BreatheSmart
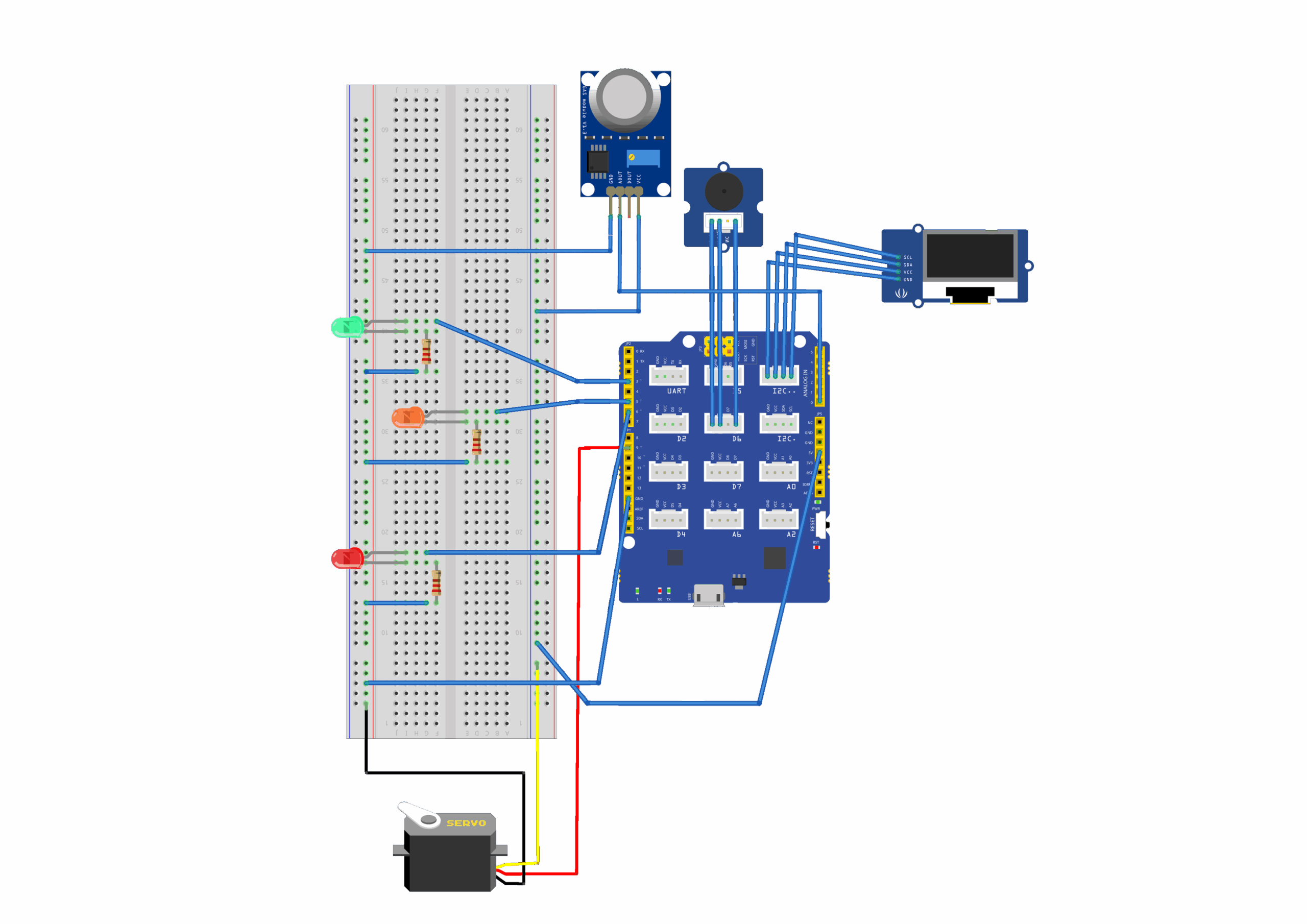
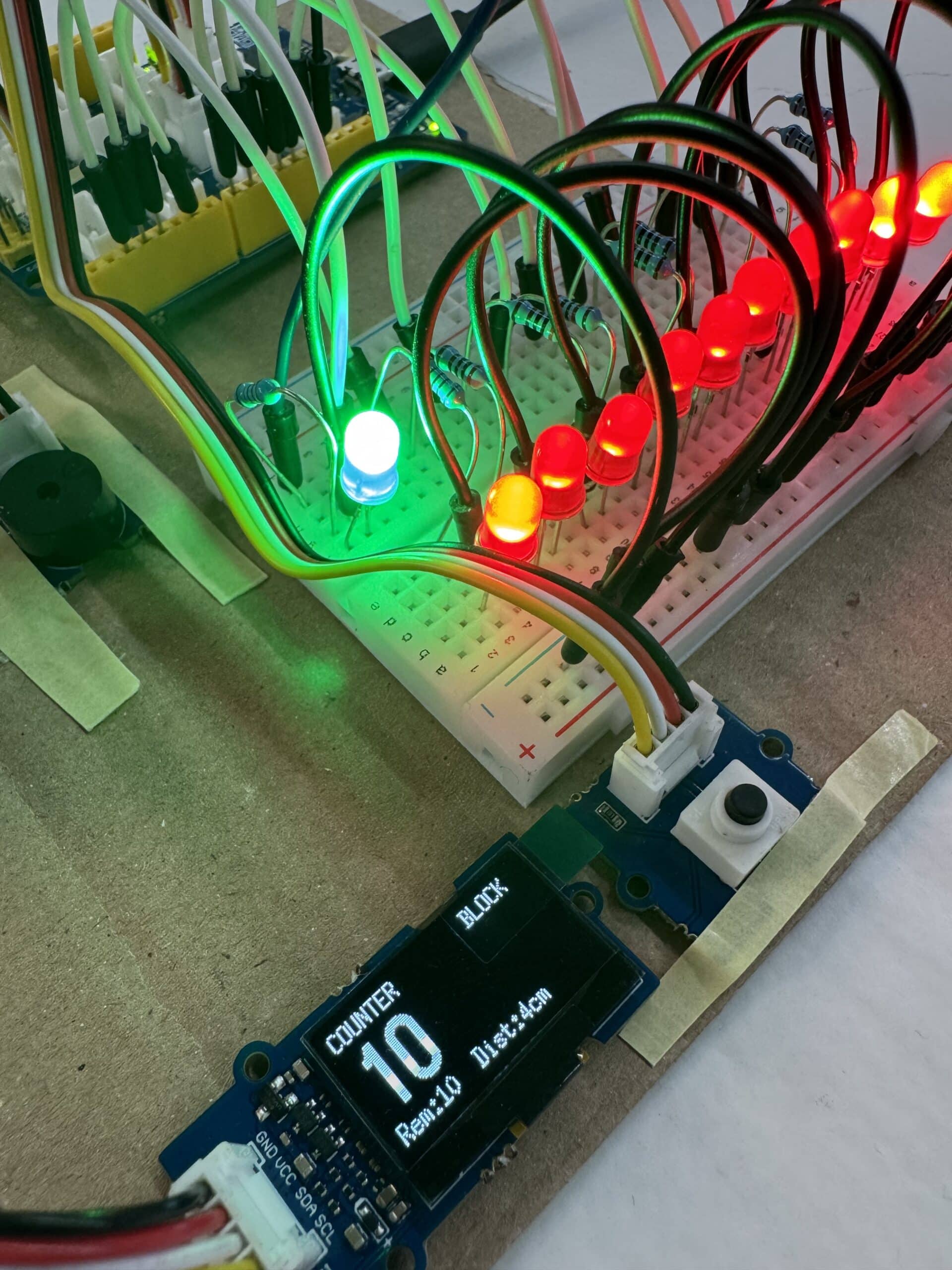
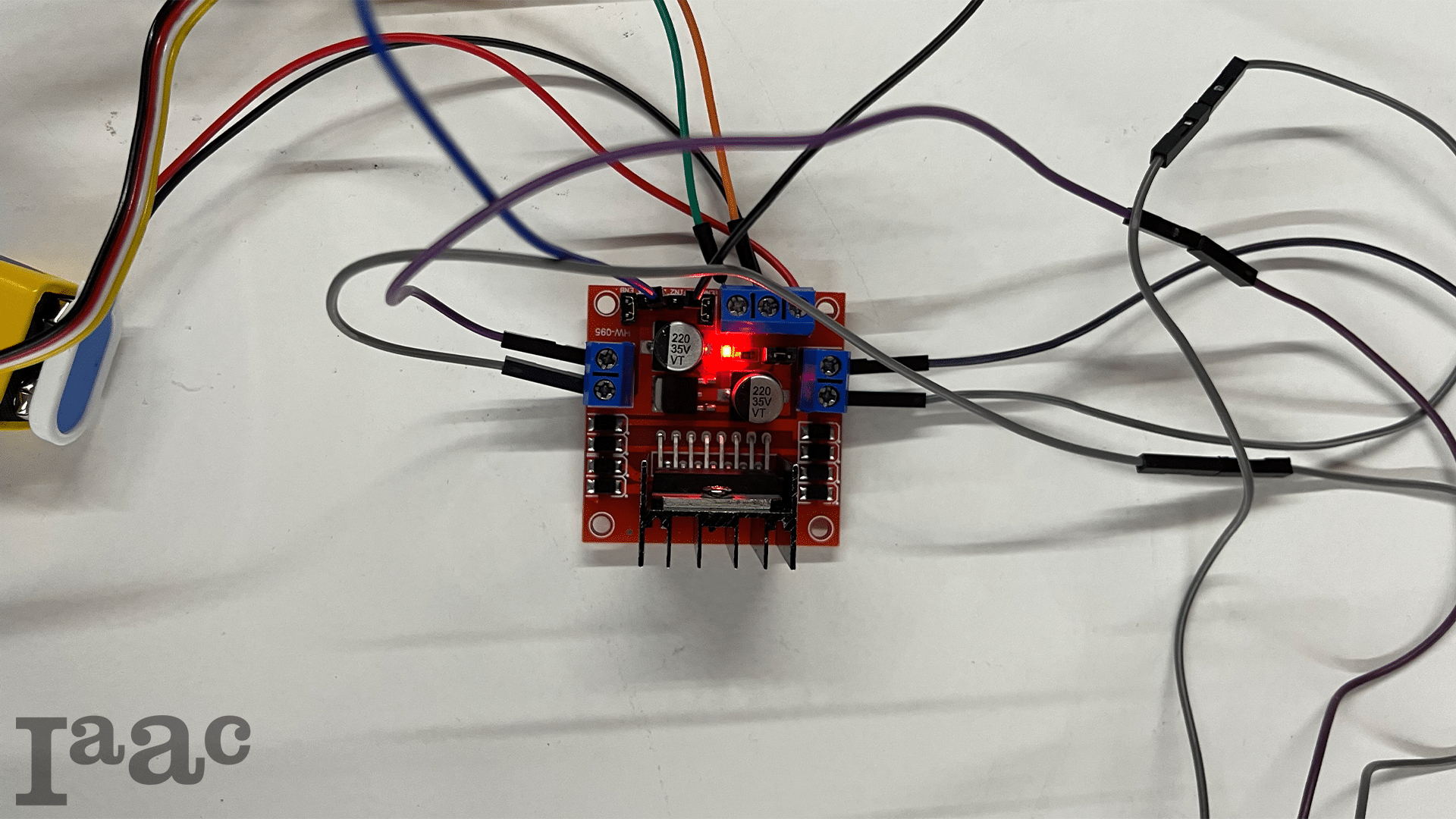
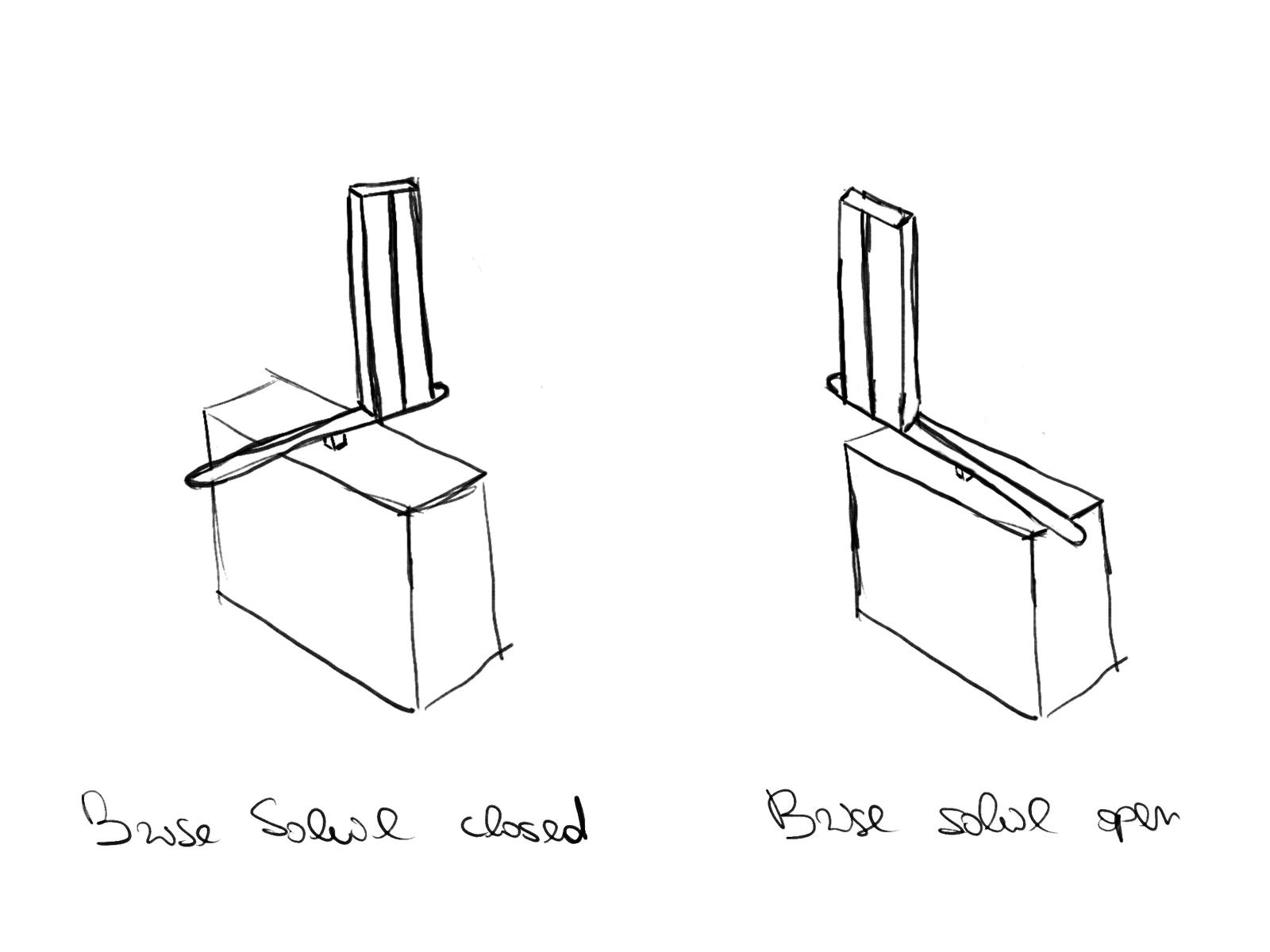
Introduction to Programming and Physical Computing Seminar This project focuses on developing a smart air quality monitoring system using a Seeed Lotus microcontroller, an MQ-135 air quality sensor, a 0.96” OLED display, a buzzer, a small motor or fan, and a panel with three LEDs to indicate air quality levels. The system continuously measures CO₂ … Read more