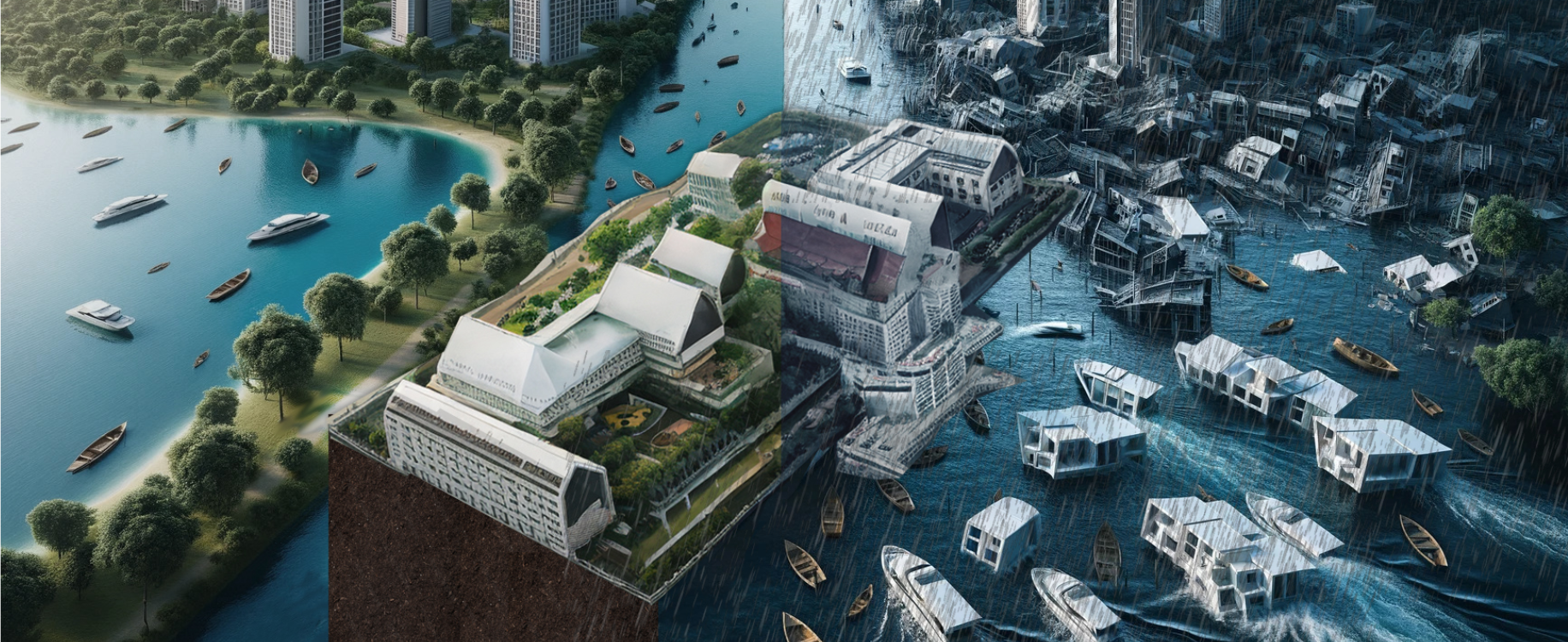
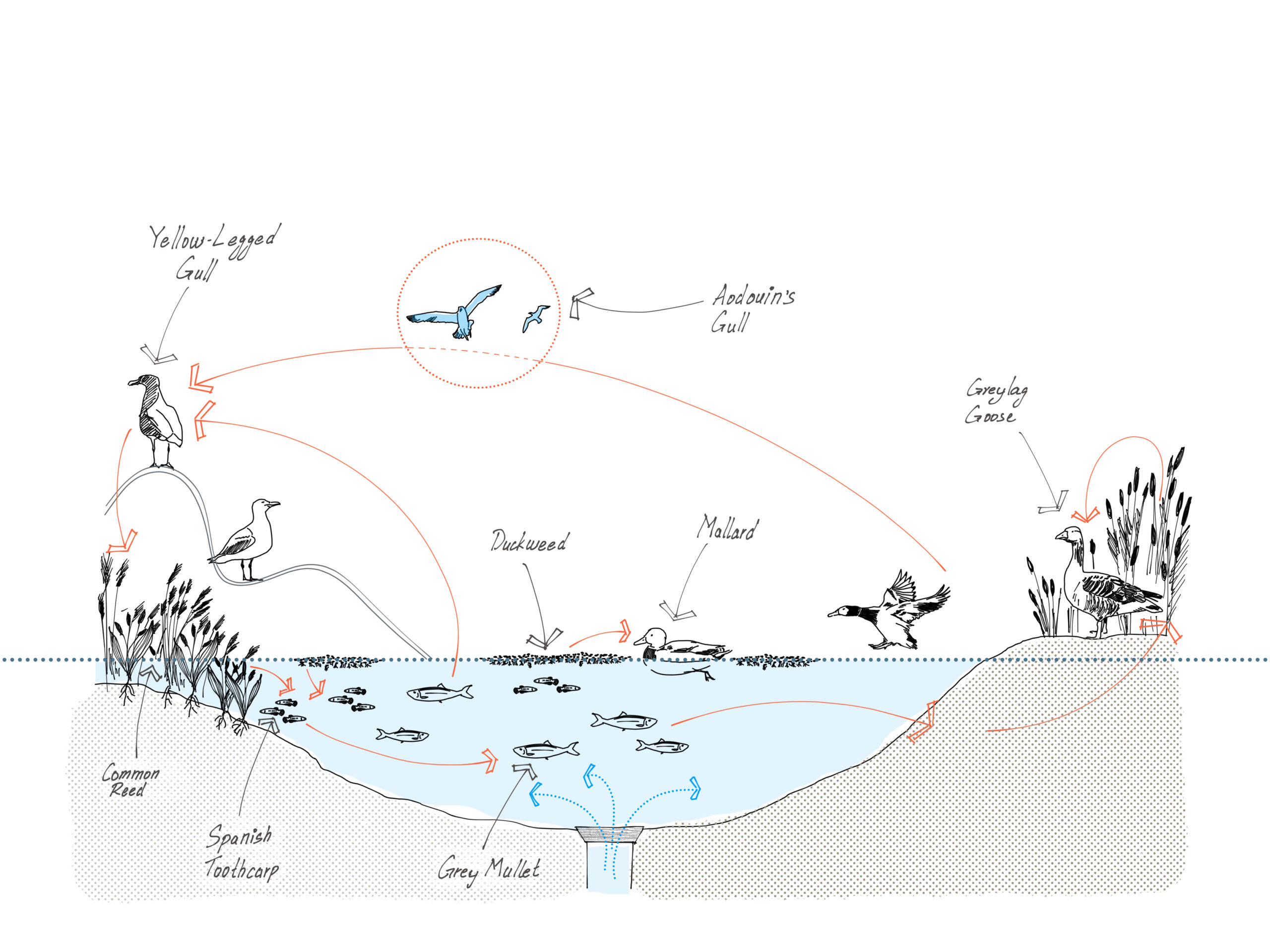
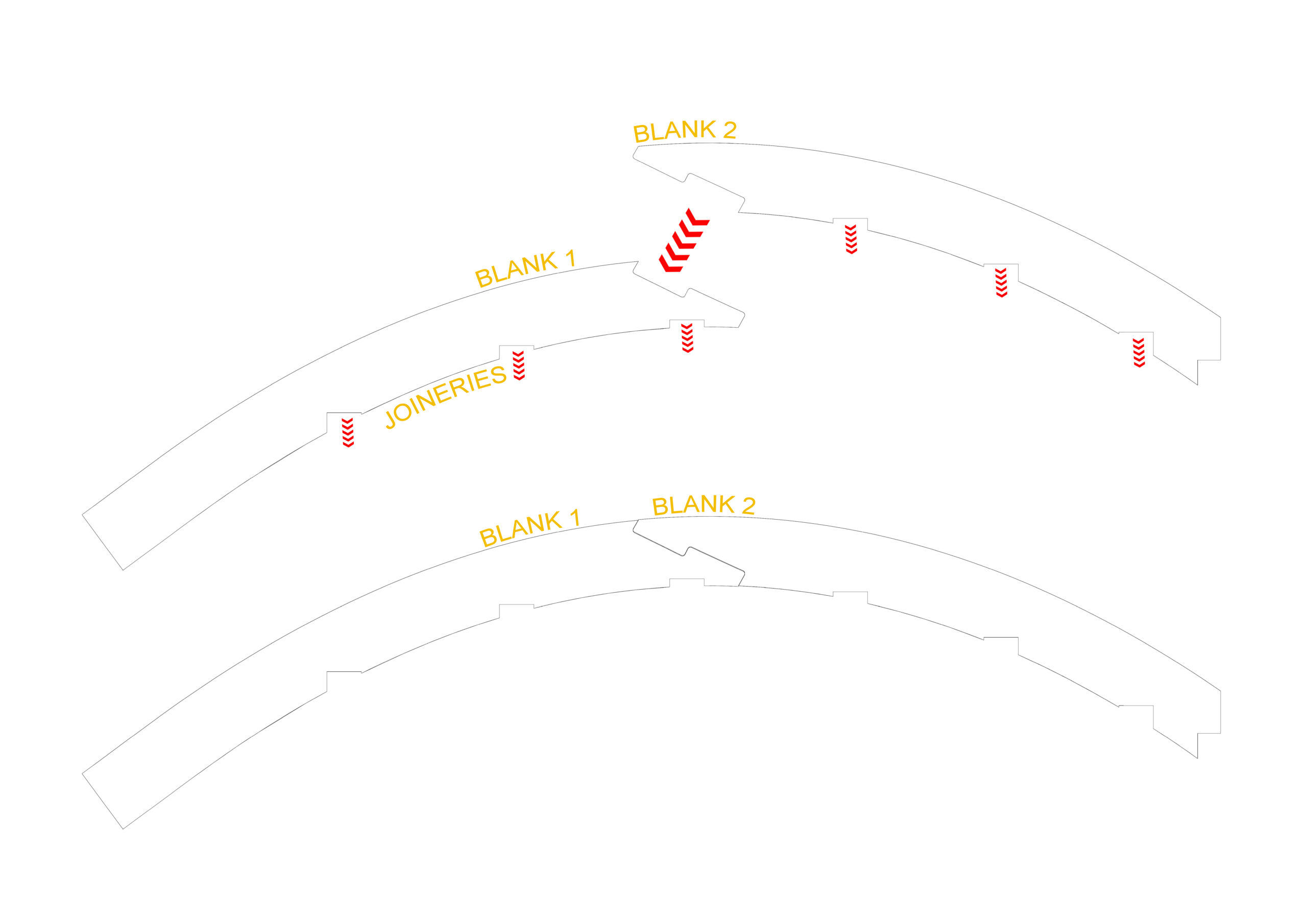
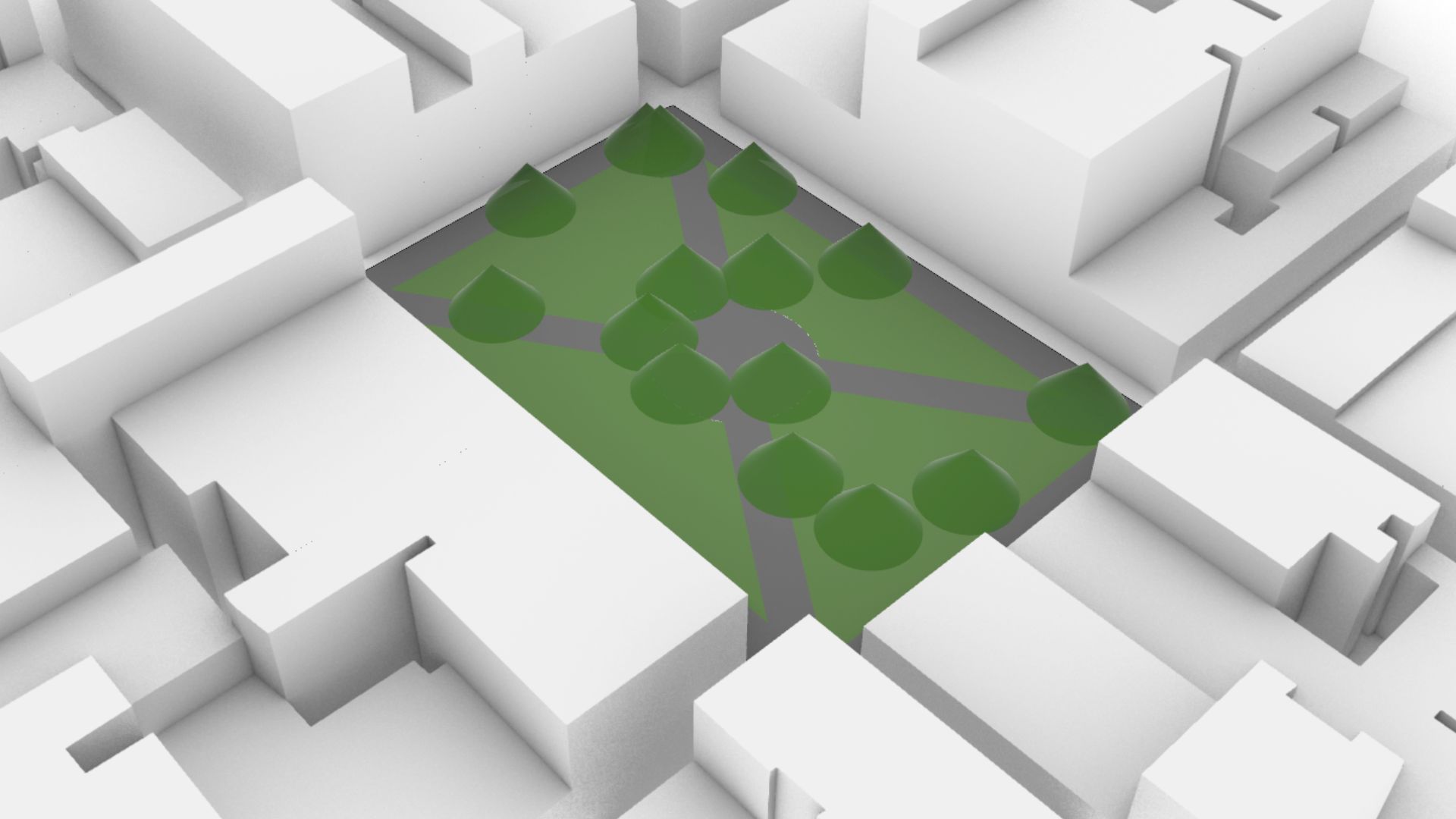
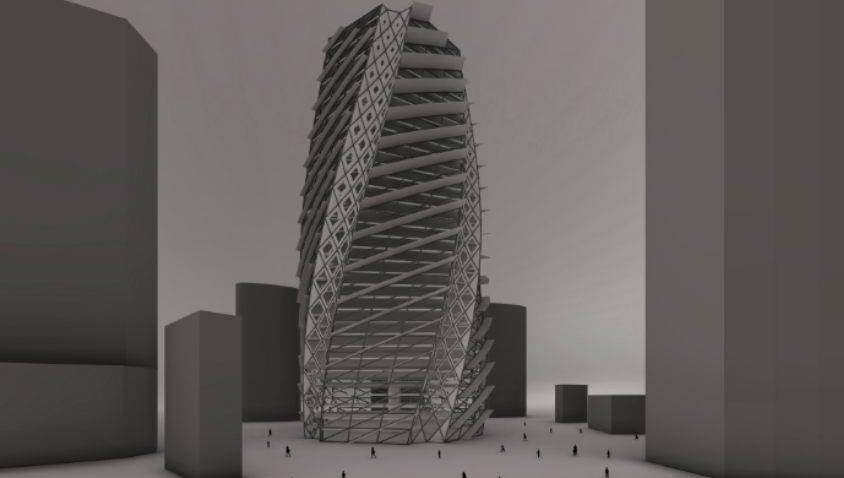
On how lopsided pyramids might emerge
“Ready Player One,” portrays a dystopian future where ‘people stopped to try to fix problems and instead try to outlive them’. The movie plays out in an informal urban landscape of juxtaposed favela-like settlements forming organic superstructures, as well as in a virtual environment supported by a virtual reality headset. These worlds exist in symbiosis, … Read more