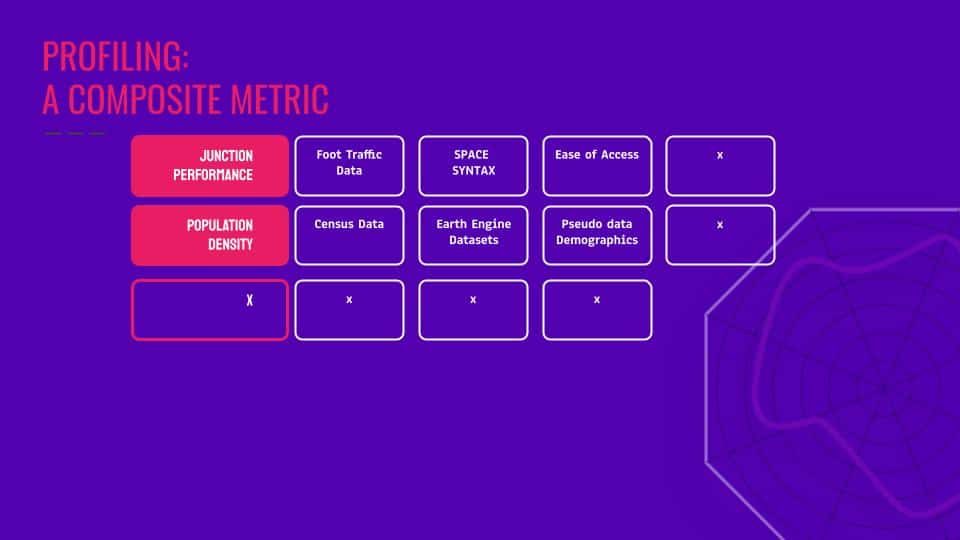
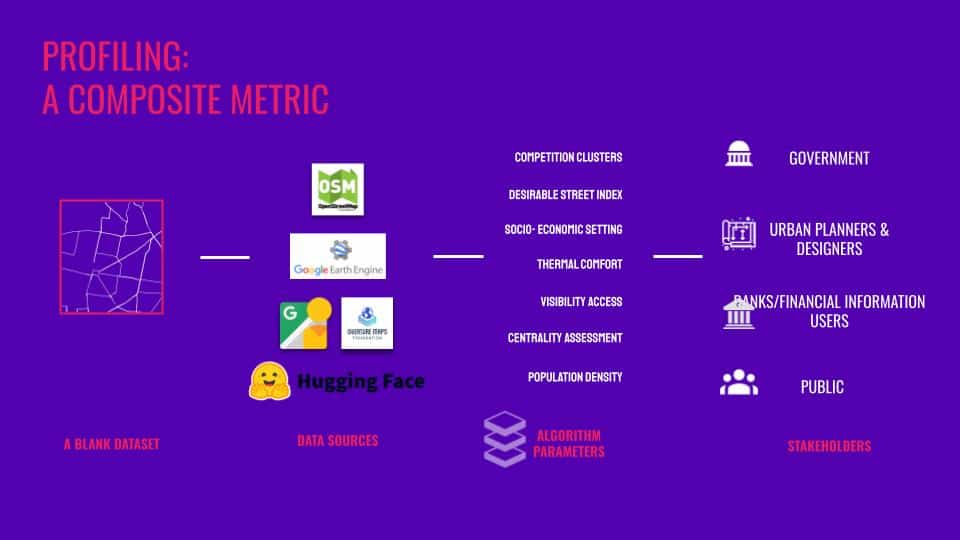
Diving deeper into building a reliable rating algorithm
The Importance & Significance of the F&B establishments in the City
Food and Beverage (F&B) service outlets are significant indicators of urban progress as they reflect evolving consumer preferences, economic vitality, and the integration of social spaces within urban landscapes. These establishments act as hubs for community interaction, fostering cultural exchange and social cohesion, especially in precinct-driven neighborhoods. Strategically planned F&B spaces enhance foot traffic, create vibrant environments, and contribute to economic growth by attracting both locals and tourists. They also serve as anchors in retail, dining, and entertainment (RDE) developments, elevating the overall experience for residents and visitors alike.
The impact of F&B outlets on their immediate environment is profound. They not only drive economic activity but also shape the identity of urban spaces. By offering diverse culinary experiences and fostering connections among people, these establishments contribute to the social fabric of cities. Moreover, they support local businesses, create employment opportunities, and promote sustainability through initiatives like sourcing local produce and reducing waste. Their role in urban planning goes beyond dining; they are integral to creating dynamic spaces that enhance accessibility, inclusion, and community engagement.

In the Indian context, F&B establishments are transforming rapidly with urbanization extending beyond metropolitan cities to Tier-II and Tier-III cities like Indore, Surat, and Raipur. These regions are witnessing a retail revolution driven by rising disposable incomes and aspirations for branded experiences. National and global F&B brands are increasingly investing in these markets, leveraging evolving consumer preferences for organized dining and cosmopolitan lifestyles. This expansion not only boosts local economies but also bridges gaps in infrastructure development while fostering cultural diversity through food
Banking Realities


Focusing on Chennai
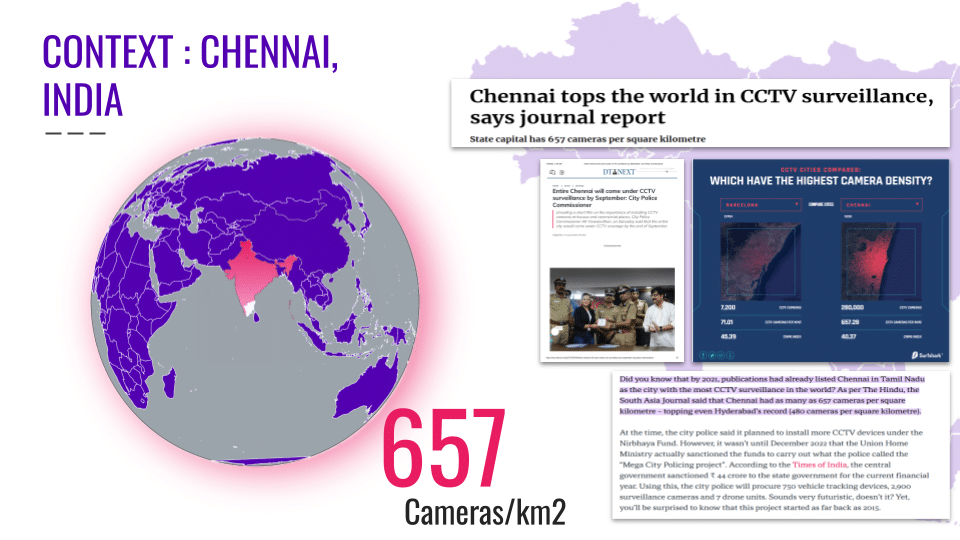
Chennai presents both opportunities and challenges as a test bed for studying the impact of F&B establishments and the significance of geolocation factors on their success. The city holds the 4th largest food service market in India, valued at ₹15.6 thousand crores ($18.72 billion USD), with Quick Service Restaurants (QSRs) and cloud kitchens leading the organized segment. Its diverse population, rich culinary heritage, and growing appetite for experiential dining make it an ideal location to test innovative F&B formats. Areas like Anna Nagar exemplify culinary booms, offering insights into how geolocation factors like footfall, accessibility, and neighborhood demographics influence restaurant success. Additionally, Chennai’s established legacy chains and multi-brand restaurant models provide a robust framework for analyzing scalability and customer loyalty.
Revisiting the Algorithm
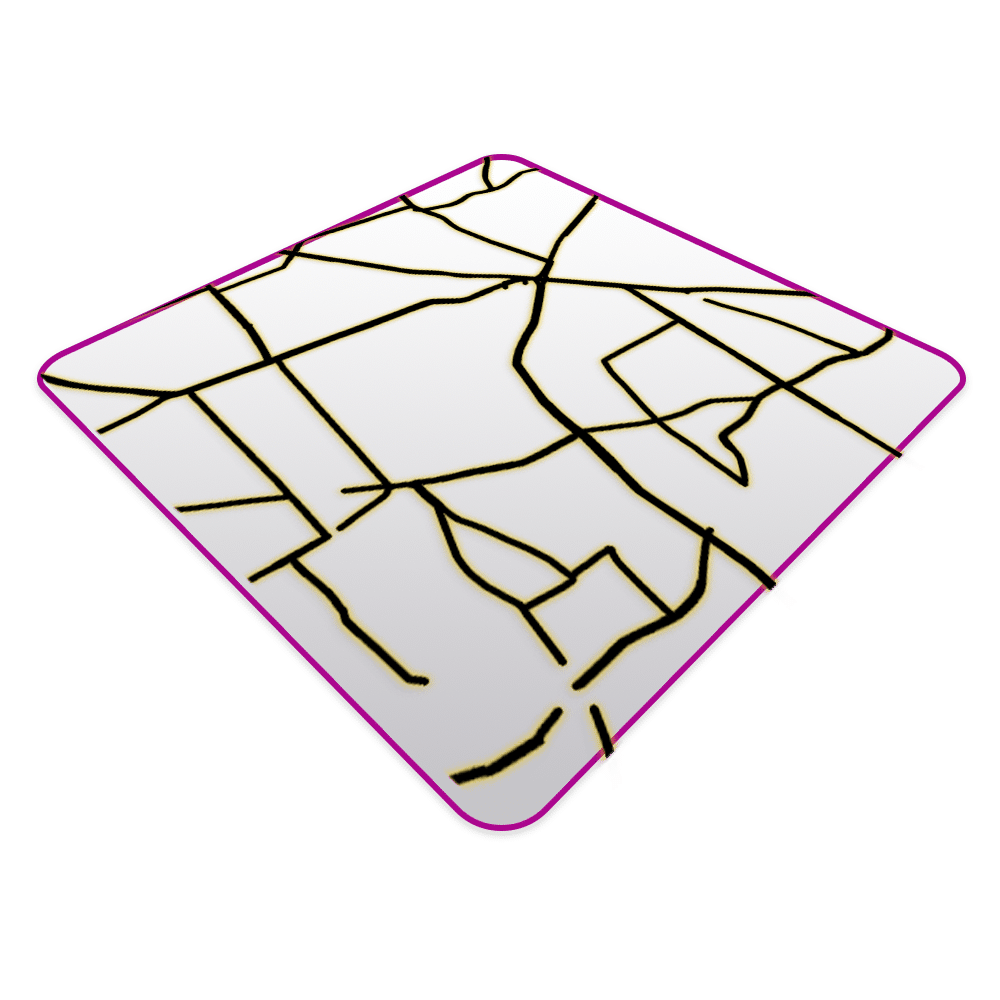
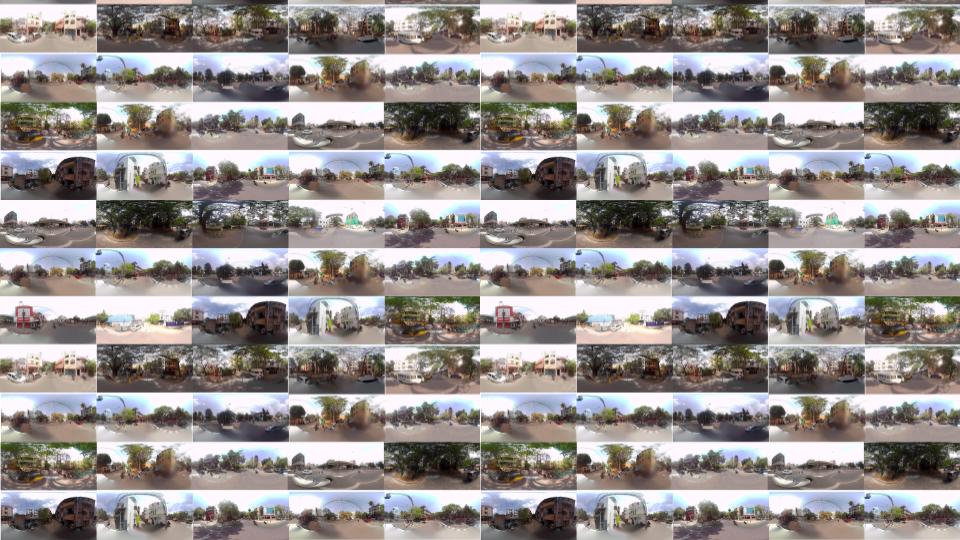
Building a Visual Library

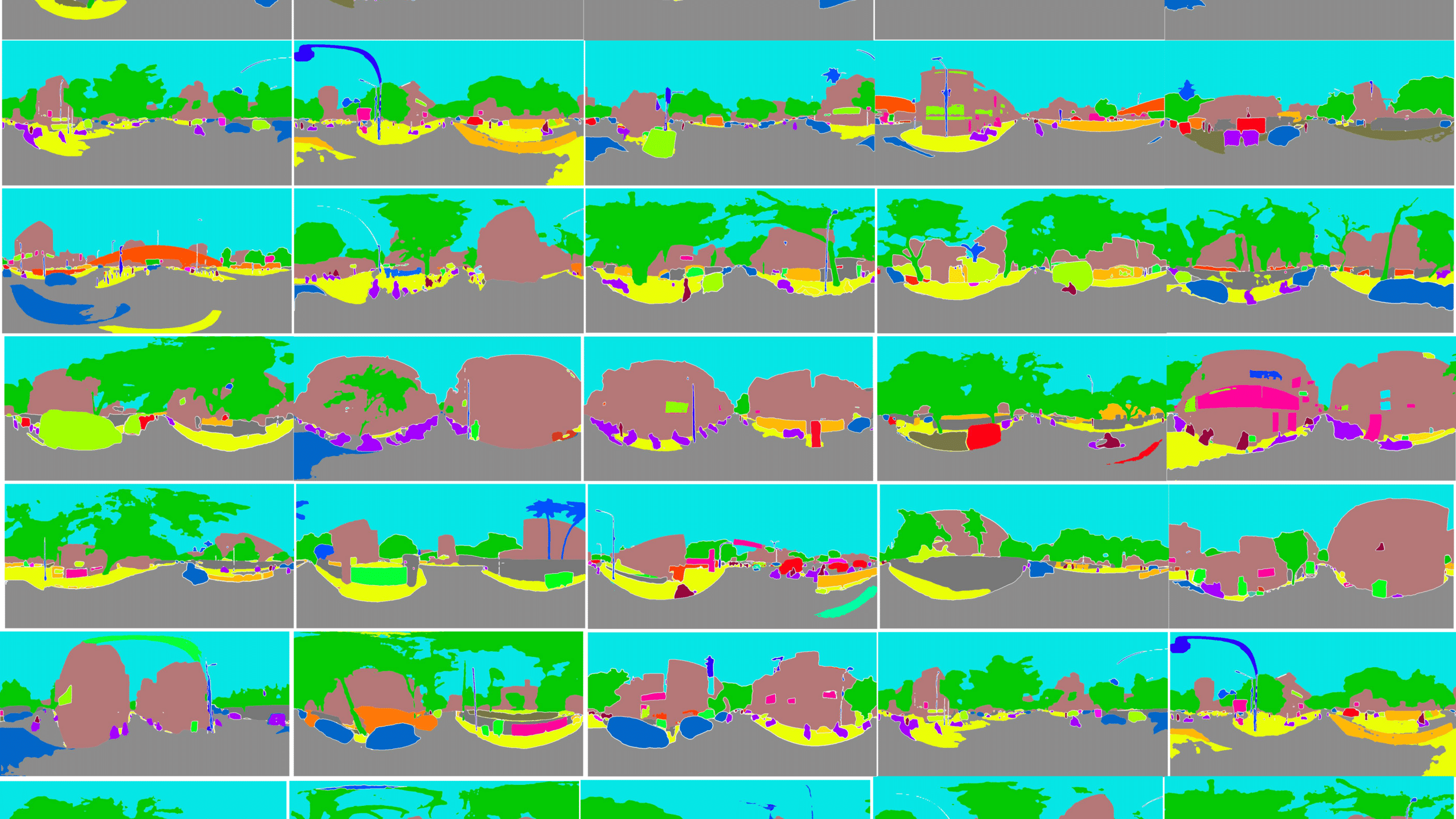
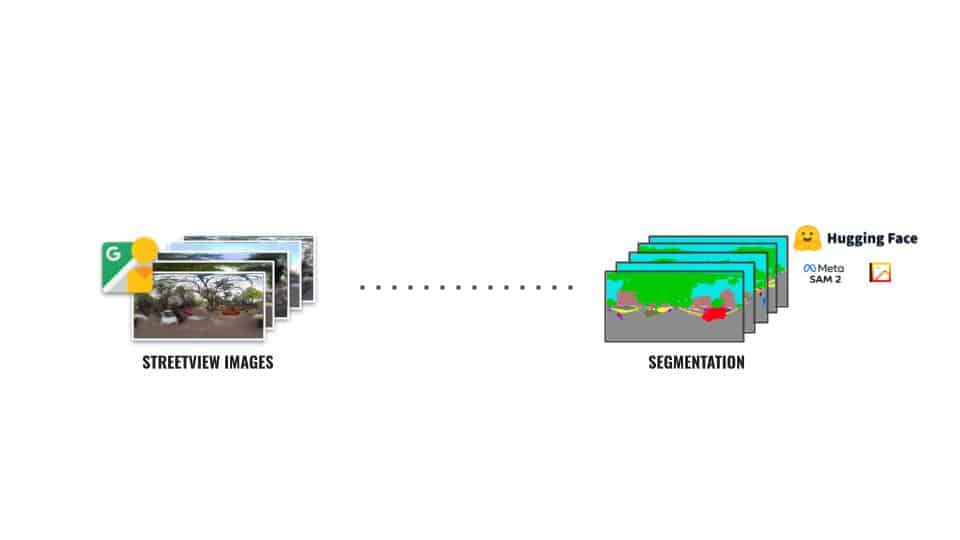
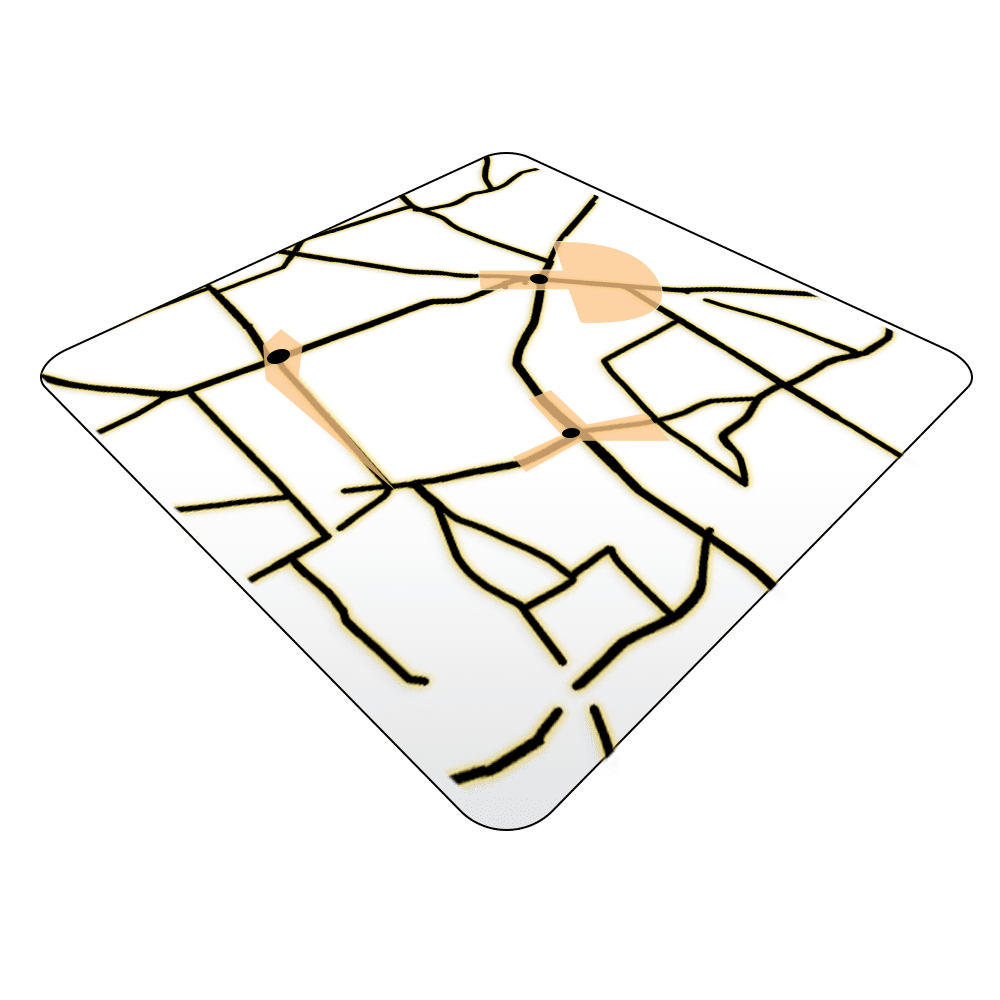
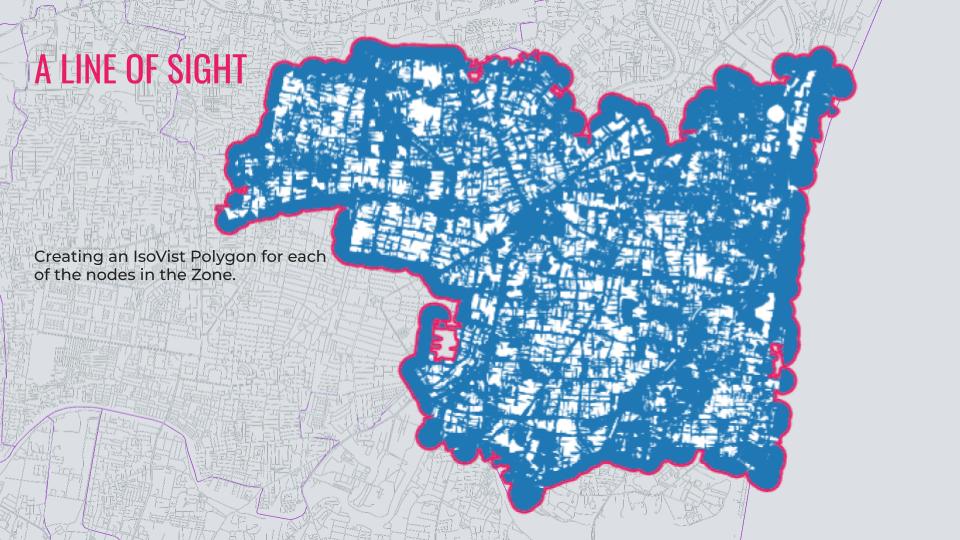
Constructing a Line of Sight Analysis
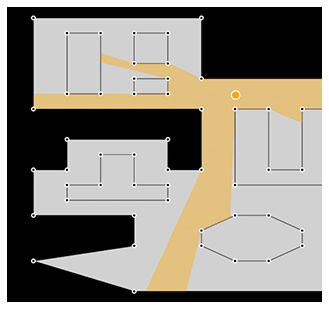
The CitySeer Python library is a powerful tool for urban analysis, particularly suited for pedestrian-scale studies of street networks and land use. One of its key applications is the Line of Sight (LoS) analysis, which evaluates visibility and spatial openness within urban environments. In the context of F&B establishments, LoS analysis is essential for understanding how visibility impacts foot traffic, customer attraction, and overall business success. By analyzing a 150-meter line of sight from each road network segment node and assigning the average isovist areas to these segments, CitySeer provides a fine-grained understanding of spatial accessibility and visibility dynamics.

Relevance to F&B Establishments
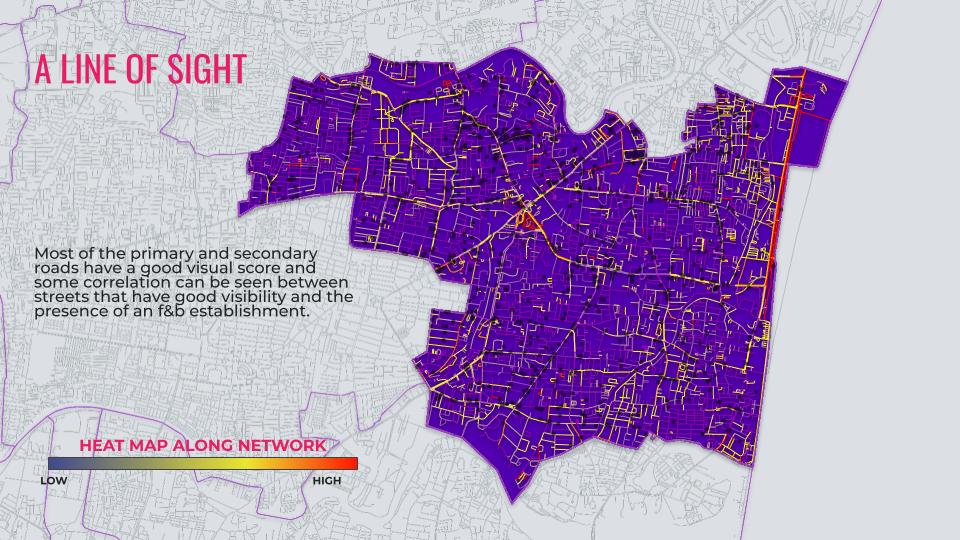
Visibility is a critical factor for F&B outlets, as it directly influences customer awareness and walk-in rates. A well-placed establishment with high visibility along key pedestrian corridors or intersections is more likely to attract spontaneous customers. The LoS analysis helps identify such strategic locations by quantifying how visible an establishment is from various vantage points along the road network. For instance, areas with larger average isovist areas typically indicate open spaces or unobstructed views, making them prime locations for businesses reliant on high footfall.
Why 150 Meters?
The 150-meter threshold is widely used in transport modeling and urban studies due to its alignment with pedestrian behavior. It represents a comfortable walking distance within which visual stimuli are likely to influence decision-making. Studies have shown that this range captures the majority of pedestrian interactions with their environment, making it an ideal metric for evaluating visibility and accessibility. In the context of F&B establishments, this distance ensures that the analysis remains focused on the immediate surroundings that are most relevant for attracting customers.
Broader Implications
Beyond individual establishments, LoS analysis using CitySeer contributes to urban planning by identifying areas with poor visibility or connectivity that could benefit from interventions such as better signage or improved urban design. This makes it a valuable tool not only for business owners but also for policymakers aiming to create vibrant, pedestrian-friendly neighborhoods.
By leveraging tools like CitySeer, urban analysts can provide actionable insights into how visibility and spatial configuration impact the success of F&B establishments, ultimately contributing to more efficient urban planning and business strategies.
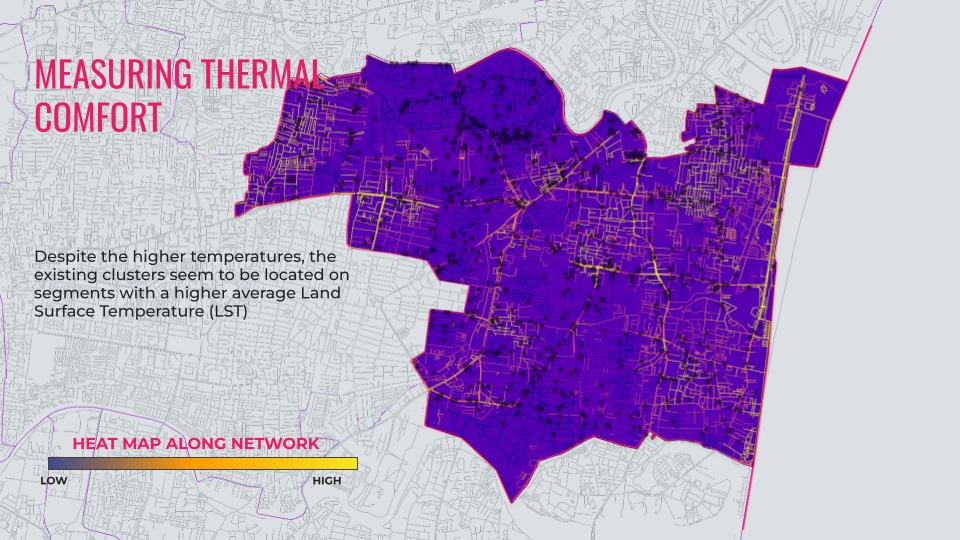
Measuring Thermal Comfort
Thermal comfort is a critical factor in urban design and planning, especially for outdoor spaces like city squares, pedestrian corridors, and areas surrounding F&B establishments. Using Land Surface Temperature (LST) raster data derived from Google Earth Engine’s remote sensing methodology provides a robust approach to assess thermal comfort levels across urban environments. This analysis involves mapping LST values across the study area to identify heat stress zones and evaluate the thermal environment’s impact on human comfort. For F&B establishments, understanding thermal comfort is essential as it influences customer behavior, outdoor seating preferences, and overall business sustainability.
Relevance to F&B Establishments
F&B establishments often rely on outdoor spaces for dining and social interaction. High LST values can deter customers from choosing outdoor seating, directly impacting revenue. By analyzing thermal comfort using LST data, businesses can identify optimal locations for outdoor seating or implement mitigation strategies such as vegetation, shading structures, or cooling technologies. Additionally, areas with lower LST values may attract more foot traffic, making them ideal for new establishments. This analysis also aids urban planners in designing thermally comfortable environments that support vibrant commercial activity.
The Question of Centrality
Centrality is a key concept in urban planning and spatial analysis, measuring the importance or accessibility of a location within a network. For F&B establishments, centrality plays a crucial role in determining visibility, foot traffic, and proximity to complementary points of interest (POIs) such as temples, school districts, and commercial hubs. High-centrality locations are often more accessible and visible, making them ideal for attracting spontaneous customers and ensuring consistent patronage.
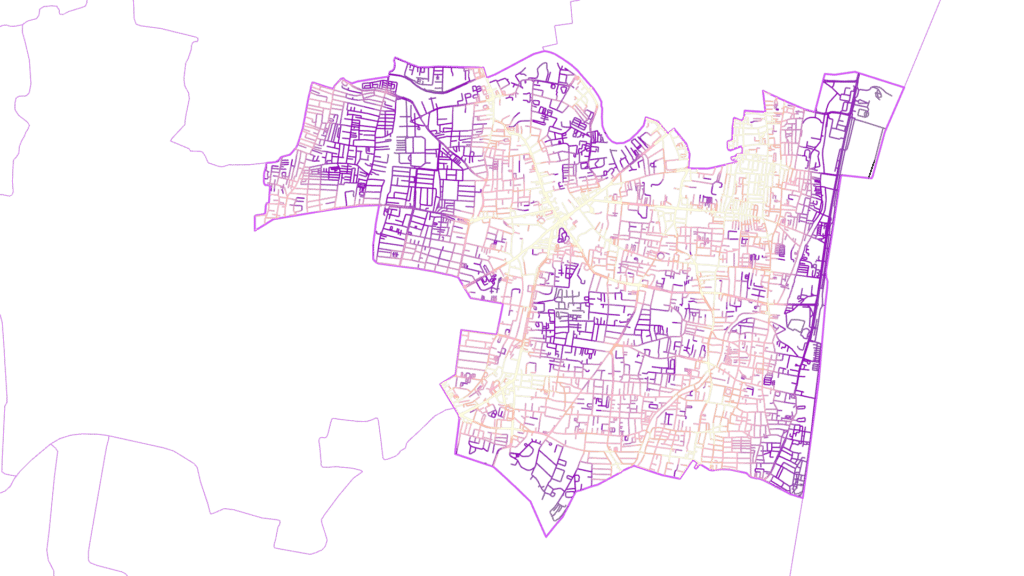
Algorithmically, centrality can be calculated using measures like Betweenness Centrality, which quantifies how often a node (or street segment) lies on the shortest path between other nodes in a network. In this study, a Space Syntax analysis was performed using a 1200-meter radius of network betweenness. This approach identifies street segments that act as critical connectors within the urban grid. Betweenness is particularly relevant for F&B establishments because it highlights areas with high movement potential—locations where people naturally converge due to the spatial configuration of the city.
Space Syntax Analysis and Its Importance
Space Syntax is an analytical framework used to study spatial networks by evaluating their connectivity and accessibility. The 1200-meter network betweenness analysis captures pedestrian-scale movement patterns within a comfortable walking distance. This metric is significant because it aligns with human mobility behaviors, focusing on areas where people are likely to interact with their surroundings. For F&B establishments, such analysis can pinpoint high-traffic zones near POIs like temples or schools, where visibility and accessibility are maximized.
Consider Restaurant Typology

Restaurant typology—the concept that defines the type of dining establishment (e.g., fine dining, casual dining, fast food, cafes)—is a crucial factor in designing algorithms that rate a location’s business potential. Different restaurant types cater to specific customer demographics, dining occasions, and service expectations, which directly influence their success in particular locations. For example, fine dining establishments thrive in affluent areas with high disposable income, while fast food outlets perform better near universities or business districts with high foot traffic and demand for quick meals.
Relevance of Typology in Location Analysis
The typology determines the compatibility of a restaurant with its surrounding environment. For instance:
- Fine Dining: Requires proximity to affluent neighborhoods, luxury commercial hubs, or cultural landmarks.
- Casual Dining: Benefits from mixed-use areas combining residential and commercial zones.
- Fast Food: Performs well near schools, transit hubs, or densely populated urban areas.
- Cafes: Thrive near educational institutions, coworking spaces, or leisure districts.
By incorporating typology into location rating algorithms, the algorithm can assess how well the characteristics of a location align with the operational needs and target demographics of a specific restaurant type.
Further Explorations