Anatomy of a Machine: Stroke
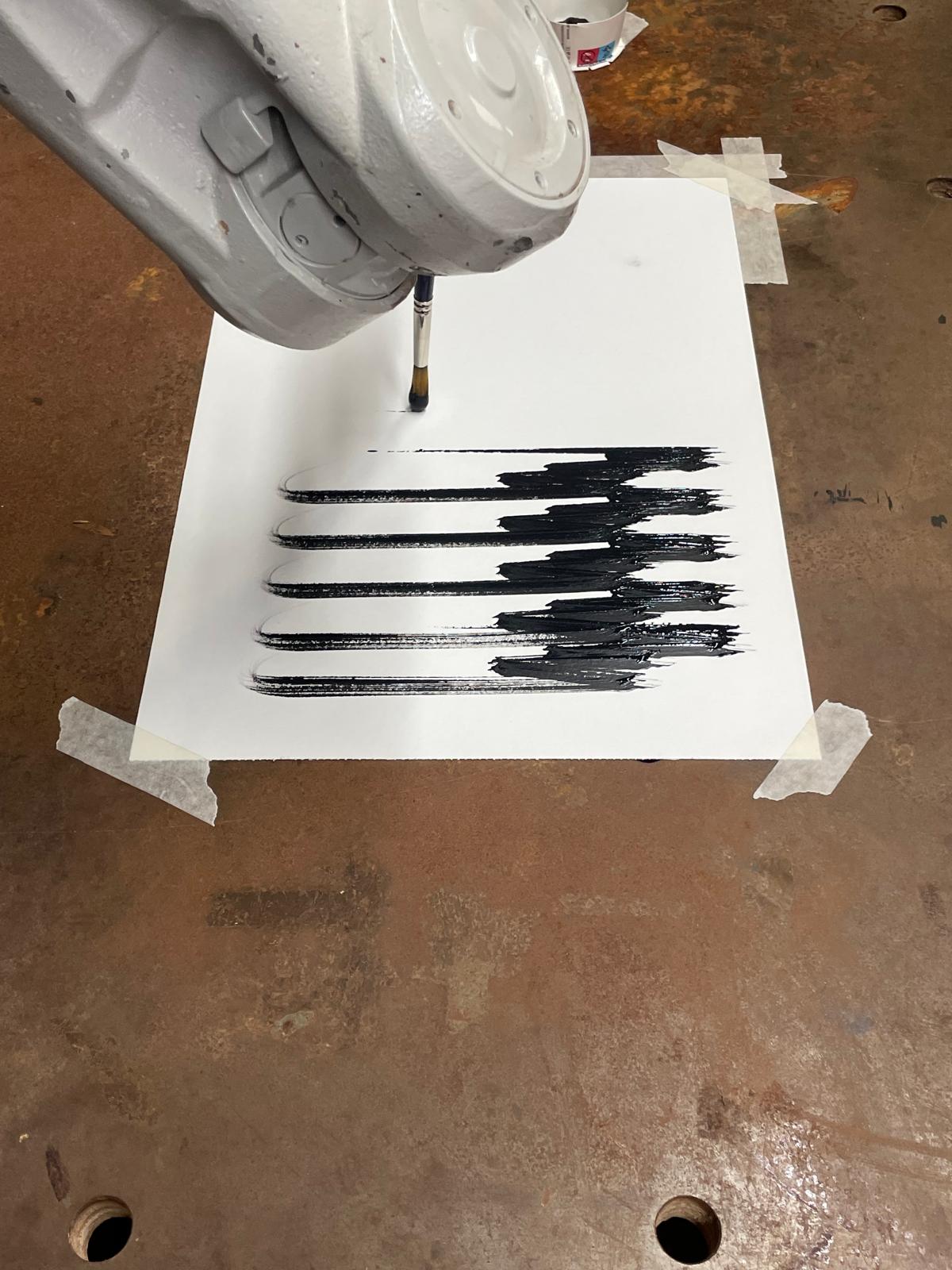
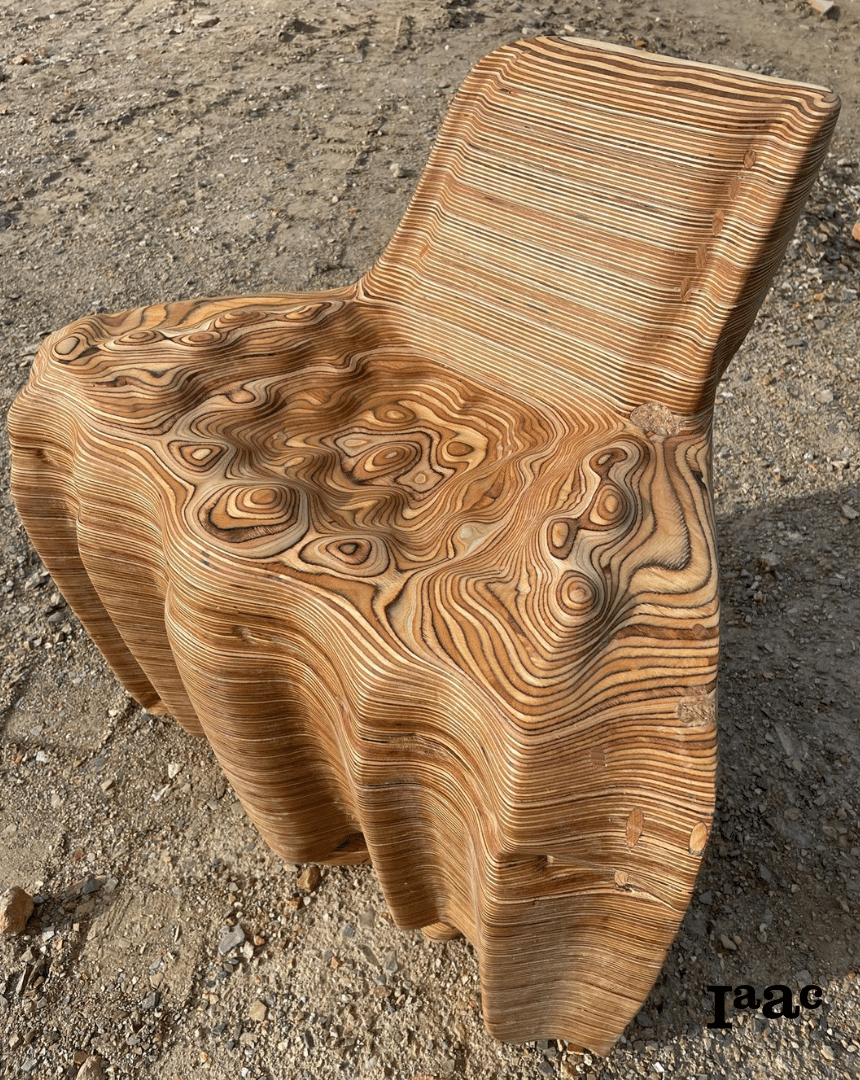
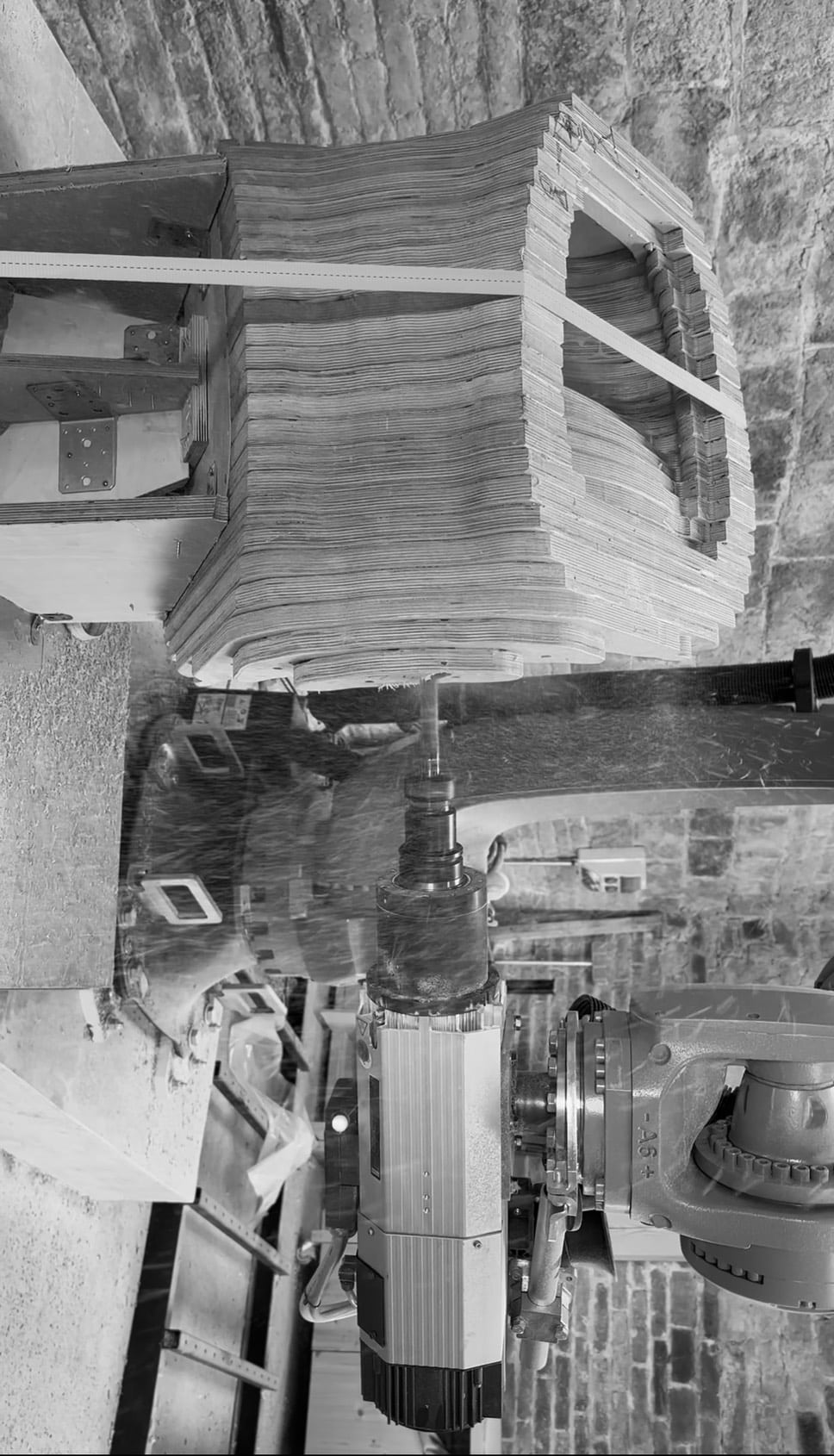
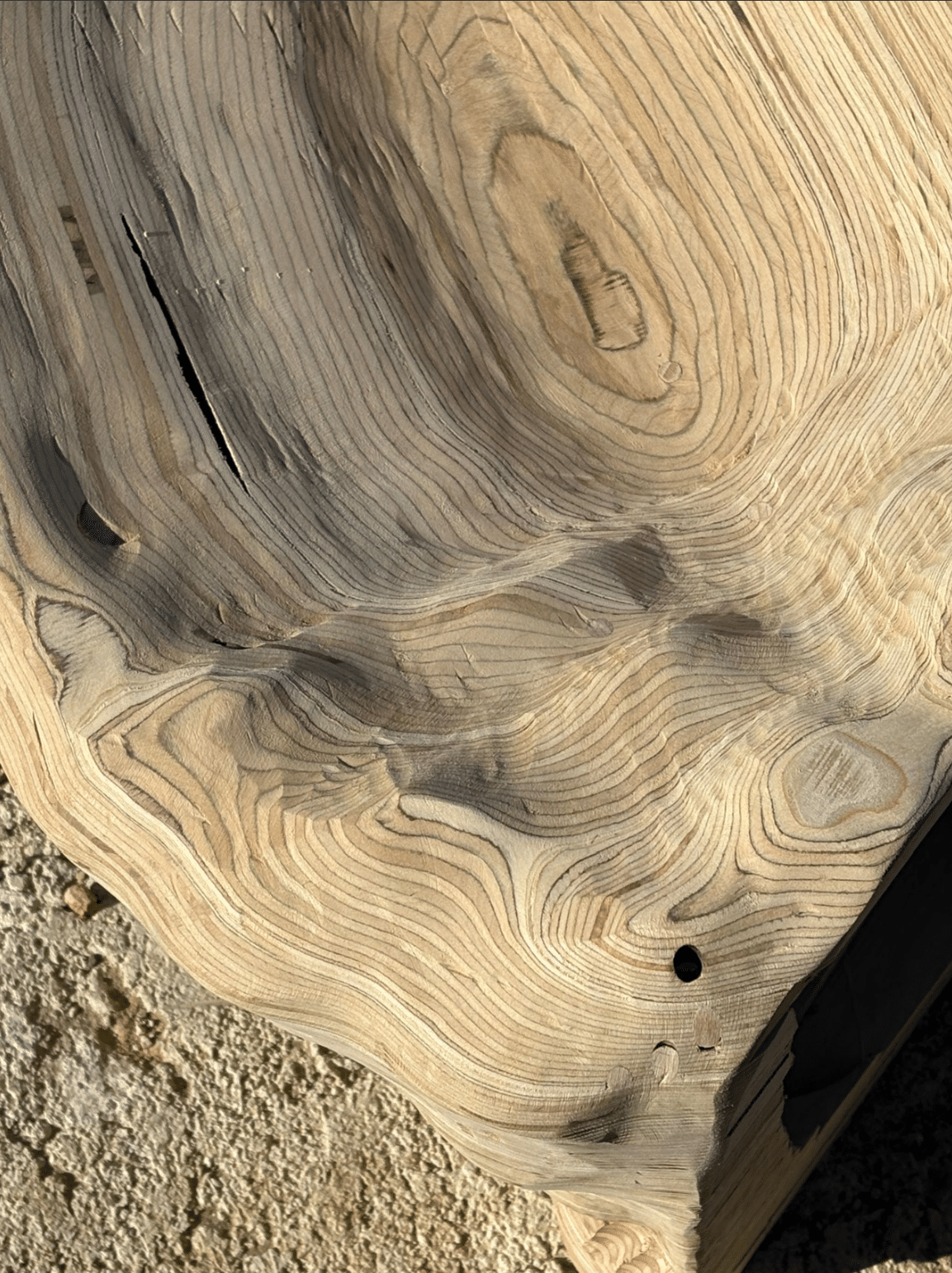
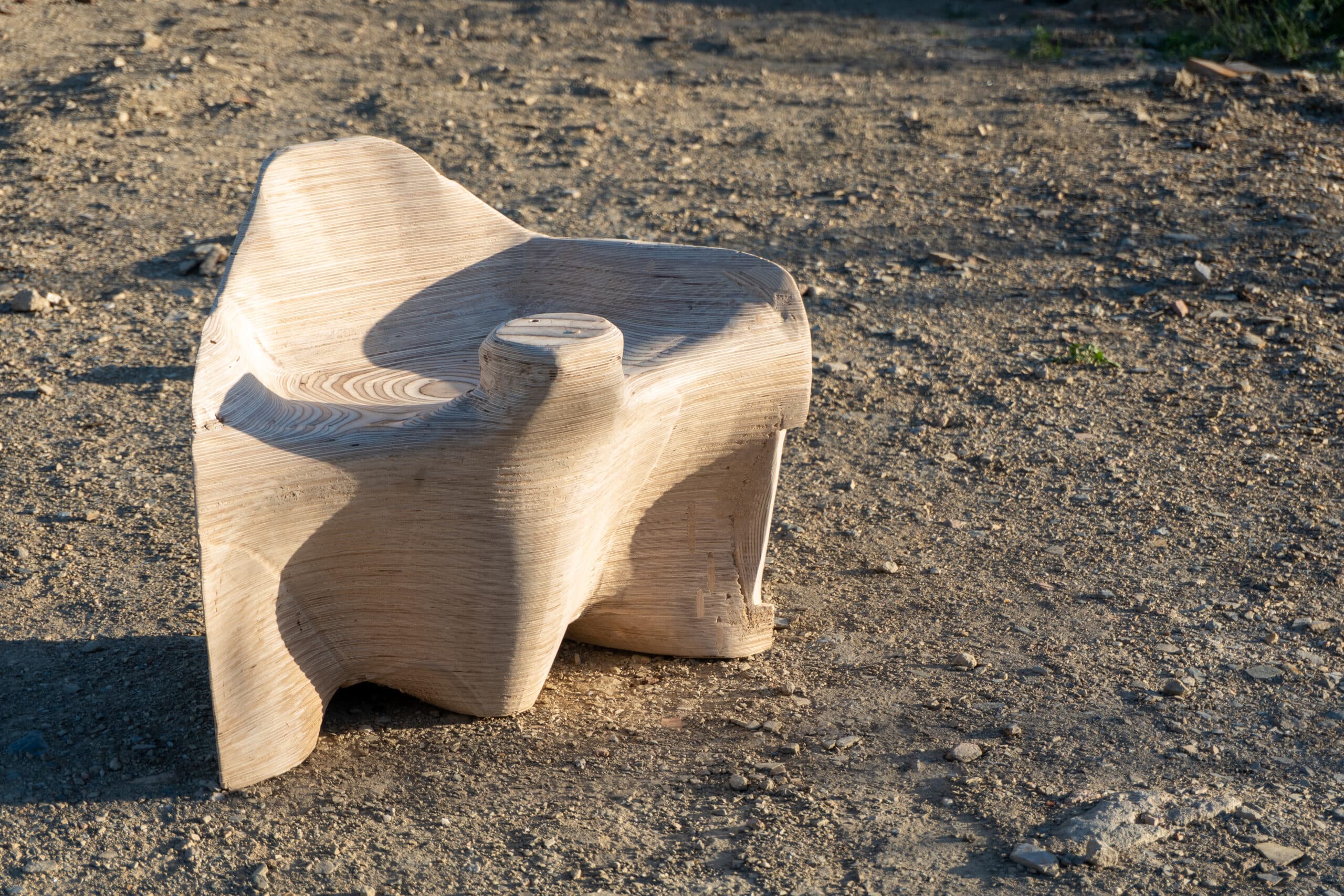
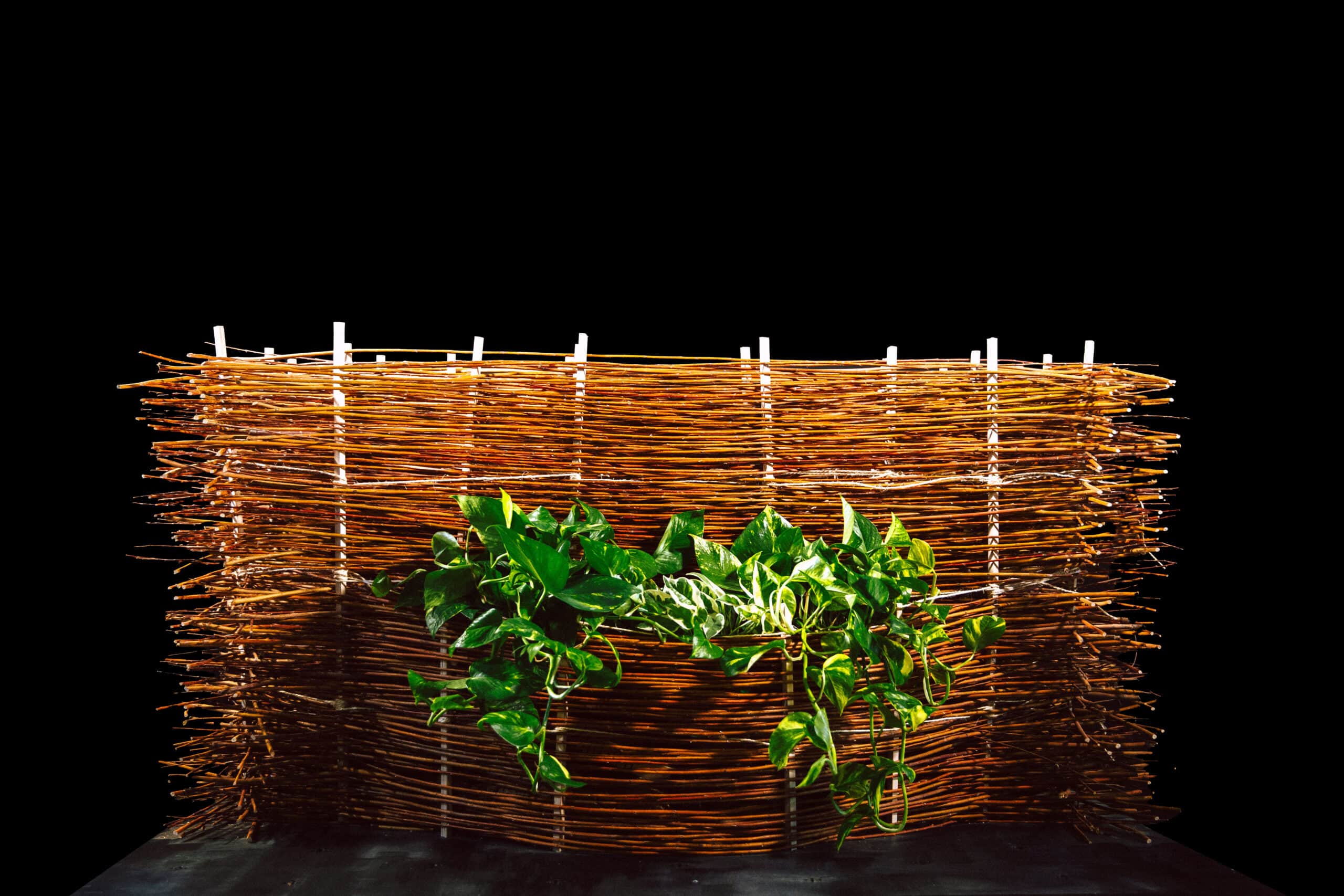
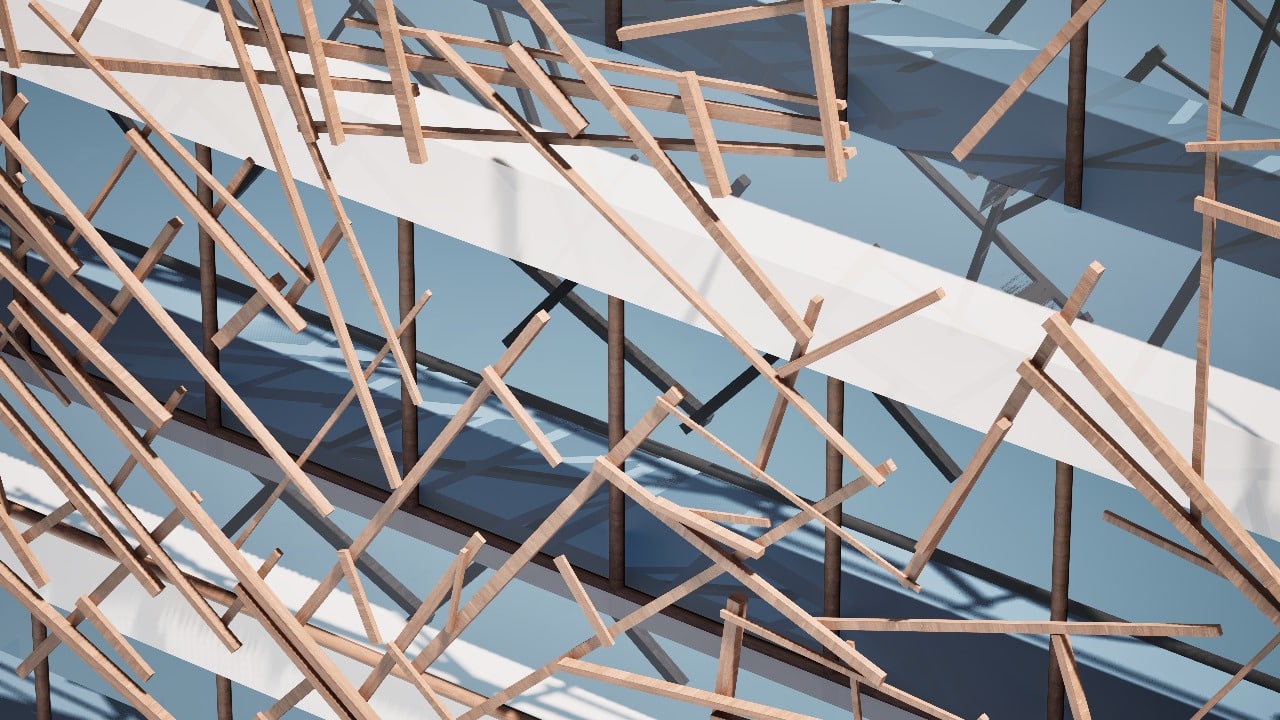
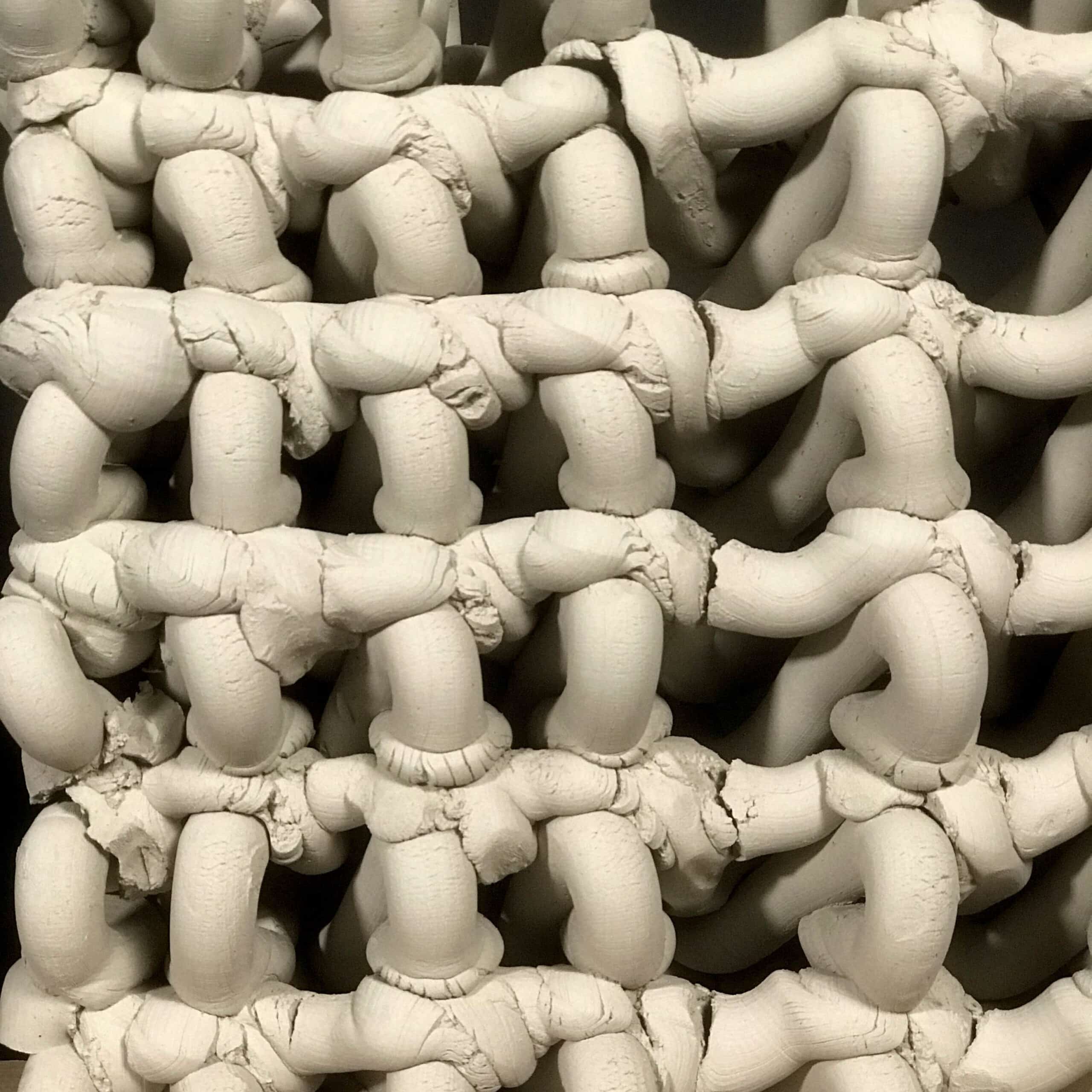
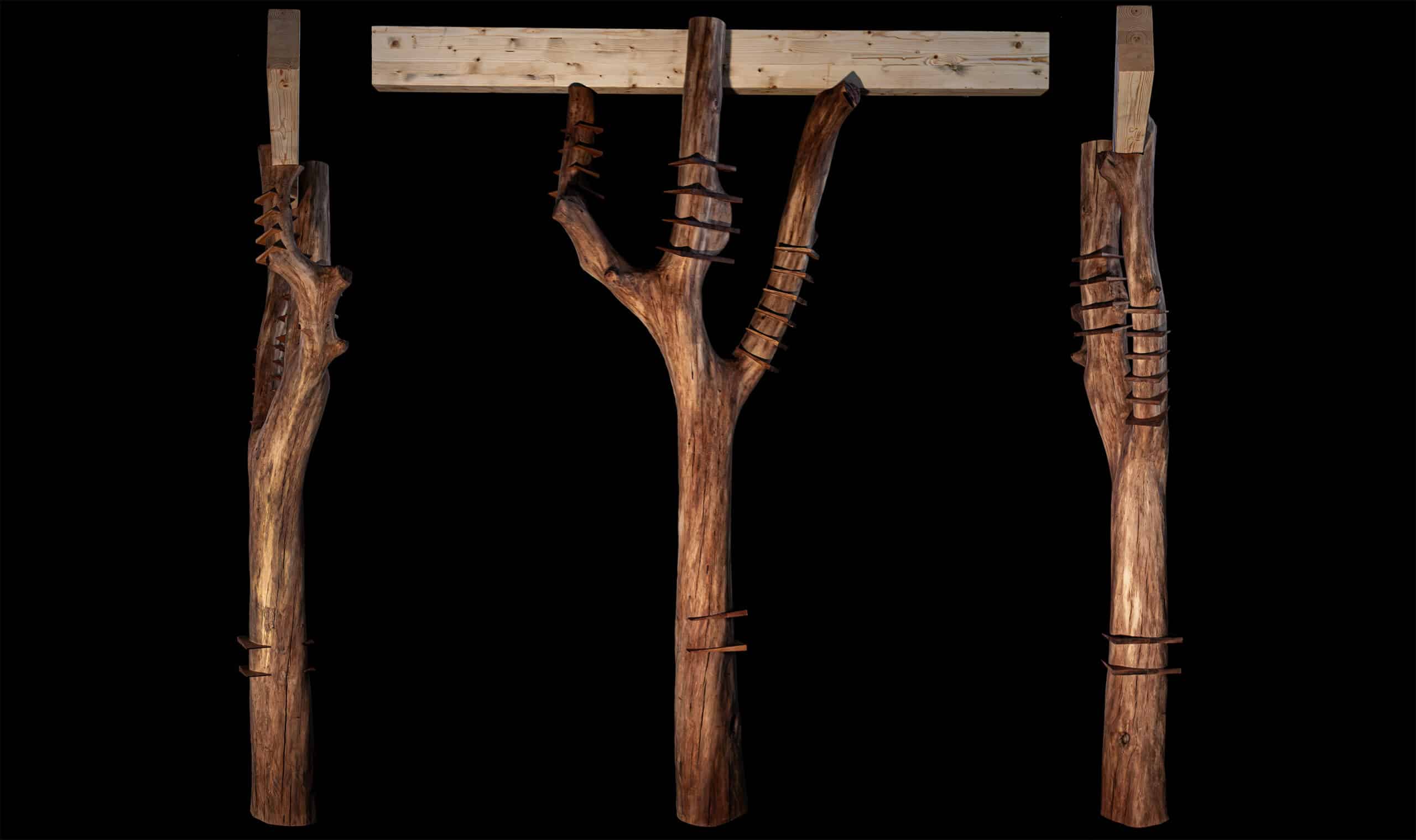
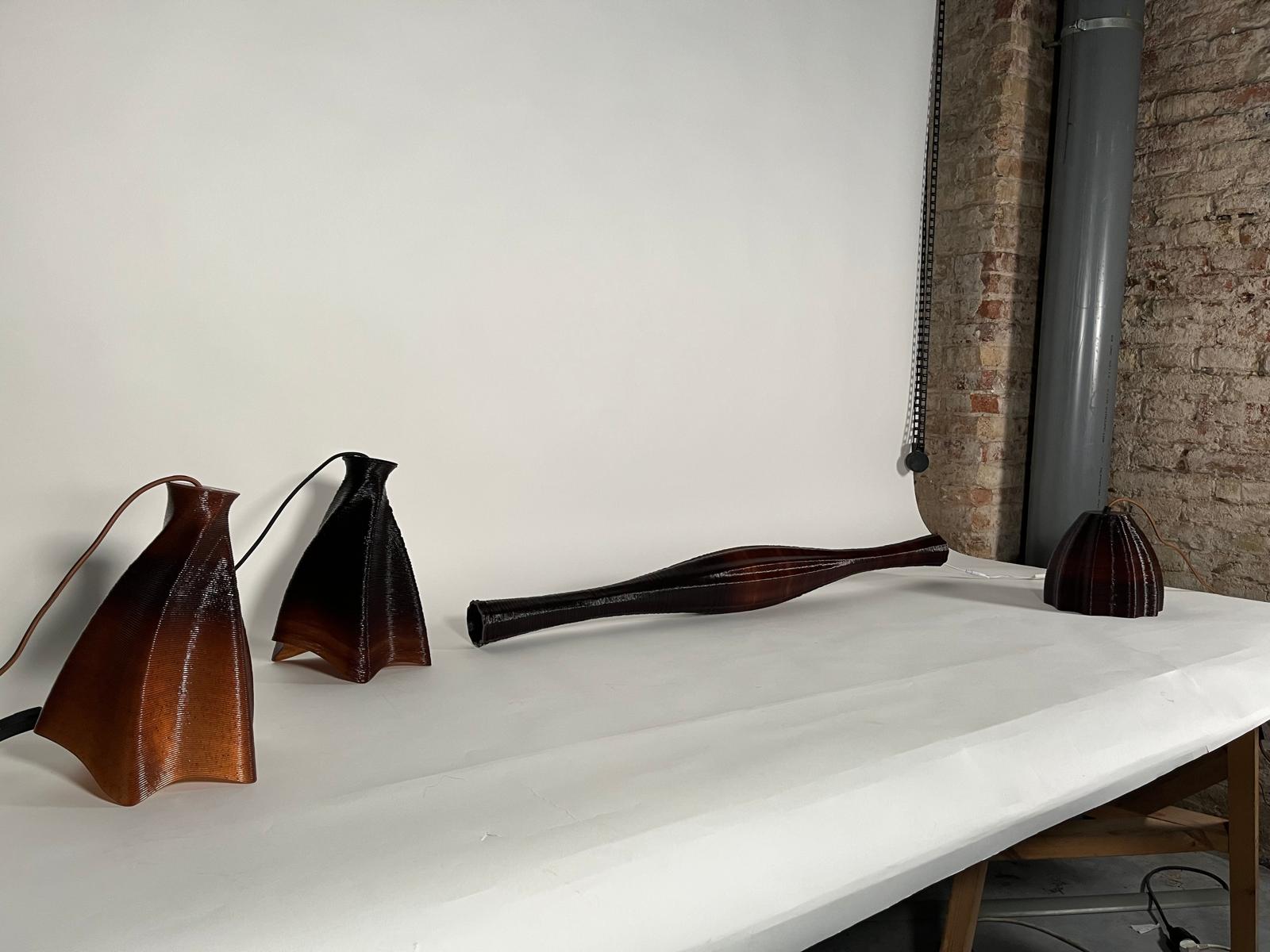
Introduction The Anatomy of a Machine: Stroke project explores the dialogue between human and robotic motion through painting. Conducted during the first MRAC studio, the exercise investigates how the physical behavior of paint, brush, and hand movement can be translated into robotic articulation. Over three weeks, we studied the anatomy of a brushstroke — first … Read more