Abstract
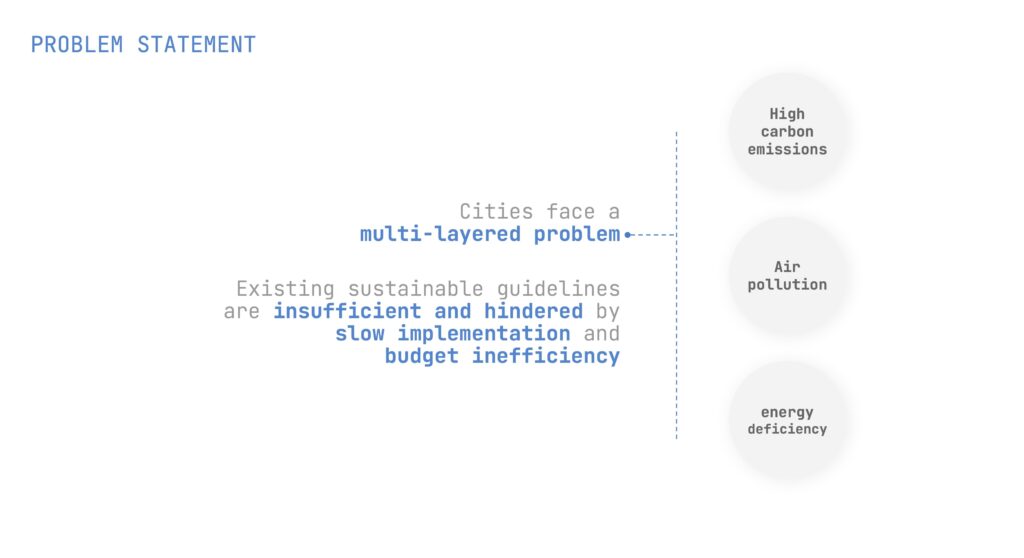
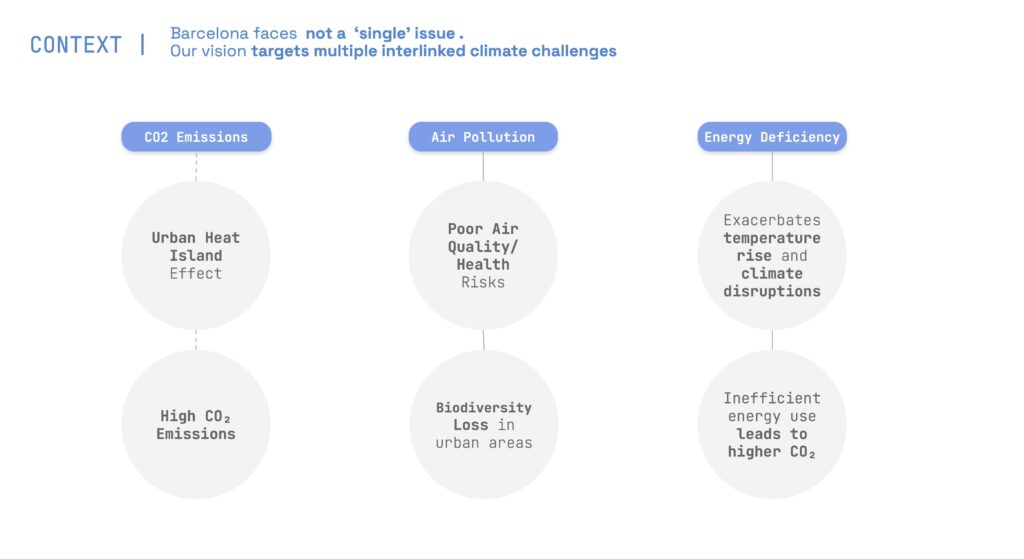
The project explores innovative ways to address Barcelona’s sustainability challenges, such as carbon emissions, air pollution, and energy inefficiency.
By leveraging AI, IoT sensors, and Nature-Based Solutions (NBS), the project aims to optimize municipal budgets for interventions that transform underutilized urban spaces into productive assets.
The study highlights solutions like urban farming, greenery, and solar catchment systems, evaluated for cost-efficiency and environmental impact.
A custom dashboard provides planners with actionable insights and tools to prioritize interventions, aligning with Barcelona’s Climate Plan and contributing to a 45% CO₂ reduction by 2030.
This initiative offers a scalable and data-driven framework for sustainable urban transformation.


Project Aim and Objectives
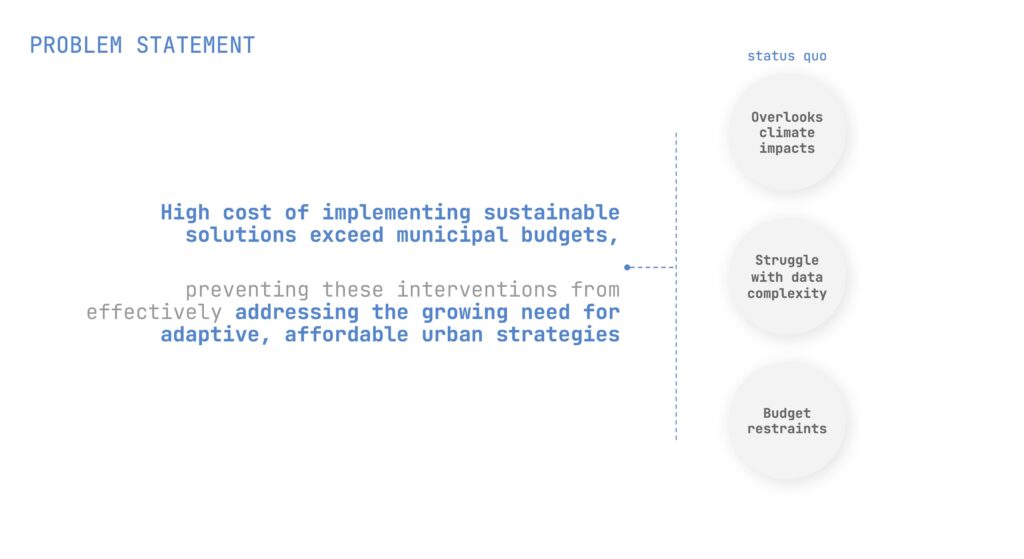
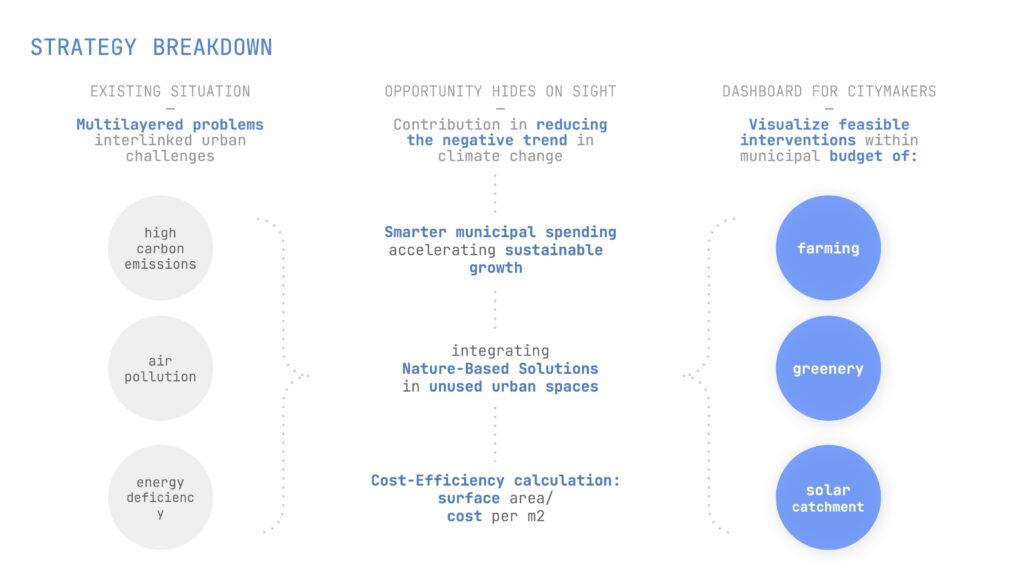
The project aims to develop an AI-driven tool that maximizes municipal budgets for sustainability interventions.
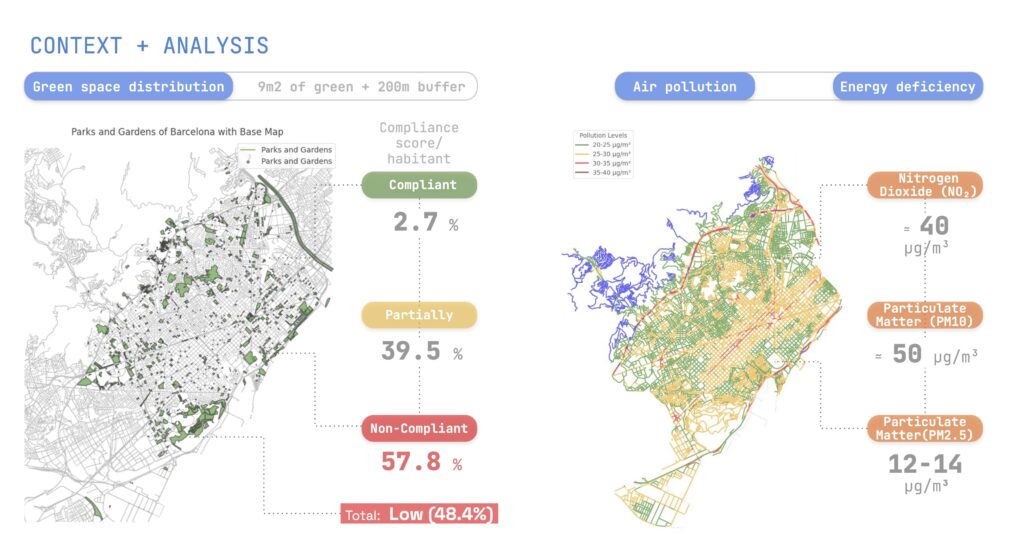
Objectives include localizing underutilized urban spaces, predicting unknown climatic data using IoT sensors, and generating recommendations for implementing Nature-Based Solutions (NBS).


_ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _
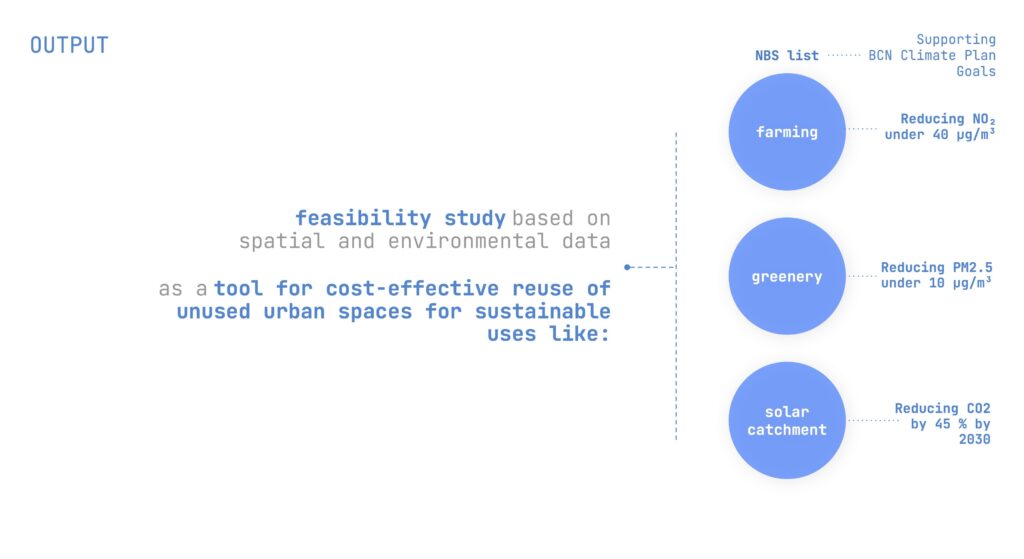
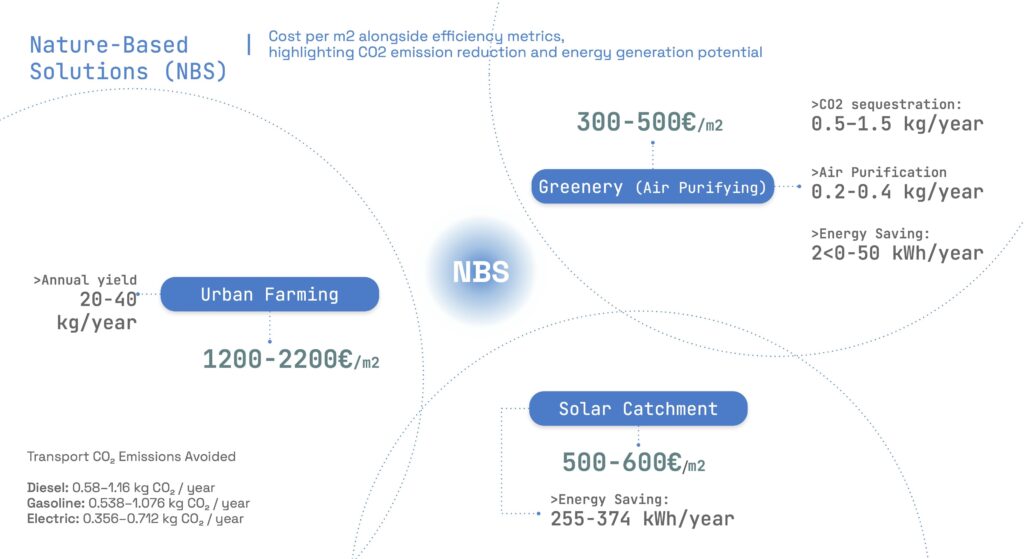
Three primary Nature-Based Solutions (NBS) identified:
- Solar Catchment through panels: Costs €500-600/m² and enhances energy efficiency.
Each solution is evaluated for its environmental impact, including CO₂ reduction and energy optimization. - Urban Farming: Costs €1,200-2,200/m² with a yield of 20-40 kg/year.
- Air Purifying Greenery: Costs €300-500/m², providing air purification and energy savings
_ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _
Methodology
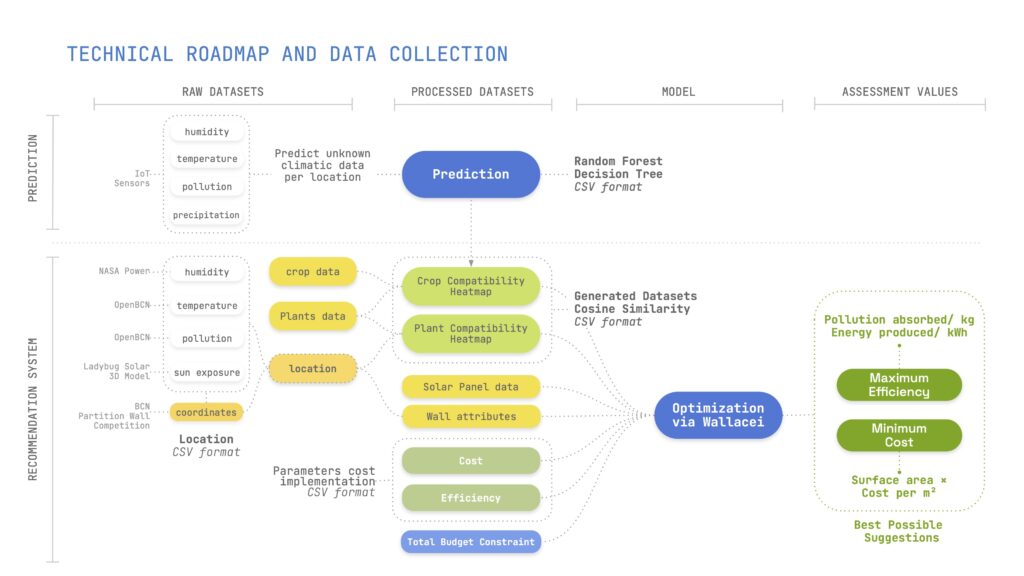
The study employs a structured workflow:
- Data collection via IoT sensors, AI-driven environmental assessment, and raw open data collection.
- Budget-tuned fund parameters for further allocation.
- Predictive models, such as Random Forest and K-Means clustering for Compatibility assessment,
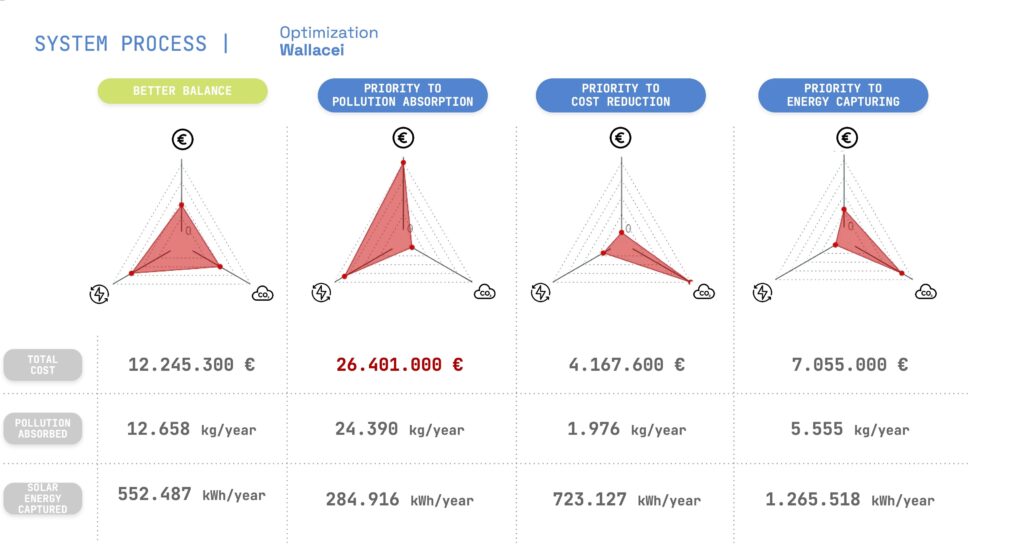
- Optimization is achieved using Wallacei to balance pollution reduction, cost efficiency, and energy savings
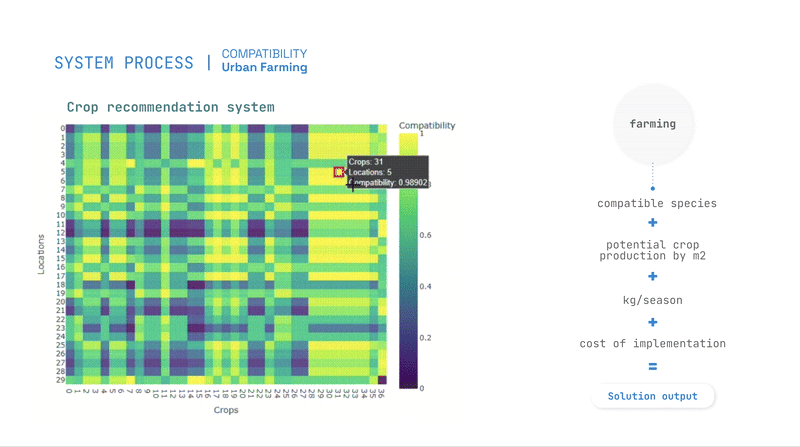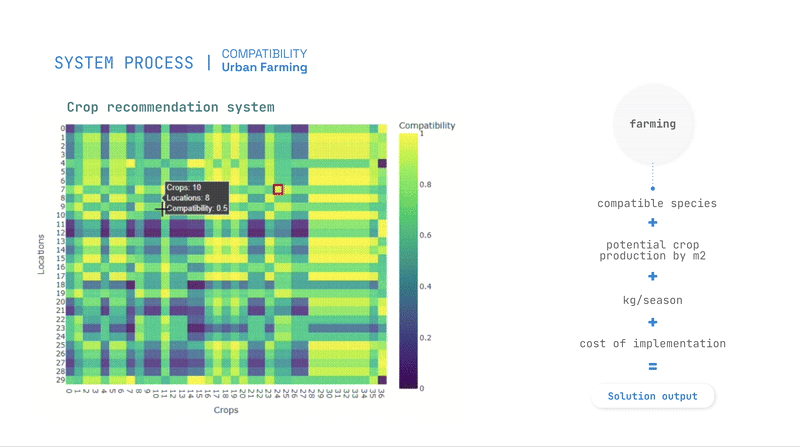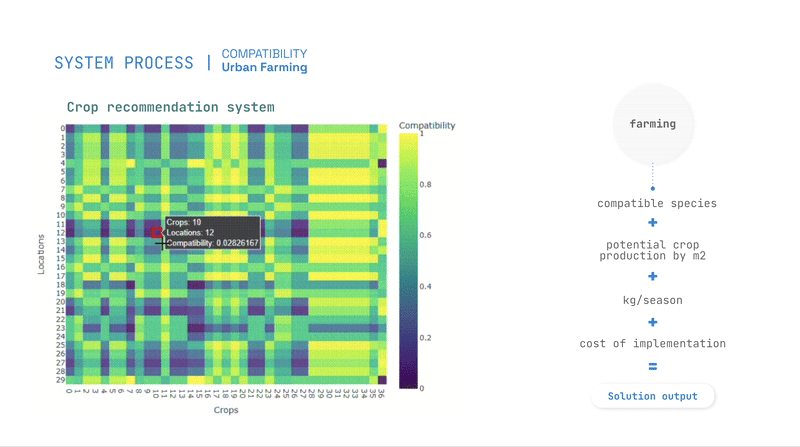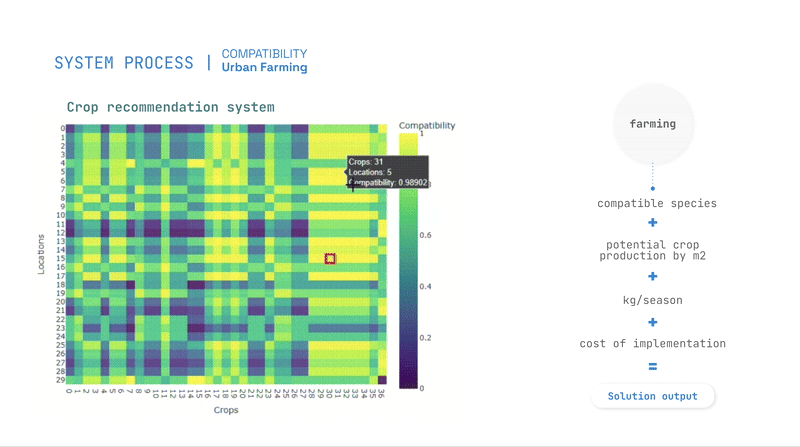
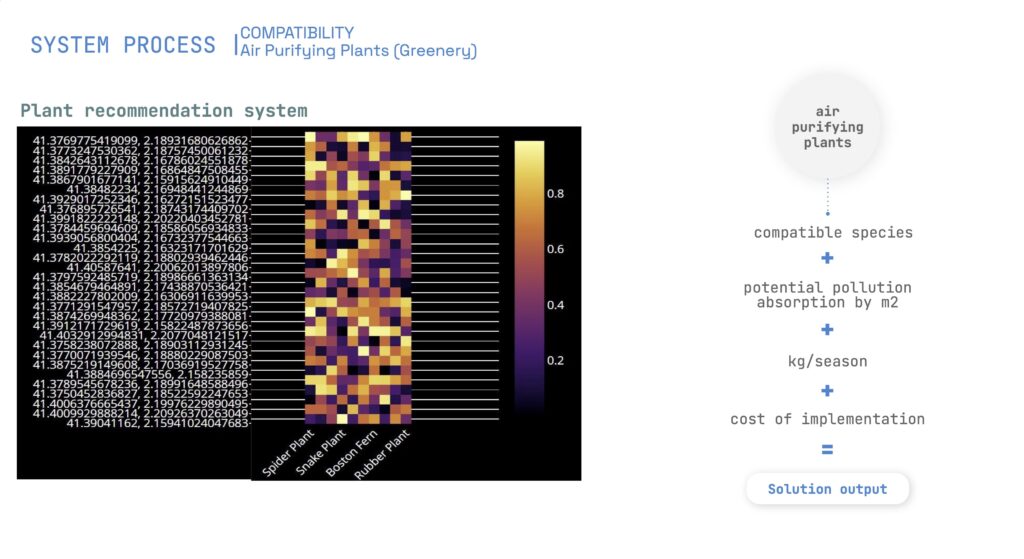
Optimization and Recommendations
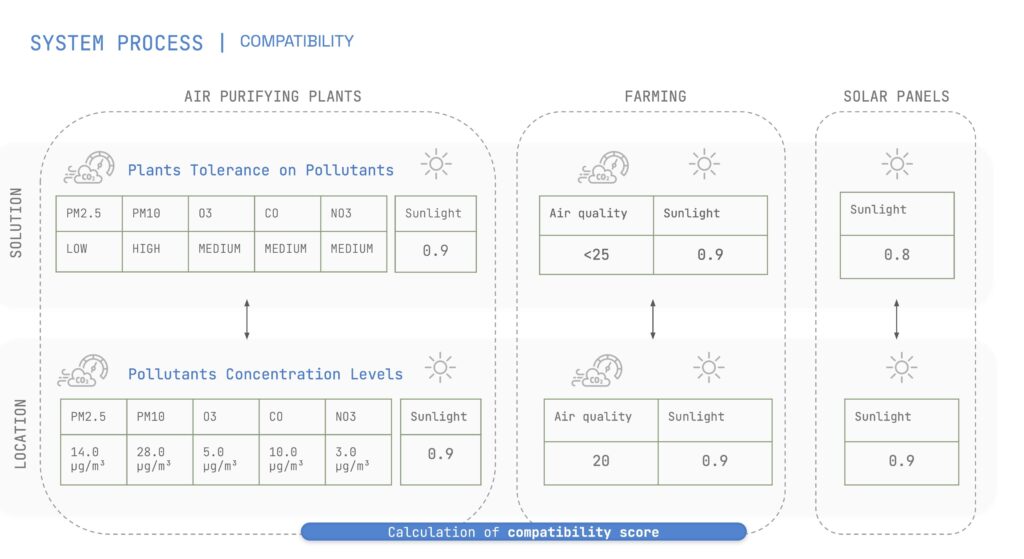
Optimization is guided by evolutionary algorithms, balancing priorities such as pollution absorption, cost reduction, and energy generation.
The study produces compatibility scores for interventions, allowing planners to identify the best locations for urban farming, greenery, and solar panels.
Dashboard Design
A user-friendly dashboard is presented to visualize intervention opportunities within municipal budgets. It allows planners to explore feasible solutions,
analyze costs and benefits, and monitor compliance with climate goals in real-time.
Outputs
The feasibility study outlines cost-effective methods to repurpose unused urban spaces.
Recommendations support Barcelona’s Climate Plan, targeting a 45% CO₂ reduction by 2030.
The study also introduces a dashboard for city planners, offering visual tools to identify and assess potential interventions.



