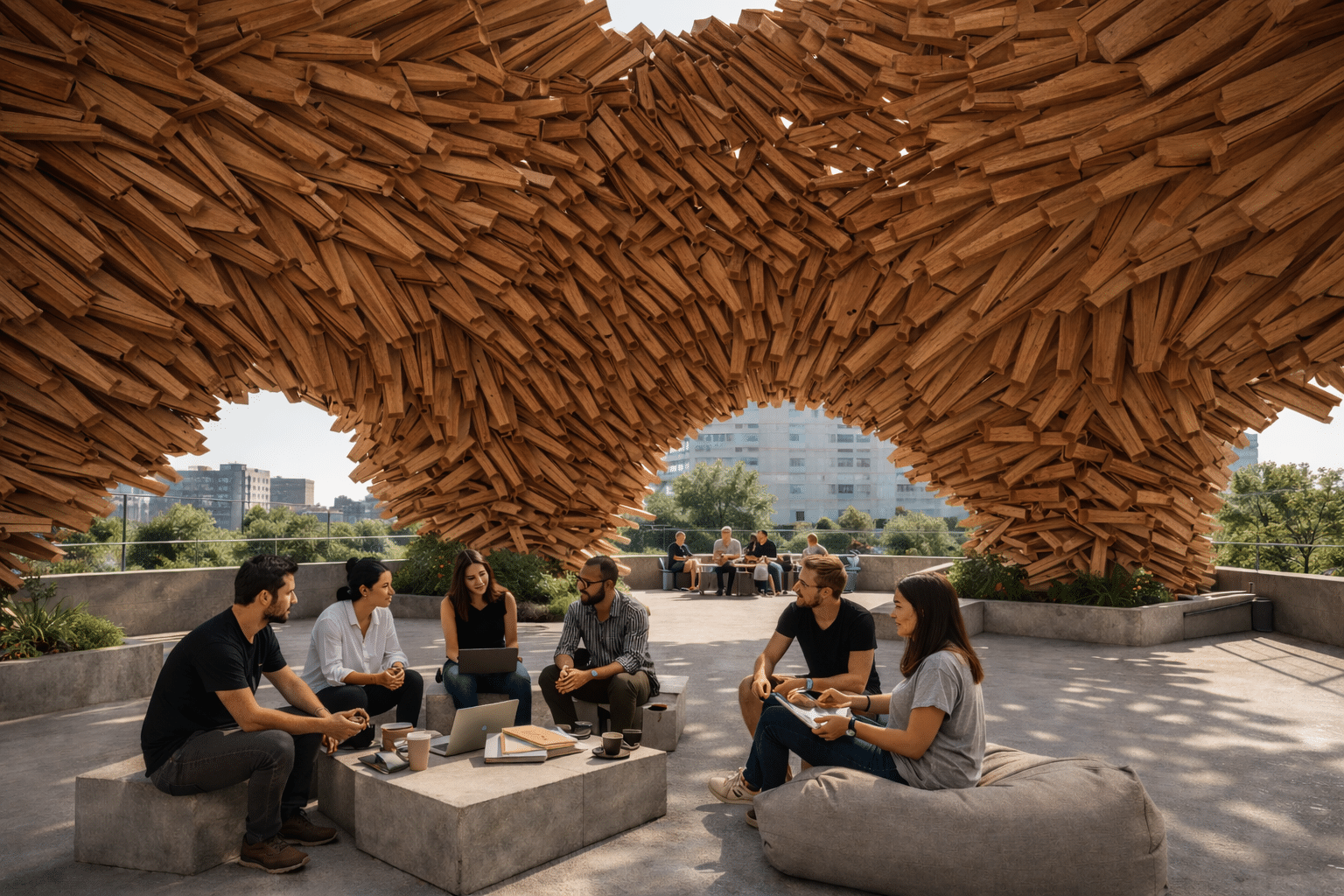
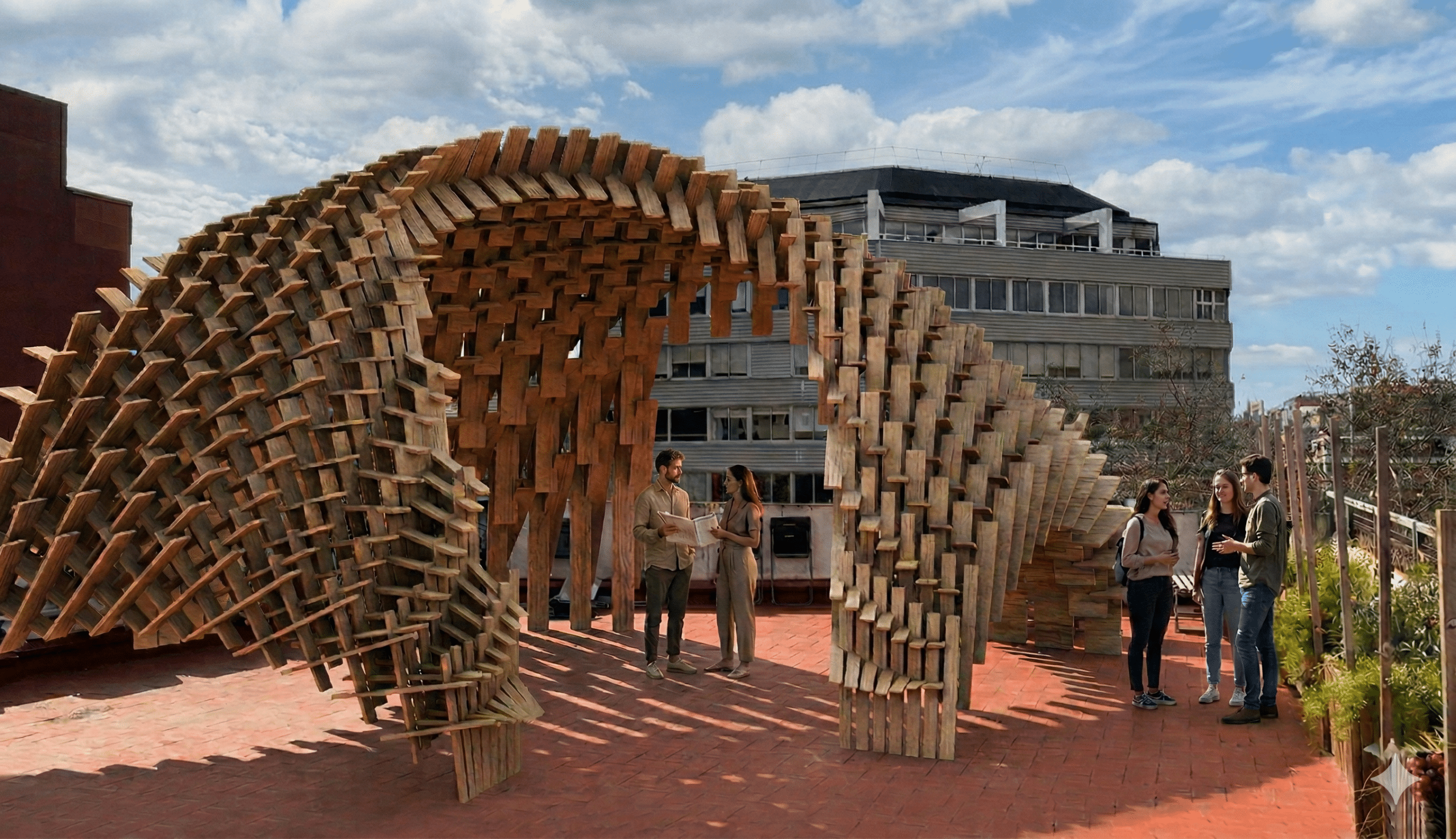
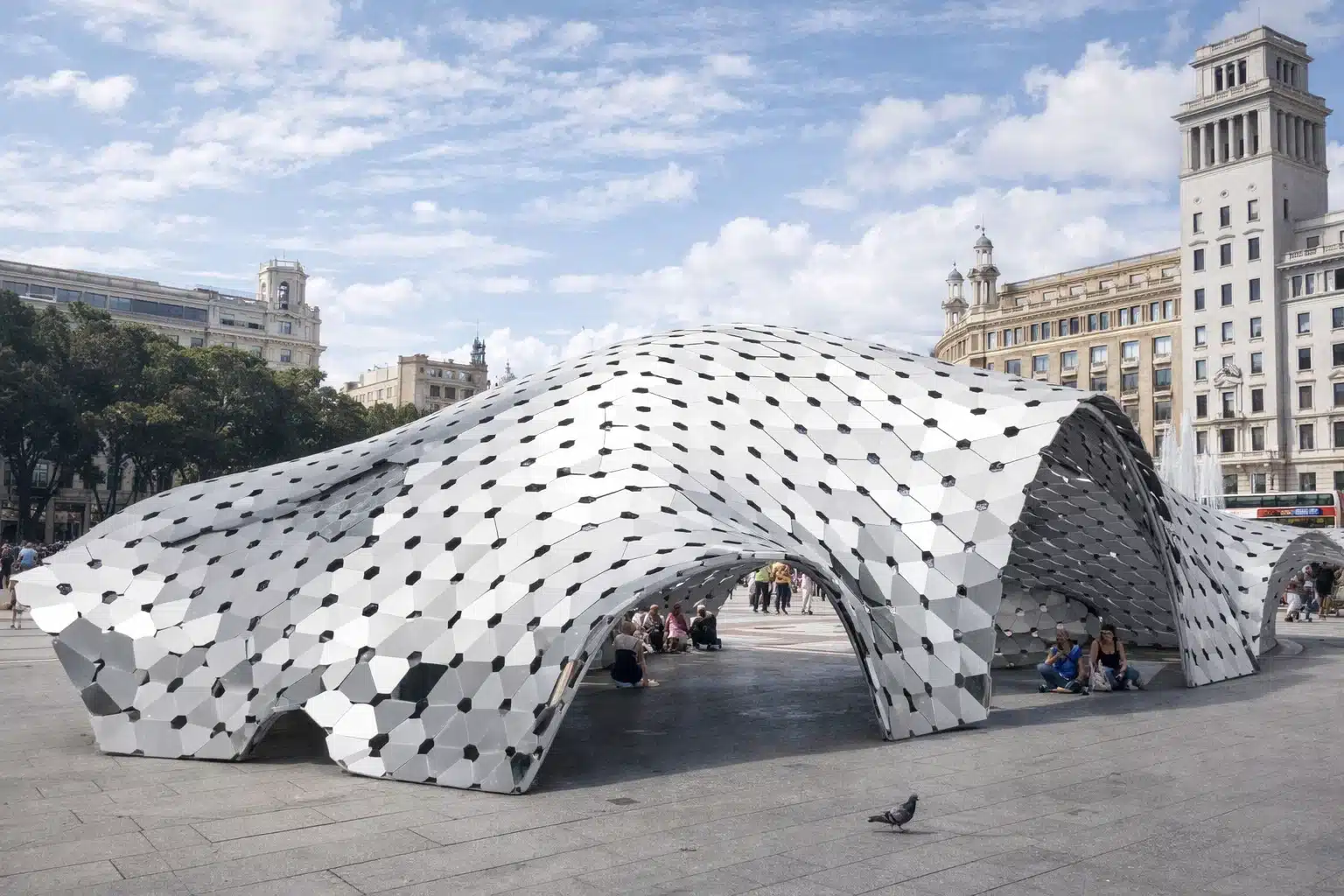
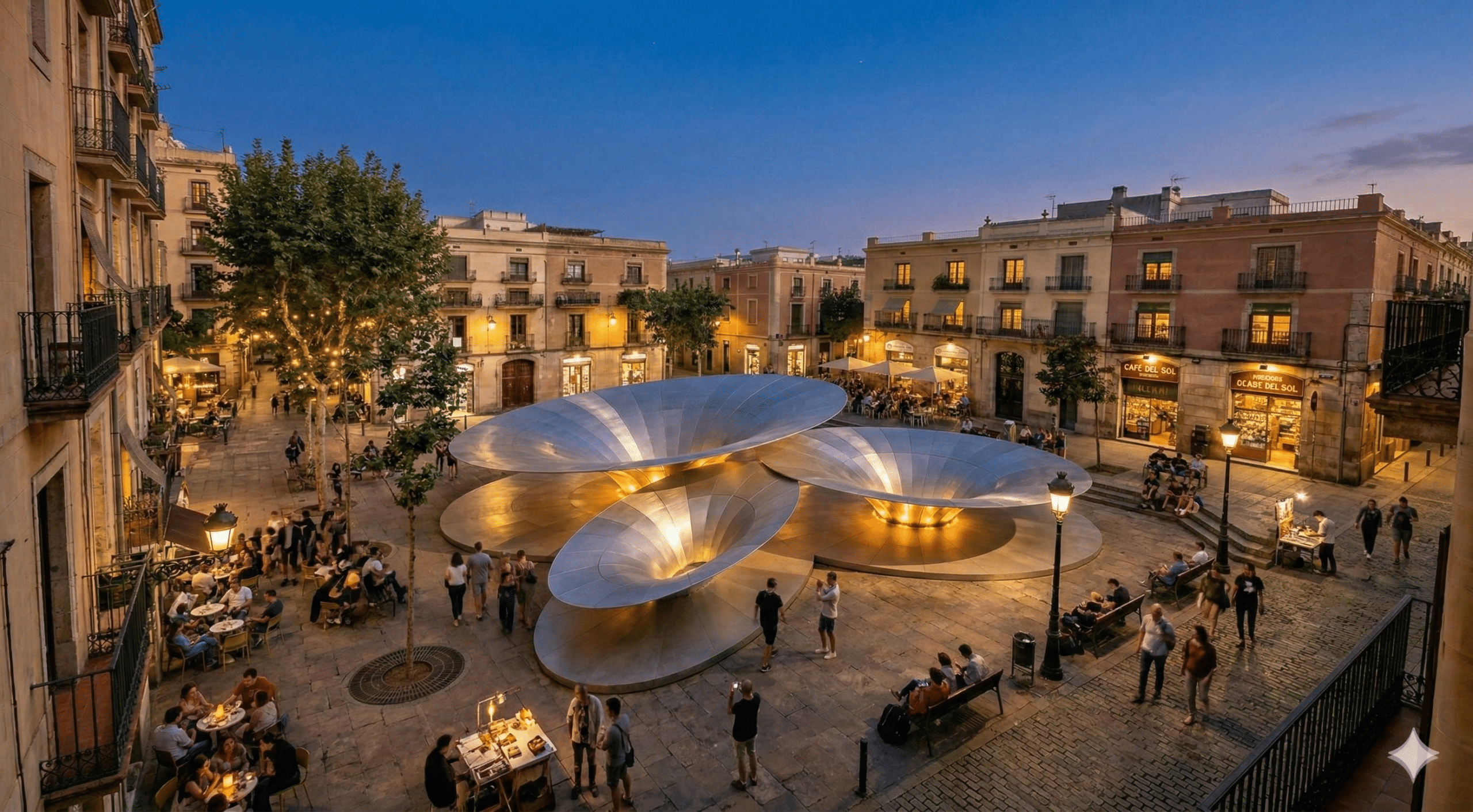
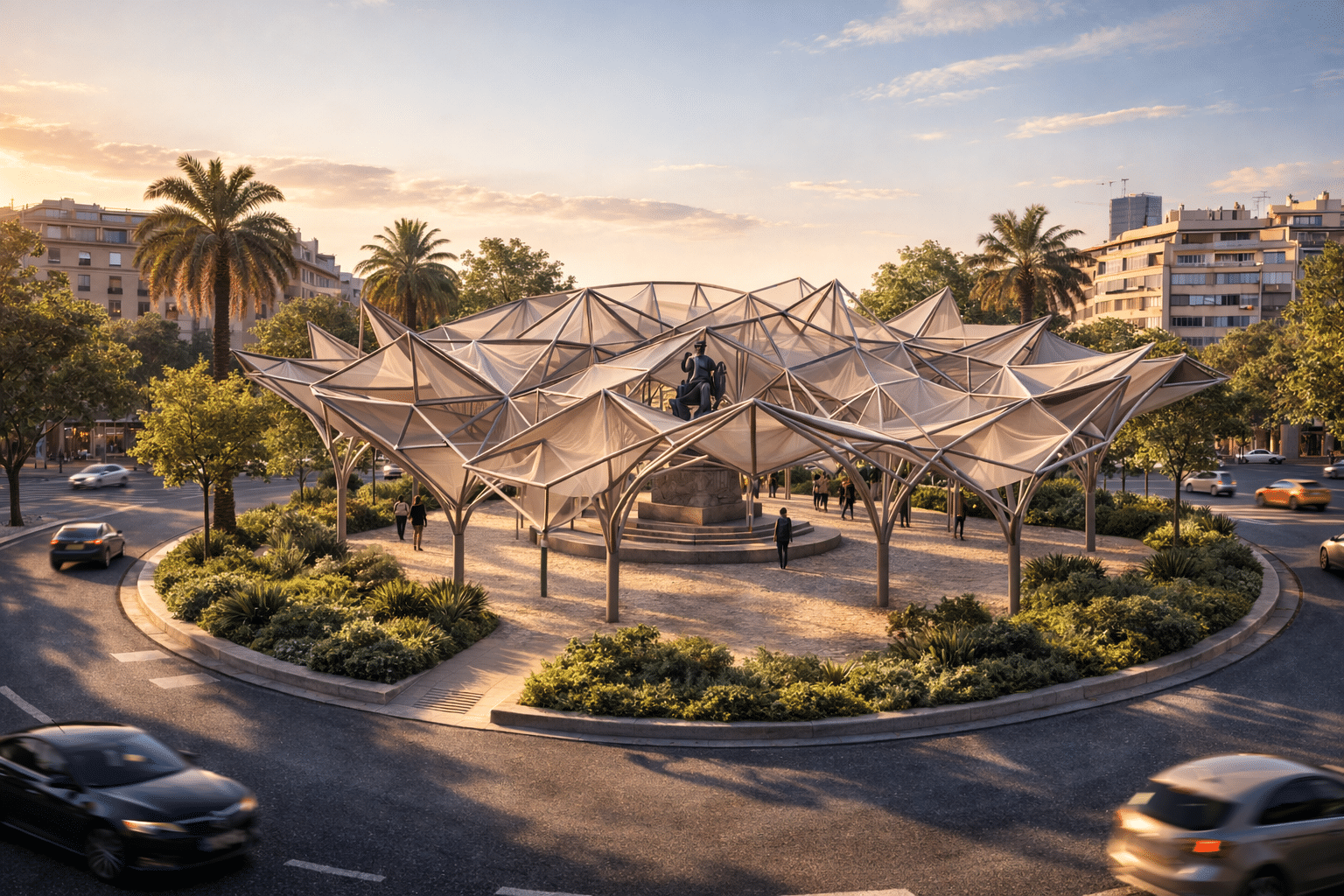
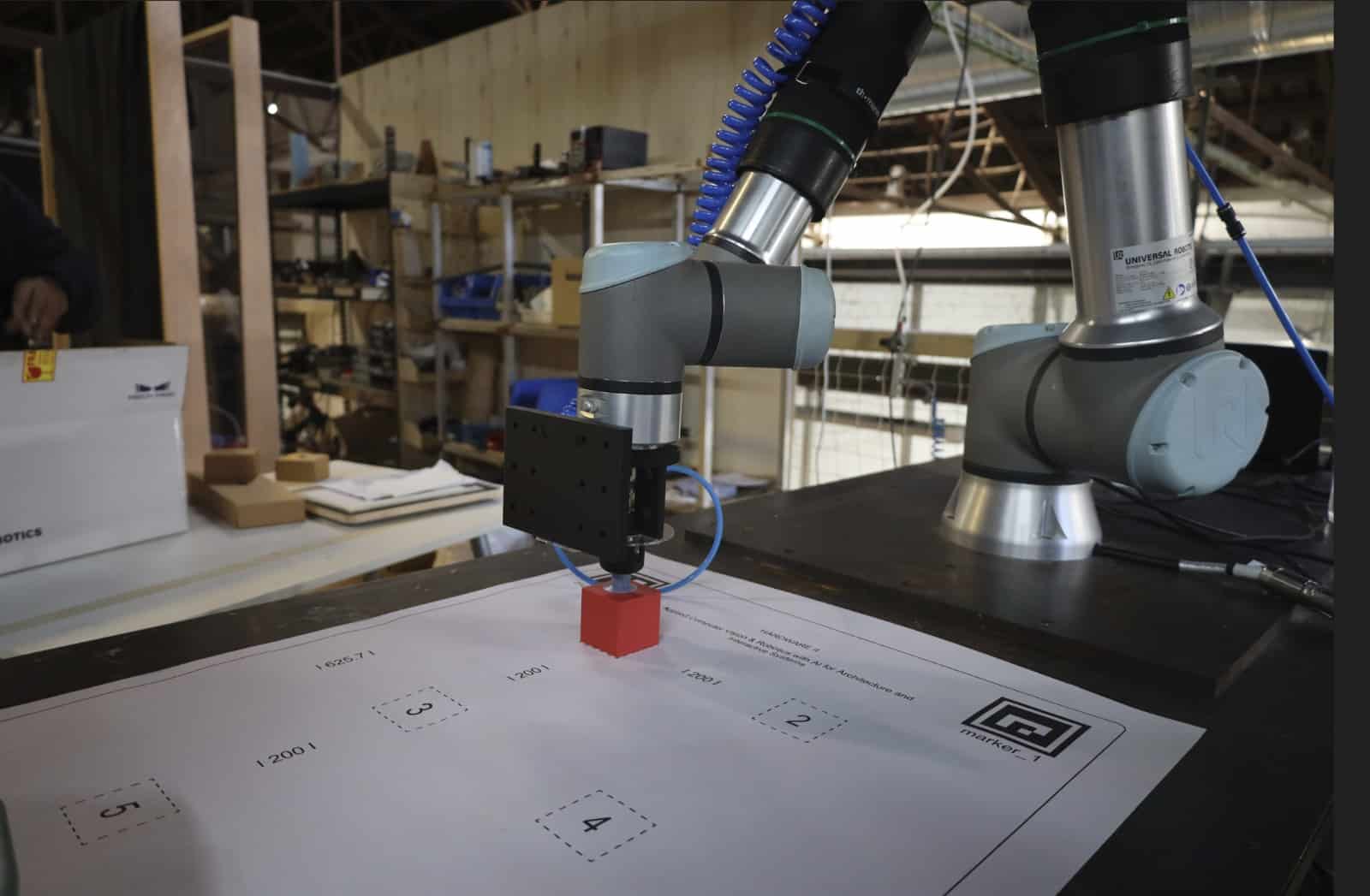
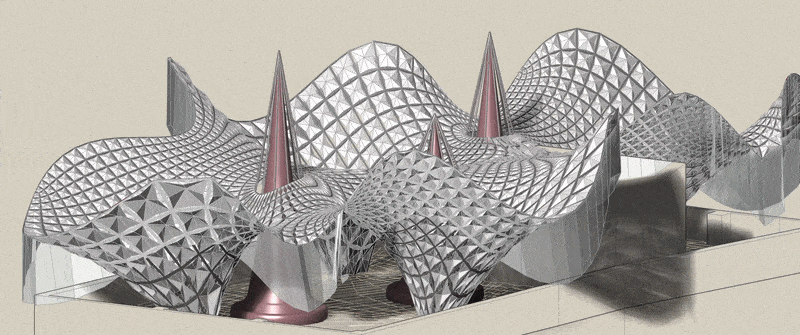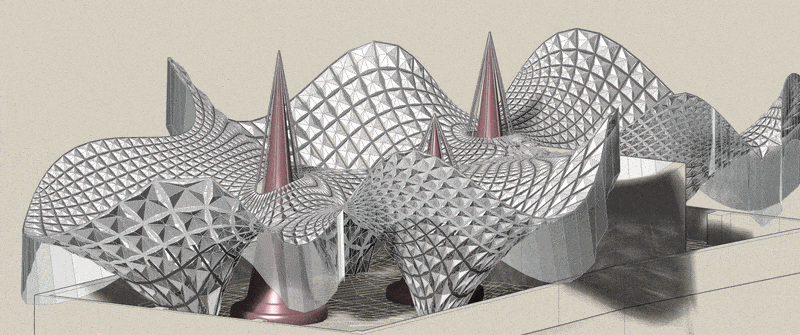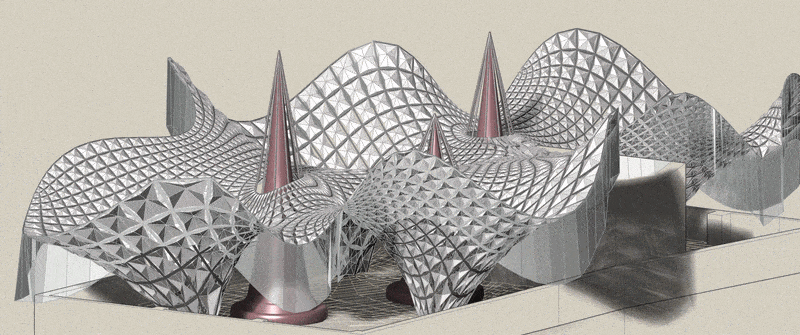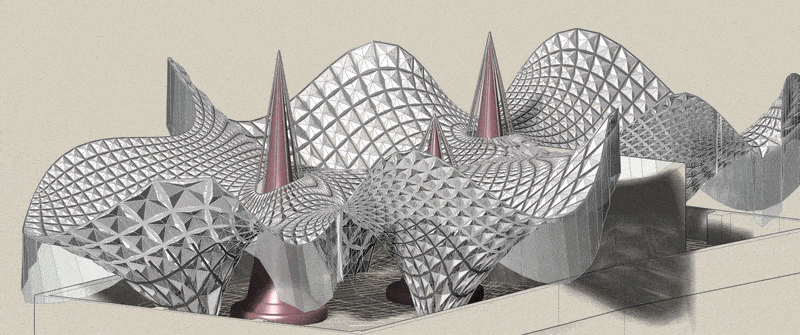
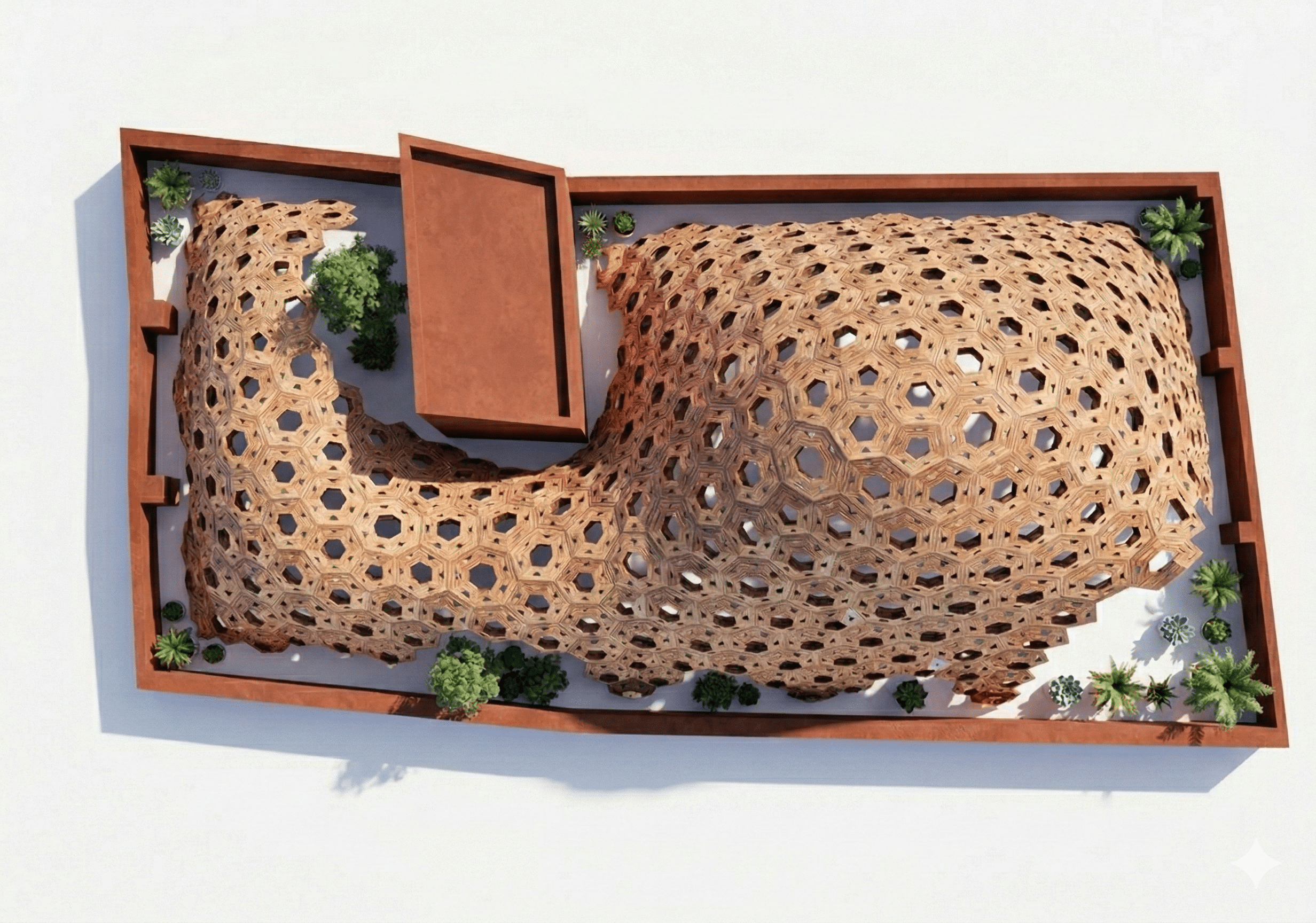
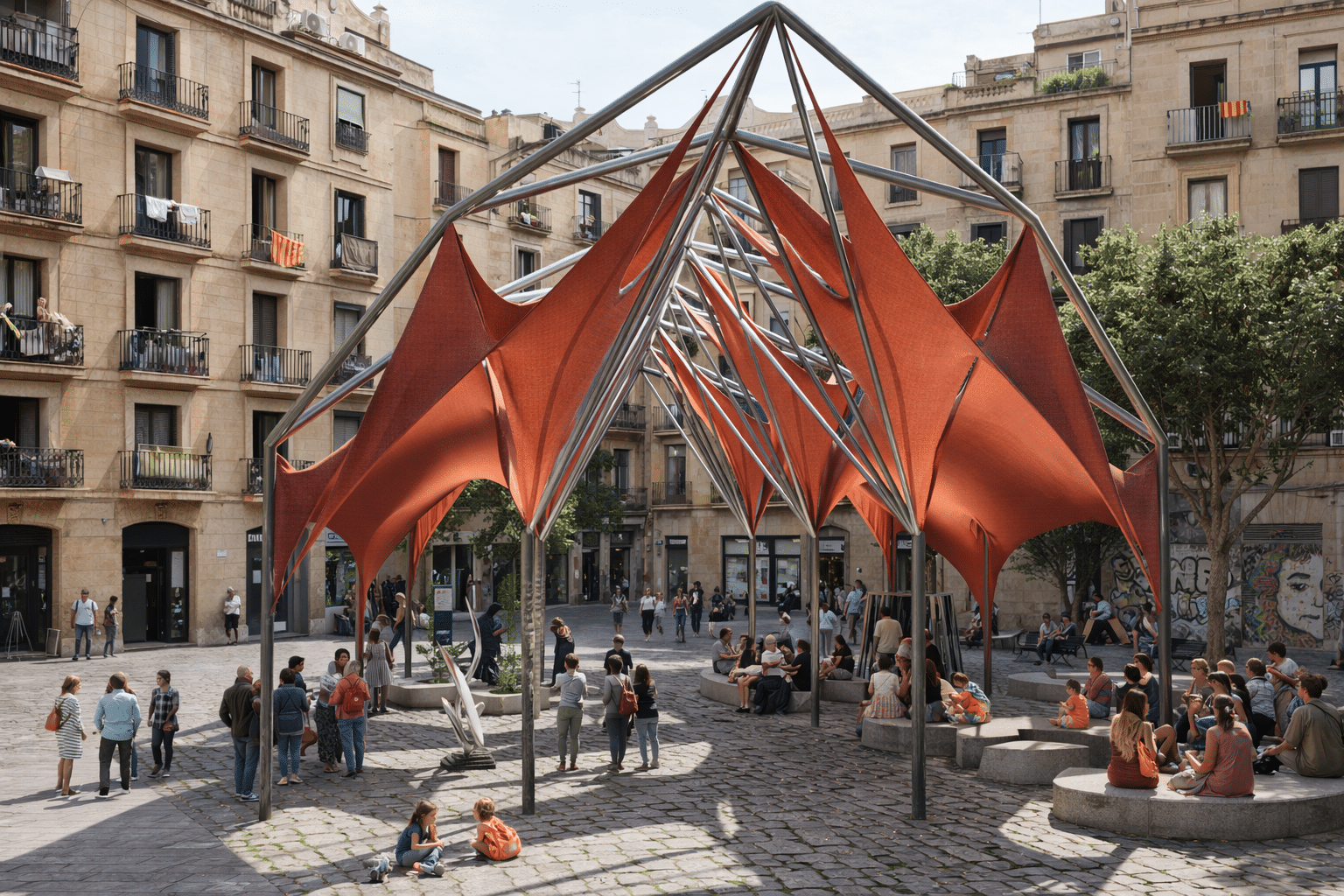Community Connections
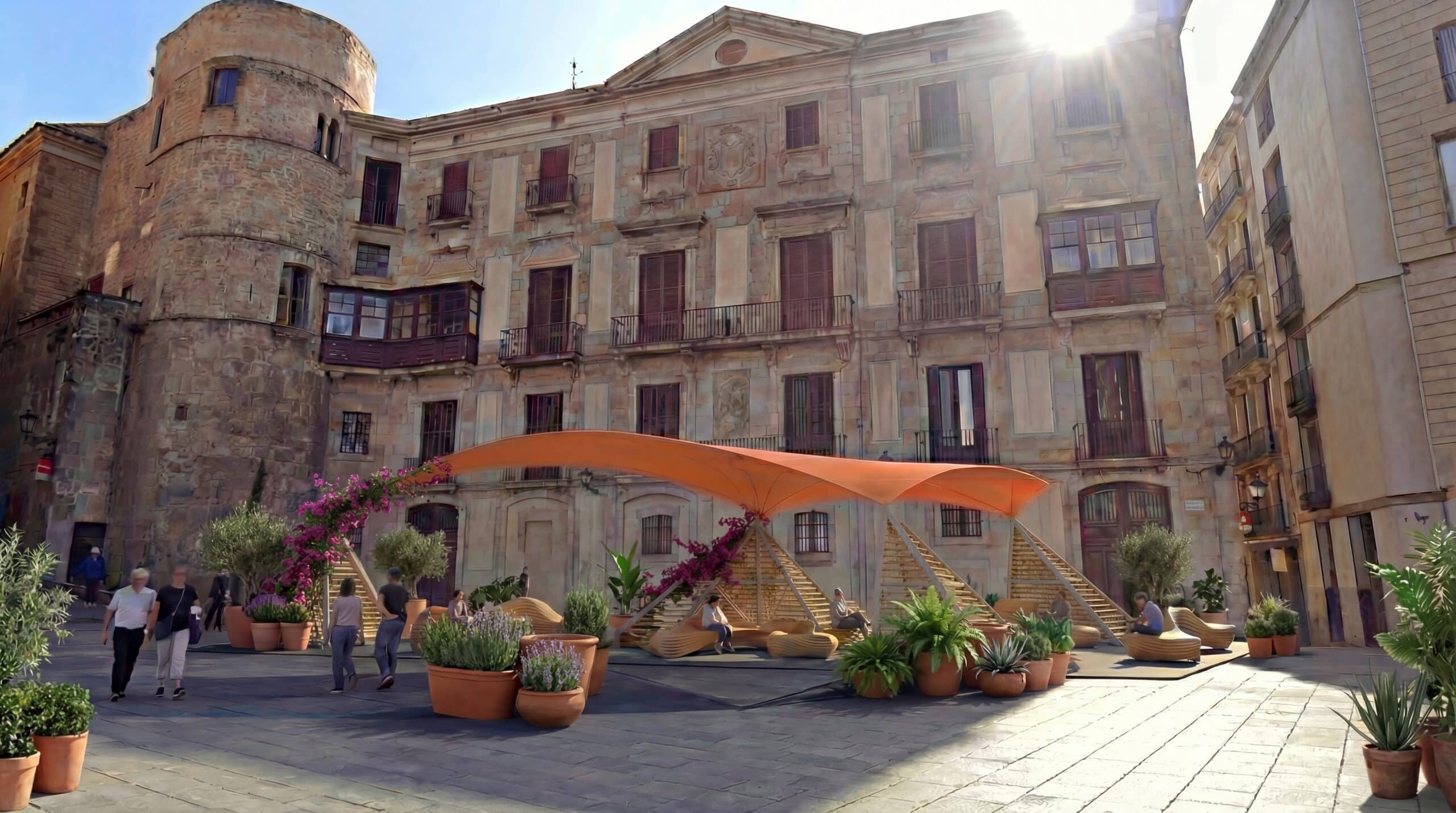
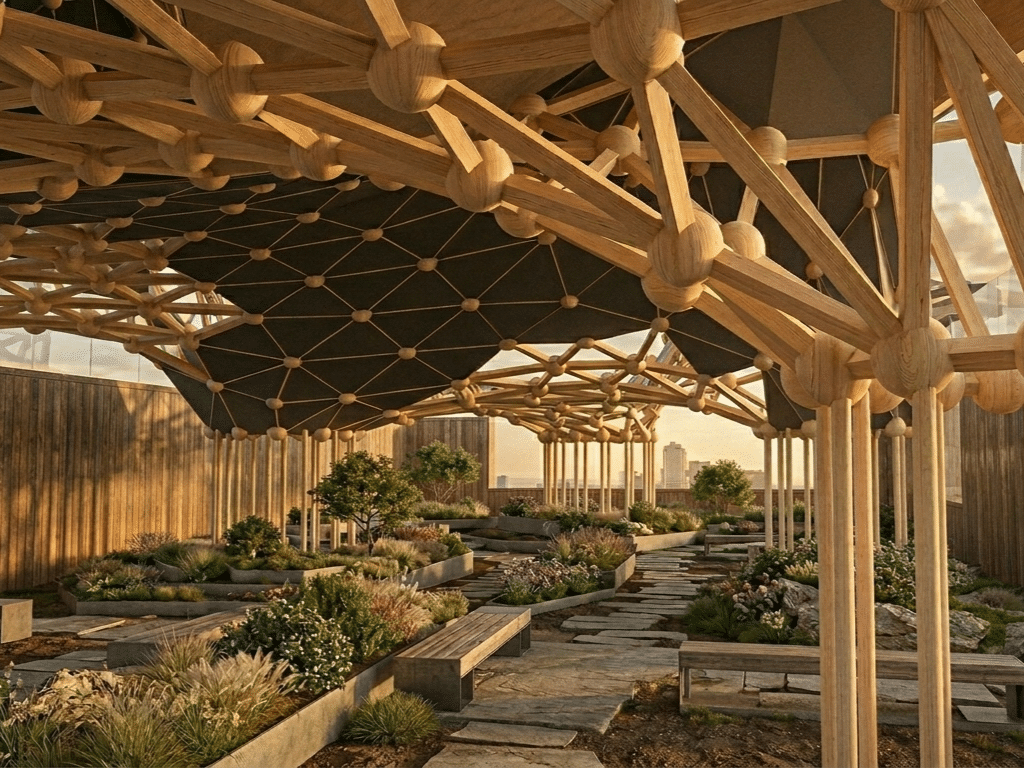
Trinitat Nova and Trinitat Vella Scavenger Hunt Moving between the neighborhoods of Trinitat Nova and Trinitat Vella in Barcelona, and reaching natural landscapes nearby, like the Collserola hillside or the Besòs River, can already feel a bit like a scavenger hunt. Large highway infrastructures carve through the area, creating barriers that make simple trips … Read more